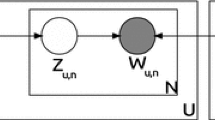
Abstract
Online social network is a great medium to express one’s opinion, sentiment, preference, and reaction on a topic. Tweets posted by Twitter users are used as a mechanism to share information. By retweeting a tweet, users not only approve the information provided by the tweet but also share the similar emotions and sentiment expressed by the tweet. Analyzing tweets and retweets to discover user’s interest is a challenging and interesting task for researchers mainly in the field of information diffusion. In the past studies, it is usually assumed that a user retweets the tweets which match his topic of interest. However, not only the topic itself but also the emotion and sentiment related to the topic might have impact on user’s retweet decision. In this research, our objective is to explore the impact of user’s topic specific emotion on his retweet decisions. With different latent features, we could find out user’s preferences on different topics at different emotional levels. This research has shown that along with topic, user’s emotion towards a topic is a useful factor in modeling user’s retweet decision.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Abel F, Gao Q, Houben GJ, Tao K (2011) Analyzing user modeling on twitter for personalized news recommendations. In: International conference on user modeling, adaptation, and personalization. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 1–12
Adali S, Escriva R, Goldberg MK, Hayvanovych M, Magdon-Ismail M, Szymanski BK, Wallace WA, Williams G (2010) Measuring behavioral trust in social networks. In: 2010 IEEE International conference intelligence and security informatics (ISI). IEEE, pp 150–152
Asur S, Huberman BA (2010) Predicting the future with social media. In: 2010 IEEE/WIC/ACM international conference web intelligence and intelligent agent technology (WI-IAT), vol 1, pp 492–499
Blei DM, Ng AY, Jordan MI (2003) Latent dirichlet allocation. J Mach Learn Res 3:993–1022
Boecking B, Hall M, Schneider J (2015) Event prediction with learning algorithmsA study of events surrounding the egyptian revolution of 2011 on the basis of micro blog data. Policy Internet 7(2):159–84
Bravo-Marquez F, Frank E, Mohammad SM, Pfahringer B (2016) Determining wordemotion associations from tweets by multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/WIC/ACM international conference on web intelligence, USA, 2016, IEEE Computer Society, p 536539, https://doi.org/10.1109/WI.2016.90
Chen J, Nairn R, Nelson L, Bernstein M, Chi E (2010) Short and tweet: experiments on recommending content from information streams. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems 2010, ACM, pp 1185–1194
Chen K, Chen T, Zheng G, Jin O, Yao E, Yu Y (2012) Collaborative personalized tweet recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 35th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval 2012, ACM, pp 661–670
Deng Z, Yan M, Sang J, Xu C (2015) Twitter is faster: personalized time-aware video recommendation from Twitter to YouTube. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl (TOMM) 11(2):31
Gupta M, Gao J, Zhai C, Han J (2012) Predicting future popularity trend of events in microblogging platforms. Proc Assoc Inf Sci Technol 49(1):1
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH (2009) The WEKA data mining software: an update. ACM SIGKDD Explor Newsl 11(1):10–8
Hoang TA, Lim EP (2012) Virality and susceptibility in information diffusions. In Sixth international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media, May 2012
Huang D, Zhou J, Mu D, Yang F (2014) Retweet behavior prediction in twitter. In 2014 IEEE Seventh international symposium computational intelligence and design (ISCID), vol 2, pp 30–33
Islam M, Ding C, Chi CH (2014) Personalized recommender system on whom to follow in Twitter. In 4th International conference on big data and cloud computing (BdCloud), Dec 2014, IEEE, pp 326–333
Jenders M, Kasneci G, Naumann F (2013) Analyzing and predicting viral tweets. In Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on world wide web 2013, ACM, pp 657–664
Jonnalagedda N, Gauch S (2013) Personalized news recommendation using twitter. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/WIC/ACM international joint conferences on web intelligence (WI) and intelligent agent technologies (IAT) vol 03, IEEE Computer Society, pp 21–25
