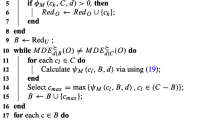Abstract
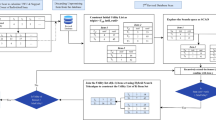
Knowledge reduction is complicated with the dynamic change of the object set in applications. In this paper, we propose incremental approaches to computing the type-1 and type-2 characteristic matrices of coverings with respect to variation of objects. Also we present two incremental algorithms of calculating the second and sixth lower and upper approximations of sets when adding and deleting more objects in dynamic covering approximation spaces. Subsequently, we employ experiments to validate that the incremental approaches are more effective and efficient to construct approximations of sets in dynamic covering information systems. Finally, we preform knowledge reduction of dynamic covering decision information systems by using the incremental approaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y (2015) Forward approximation and backward approximation in fuzzy rough sets. Inf Sci 148(19):340–353
Chen HM, Li TR, Qiao SJ, Ruan D (2010) A rough set based dynamic maintenance approach for approximations in coarsening and refining attribute values. Int J Intell Syst 25(10):1005–1026
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D (2012) Maintenance of approximations in incomplete ordered decision systems while attribute values coarsening or refining. Knowl Based Syst 31:140–161
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D, Lin JH, Hu CX (2013) A rough-set based incremental approach for updating approximations under dynamic maintenance environments. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(2):174–184
Chen DG, Wang CZ, Hu QH (2007) A new approach to attributes reduction of consistent and inconsistent covering decision systems with covering rough sets. Inf Sci 177:3500–3518
Deng T, Chen Y, Xu W, Dai Q (2007) A noval approach to fuzzy rough sets based on a fuzzy covering. Inf Sci 177:2308–2326
Diker M, Ugur AA (2012) Textures and covering based rough sets. Inf Sci 184(1):44–63
Du Y, Hu QH, Zhu PF, Ma PJ (2011) Rule learning for classification based on neighborhood covering reduction. Inf Sci 181(24):5457–5467
Fan YN, Tseng TL, Chen CC, Huang CC (2009) Rule induction based on an incremental rough set. Expert Syst Appl 36(9):11439–11450
Fang Y, Liu ZH, Min F (2014) Multi-objective cost-sensitive attribute reduction on data with error ranges. Int J Mach Learn Cyber. doi:10.1007/s13042-014-0296-3
Feng T, Zhang SP, Mi JS, Feng Q (2011) Reductions of a fuzzy covering decision system. Int J Model Identif Control 13(3):225–233
Hu LS, Lu SX, Wang XZ (2013) A new and informative active learning approach for support vector machine. Inf Sci 244:142–160
Huang CC, Tseng TL, Fan YN, Hsu CH (2013) Alternative rule induction methods based on incremental object using rough set theory. Appl Soft Comput 13:372–389
Jiang F, Sui YF, Cao CG (2013) An incremental decision tree algorithm based on rough sets and its application in intrusion detection. Arti Intell Rev 40:517–530
Ju HR, Yang XB, Song XN, Qi YS (2014) Dynamic updating multigranulation fuzzy rough set: approximations and reducts. Int J Mach Learn Cyber. doi:10.1007/s13042-014-0242-4
Kang XP, Li DY(2013) Dependency space, closure system and rough set theory. Int J Mach Learn Cyber 4(6): 595–599.
Lang GM, Ling QG, Yang T (2014) An incremental approach to attribute reduction of dynamic set-valued information systems. Int J Mach Learn Cyber 5(5):775–788
Li TJ, Leung Y, Zhang WX (2008) Generalized fuzzy rough approximation operators based on fuzzy coverings. Int J Approx Reason 48:836–856
Li JH, Mei CL, Lv YJ (2013) Incomplete decision contexts: approximate concept construction, rule acquisition and knowledge reduction. Int J Approx Reason 54(1):149–165
Li TR, Ruan D, Geert W, Song J, Xu Y(2007) A rough sets based characteristic relation approach for dynamic attribute generalization in data mining. Knowl-Based Syst 20(5): 485–494.
Li TR, Ruan D, Song J (2007) Dynamic maintenance of decision rules with rough set under characteristic relation. Wireless Commun Netw Mobile Comput 3713–3716.
