Abstract
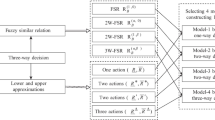
Based on Bayesian decision theory, three-way decisions model (TWDM) proposed by Yao gives new semantic interpretations of positive region, negative region and boundary region. Some extensions of TWDM have been proposed by different authors and have been successfully applied to many fields, such as soft computing, data mining and decision making. However existing three-way decisions models are almost developed in certainty environment, which limits their applications in uncertainty environment. In order to deal with this problem, based on tolerance rough fuzzy set, a TWDM is proposed in this paper. The main contributions of this paper include two aspects: (1) the tolerance rough fuzzy set which is extended from rough fuzzy set is introduced, and some basic properties of the tolerance rough fuzzy set are investigated. (2) The TWDM with respect to the tolerance rough fuzzy set is proposed. In addition, an example is given to illustrate the computation processes of the TWDM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Inf Comput Sci 11:341–356
Zhou W, Zhang SL (2015) The decision delay in finite-length MMSE–DFE systems. Wirel Pers Commun 83(1):175–189
He S, Chen HH, Zhu ZX et al (2015) Robust twin boosting for feature selection from high-dimensional OMICS data with label noise. Inf Sci 291:1–18
Pan F, Song GG, Gan XB et al (2014) Consistent feature selection and its application to face recognition. J Intell Inf Syst 43(2):307–321
Zhu ZX, Jia S, Ji Z (2010) Towards a memetic feature selection paradigm. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 5(2):41–53
Xie JY, Hone K, Xie WX et al (2013) Extending twin support vector machine classifier for multi-category classification problems. Intell Data Anal 17(4):649–664
Yang R, Ren OY (2014) Classification based on Choquet integral. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 27(4):1693–1702
Yang R, Wang ZY (2015) Cross-oriented choquet integrals and their applications on data classification. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(1):205–216
He YL, Wang XZ, Huang ZX (2016) Recent advances in multiple criteria decision making techniques. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-015-0490-y
Ziarko W (1993) Variable precision rough set model. J Comput Syst Sci 46(93):39–59
Yao YY (2003) Probabilistic approaches to rough sets. Expert Syst 20(5):287–297
Yao YY, Wong SKM (1992) A decision theoretic framework for approximating concepts. Int J Man Mach Stud 37(6):793–809
Li WT, Xu WH (2015) Double-quantitative decision-theoretic rough set. Inf Sci 316:54–67
Dou HL, Yang XB, Song XN et al (2016) Decision-theoretic rough set: a multicost strategy. Knowl Based Syst 91:71–83
Yao YY, Lin TY (1996) Generalization of rough sets using modal logics. Intell Autom Soft Comput Int J 2(2):103–120
Skowron A (2000) Tolerance approximation spaces. Fundam Inf 64(2–3):245–253
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R (1999) Rough approximation of a preference relation by dominance relations. Eur J Oper Res 117(98):63–83
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17(2):191–208
Kuncheva LI (1992) Fuzzy rough sets: application to feature selection. Fuzzy Sets Syst 51(2):147–153
Nanda S (1992) Fuzzy rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 45(2):157–160
Yao YY (1997) Combination of rough and fuzzy sets based on-level sets. In: Lin TY, Cercone N (eds) Rough sets and data mining: analysis for imprecise data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 301–321
Chen Y (2015) An adjustable multigranulation fuzzy rough set. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 7(2):1–8
Zhang C, Li DY, Liang JY (2016) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic rough set over two universes model and its applications. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-016-0541-z
Zhao SY, Chen H, Li CP et al (2014) RFRR: robust fuzzy rough reduction. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 21(5):825–841
Zhao SY, Tsang ECC, Chen DG et al (2009) Building a rule-based classifier—a fuzzy-rough set approach. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(5):624–638
Zhao SY, Chen H, Li CP et al (2015) A novel approach to building a robust fuzzy rough classifier. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(4):769–786
Wang XZ, Xing HJ, Li Y et al (2015) A study on relationship between generalization abilities and fuzziness of base classifiers in ensemble learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(5):1638–1654
Wang XZ, Ashfaq RAR, Fu AM (2015) Fuzziness based sample categorization for classifier performance improvement. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 29(3):1–12
Wang XZ (2015) Learning from big data with uncertainty—editorial. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(5):2329–2330
Ashfaq RAR, Wang XZ, Huang JZX et al (2016) Fuzziness based semi-supervised learning approach for intrusion detection system. Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.04.019
He YL, Wang XZ, Huang JZX (2016) Fuzzy nonlinear regression analysis using a random weight network. Inf Sci 364–365:222–240
He YL, Liu JNK, Hu YX et al (2015) OWA operator based link prediction ensemble for social network. Expert Syst Appl 42(1):21–50
Gong ZT, Zhang XX (2016) The further investigation of variable precision intuitionistic fuzzy rough set model. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-016-0528-9
Yao YY (2010) Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf Sci 180(3):341–353
Fujita H, Li TR, Yao YY (2016) Advances in three-way decisions and granular computing. Knowl Based Syst 91:1–3
Liu D, Liang DC, Wang CC (2016) A novel three-way decision model based on incomplete information system. Knowl Based Syst 91:32–45
Liang DC, Liu D, Kobina A (2016) Three-way group decisions with decision-theoretic rough sets. Inf Sci 345:46–64
Zhao XR, Hu BQ (2016) Fuzzy probabilistic rough sets and their corresponding three-way decisions. Knowl Based Syst 91:126–142
Chen YM, Zeng ZQ, Zhu QX et al (2016) Three-way decision reduction in neighborhood systems. Appl Soft Comput 38:942–954
Peters JF, Ramanna S (2016) Proximal three-way decisions: theory and applications in social networks. Knowl Based Syst 91:4–15
Zhang HR, Min F, Shi B (2016) Regression-based three-way recommendation. Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.03.019
Li HX, Zhang LB, Huang B et al (2016) Sequential three-way decision and granulation for cost-sensitive face recognition. Knowl Based Syst 91:241–251
Li WW, Huang ZQ, Li Q (2016) Three-way decisions based software defect prediction. Knowl Based Syst 91:263–274
Yang HL, Guo ZL (2015) Multigranulation decision-theoretic rough sets in incomplete information systems. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 6(6):1005–1018
Li JH, Huang CC, Qi JJ (2016) Three-way cognitive concept learning via multi-granularity. Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.04.051
Liang DC, Liu D (2015) Deriving three-way decisions from intuitionistic fuzzy decision-theoretic rough sets. Inf Sci 300:28–48
Hu BQ (2014) Three-way decisions space and three-way decisions. Inf Sci 281:21–52
Hu BQ (2016) Three-way decision spaces based on partially ordered sets and three-way decisions based on hesitant fuzzy sets. Knowl Based Syst 91:16–31
Yao YY (2016) Interval sets and three-way concept analysis in incomplete contexts. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-016-0568-1
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by Basic Research Project of Knowledge Innovation Program in Shenzhen (JCYJ20150324140036825), by National Natural Science Foundations of China (71371063), by Key Scientific Research Foundation of Education Department of Hebei Province (ZD20131028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, J., Zhang, Y. & Zhu, H. Three-way decisions model based on tolerance rough fuzzy set. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 8, 35–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0591-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0591-2