Li SY, Li TR, Liu D (2013) Incremental updating approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of the attribute set. Knowl Based Syst 40:17–26
Li SY, Li TR, Liu D (2013) Dynamic maintenance of approximations in dominance-based rough set approach under the variation of the object set. Int J Intell Syst 28(8):729–751
Liang JY, Wang F, Dang CY, Qian YH (2014) A group incremental approach to feature selection applying rough set technique. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(2):294–308
Liu D, Li TR, Ruan D, Zou WL (2009) An incremental approach for inducing knowledge from dynamic information systems. Fund Inform 94(2):245–260
Liu D, Li TR, Ruan D, Zhang JB (2011) Incremental learning optimization on knowledge discovery in dynamic business intelligent systems. J Global Optim 51(2):325–344
Liu D, Li TR, Zhang JB (2014) A rough set-based incremental approach for learning knowledge in dynamic incomplete information systems. Int J Approx Reason doi:10.1016/j.ijar.2014.05.009
Liu X, Qian YH, Liang JY (2014) A rule-extraction framework under multigranulation rough sets. Int J Mach Learn Cyber 5(2):319–326
Luo C, Li TR, Chen HM (2013) Dynamic maintenance of approximations in set-valued ordered decision systems under the attribute generalization. Inf Sci 257:210–228
Luo C, Li TR, Chen HM, Liu D (2013) Incremental approaches for updating approximations in set-valued ordered information systems. Knowl Based Syst 50:218–233
Ma LW (2012) On some types of neighborhood-related covering rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 53(6):901–911
Ma JM, Leung Y, Zhang WX (2014) Attribute reductions in object-oriented concept lattices. Int J Mach Learn Cyber 5:789–813
Min F, Zhu W (2012) Attribute reduction of data with error ranges and test costs. Inf Sci 211:48–67
Min F, Hu QH, Zhu W (2014) Feature selection with test cost constraint. Int J Approx Reason 55(1):167–179
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Restrepo M, Cornelis C, Gómez J (2013) Duality, conjugacy and adjointness of approximation operators in covering-based rough sets. Int J Approx Reason. doi:10.1016/j.ijar.2013.08.002
Shan N, Ziarko W (1995) Data-based acquisition and incremental modification of classification rules. Comput Intell 11(2):357–370
Shu WH, Shen H (2013) Updating attribute reduction in incomplete decision systems with the variation of attribute set. Int J Approx Reason. doi:10.1016/j.ijar.2013.09.015
Shu WH, Shen H (2014) Incremental feature selection based on rough set in dynamic incomplete data. Pattern Recogn. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2014.06.002
Tsang ECC, Chen DG, Yeung DS (2008) Approximations and reducts with covering generalized rough sets. Comput Math Appl 56:279–289
Wang CZ, Chen DG, Wu C, Hu QH (2011) Data compression with homomorphism in covering information systems. Int J Approx Reason 52(4):519–525
Wang R, Chen DG, Kwong S (2014) Fuzzy rough set based active learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2291567
Wang F, Liang JY, Dang CY (2013) Attribute reduction for dynamic data sets. Appl Soft Comput 13:676–689
Wang F, Liang JY, Qian YH (2013) Attribute reduction: a dimension incremental strategy. Knowl Based Syst 39:95–108
Wang SP, Zhu W, Zhu QH, Min F (2014) Characteristic matrix of covering and its application to boolean matrix decomposition and axiomatization. Inf Sci 263(1):186–197
Yang T, Li QG (2010) Reduction about approximation spaces of covering generalized rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 51(3):335–345
Yang T, Li QG, Zhou BL (2013) Related family: a new method for attribute reduction of covering information systems. Inf Sci 228:175–191
Yang XB, Qi Y, Yu HL, Song XX, Yang JY (2014) Updating multigranulation rough approximations with increasing of granular structures. Knowl Based Syst 64:59–69
Yang XB, Zhang M, Dou HL (2011) Neighborhood systems-based rough sets in incomplete information system. Knowl Based Syst 24(6):858–867
Yao YY, Yao BX (2012) Covering based rough set approximations. Inf Sci 200:91–107
Yun ZQ, Ge X, Bai XL (2011) Axiomatization and conditions for neighborhoods in a covering to form a partition. Inf Sci 181:1735–546
Zakowski W (1983) Approximations in the space \((u, \pi )\). Demonstr Math 16:761–769
Zhang JB, Li TR, Chen HM (2014) Composite rough sets for dynamic data mining. Inf Sci 257:81–100
Zhang JB, Li TR, Ruan D, Liu D (2012) Rough sets based matrix approaches with dynamic attribute variation in set-valued information systems. Int J Approx Reason 53(4):620–635
Zhang JB, Li TR, Ruan D, Liu D (2012) Neighborhood rough sets for dynamic data mining. Int J Intell Syst 27(4):317–342
Zhang YL, Li JJ, Wu WZ (2010) On axiomatic characterizations of three pairs of covering based approximation operators. Inf Sci 180(552):274–287
Zhang YL, Luo MK (2011) On minimization of axiom sets characterizing covering-based approximation operators. Inf Sci 181:3032–3042
Zhao SY, Wang XZ, Chen DG, Tsang Eric CC (2013) Nested structure in parameterized rough reduction. Inf Sci 248:130–150
Zhu W (2007) Topological approaches to covering rough sets. Inf Sci 177(6):1499–1508
Zhu W, Wang FY (2003) Reduction and axiomization of covering generalized rough sets. Inf Sci 152:217–230
Zhu W, Wang FY (2007) On three types of covering-based rough sets. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 19(8):1131–1144
Zhu P (2011) Covering rough sets based on neighborhoods: an approach without using neighborhoods. Int J Approx Reason 52:461–472
Zhu P, Wen QY (2012) Entropy and co-entropy of a covering approximation space. Int J Approx Reason 53(4):528–540
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers very much for their professional comments and valuable suggestions. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11371130, 11401052, 11401195, 11201137, 11201490), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 14C0049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lang, G., Li, Q., Cai, M. et al. Incremental approaches to knowledge reduction based on characteristic matrices. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 8, 203–222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-014-0315-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-014-0315-4