Kanavos A, Perikos I, Vikatos P, Hatzilygeroudis I, Makris C, Tsakalidis A (2014) Modeling retweet diffusion using emotional content. In: IFIP International conference on artificial intelligence applications and innovations. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 101–110
Kim J, Yoo J (2012) Role of sentiment in message propagation: reply vs. retweet behavior in political communication. In: 2012 International conference on social informatics (SocialInformatics), 2012 Dec 14, IEEE, pp 131–136
Kwak H, Lee C, Park H, Moon S (2010) What is Twitter, a social network or a news media? In: Proceedings of the 19th international conference on World wide web 2010, ACM, pp 591–600
Lee WJ, Oh KJ, Lim CG, Choi HJ (2014) User profile extraction from twitter for personalized news recommendation. In 16th International conference on advanced communication technology 2014, IEEE, pp 779–783
Lim KW, Buntine W (2014) Twitter opinion topic model: extracting product opinions from tweets by leveraging hashtags and sentiment lexicon. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM international conference on conference on information and knowledge management 2014, ACM, pp. 1319–1328
Liu G, Fu Y, Xu T, Xiong H, Chen G (2014) Discovering temporal retweeting patterns for social media marketing campaigns. In: 2014 IEEE International conference on data mining (ICDM) 2014, IEEE, pp 905–910
Lu C, Lam W, and Zhang Y (2012) Twitter user modeling and tweets recommendation based on Wikipedia concept graph. In Workshops at the Twenty-Sixth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 2012
Luo Z, Osborne M, Tang J, Wang T (2013) Who will retweet me?: finding retweeters in twitter. In: Proceedings of the 36th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval 2013, ACM, pp 869–872
Macskassy SA, Michelson M (2011) Why do people retweet? Anti-homophily wins the day! In: Proceedings of the 5th international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media, pp 209–216
Manning CD, Raghavan P, Schtze H (2008) Introduction to information retrieval, vol 1, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 496
Mittal A, Goel A (2012) Stock prediction using twitter sentiment analysis. Standford University, CS229 (2011 http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2011/GoelMittal-StockMarketPredictionUsingTwitterSentimentAnalysis.pdf), p 15
Mohammad SM, Turney PD (2013) Crowdsourcing a wordemotion association lexicon. Comput Intell 29(3):436–65
Naveed N, Gottron T, Kunegis J, Alhadi AC (2011) Bad news travel fast: a content-based analysis of interestingness on Twitter. In Proceedings of the 3rd international web science conference 2011, ACM, p 8,
O’Connor B, Balasubramanyan R, Routledge BR, Smith NA (2010) From tweets to polls: linking text sentiment to public opinion time series. In: Proceedings of the fourth international conference on weblogs and social media, ICWSM 2010, Washington, DC, USA, 11(122–129):1–2
Peng HK, Zhu J, Piao D, Yan R, Zhang Y (2011) Retweet modeling using conditional random fields. In: 2011 IEEE 11th International conference on data mining workshops (ICDMW), 2011 Dec 11, IEEE, pp 336–343
Perikos I, Hatzilygeroudis I (2013) Recognizing emotion presence in natural language sentences. In: International conference on engineering applications of neural networks 2013. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 30–39
Pfitzner R, Garas A, Schweitzer F (2012) Emotional divergence influences information spreading in Twitter. In: Sixth international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media, vol 12, pp 2–5
Plutchik R (2001) The nature of emotions. Am Sci 89(4):344–350
Rao Y, Li Q, Wenyin L, Wu Q, Quan X (2014) Affective topic model for social emotion detection. Neural Netw 58:29–37
Ren F, Wu Y (2013) Predicting user-topic opinions in Twitter with social and topical context. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 4(4):412–24
Roberts K, Roach MA, Johnson J, Guthrie J, Harabagiu AM (2012) Empatweet: annotating and detecting emotions on Twitter. In LREC 12:3806–3813
Starbird K, Palen L (2012) (How) will the revolution be retweeted?: information diffusion and the 2011 Egyptian uprising. In: Proceedings of the acm 2012 conference on computer supported cooperative work 2012 Feb 11, ACM, pp 7–16
Starbird K, Palen L(2010) Pass It On? Retweeting in mass emergency. In: Proceedings of the 7th international ISCRAM conference seattle 2010 May, vol 1, pp 1–10
Tumasjan A, Sprenger TO, Sandner PG, Welpe IM (2010) Predicting elections with twitter: what 140 characters reveal about political sentiment. Fourth Int AAAI Conf Weblogs Soc Media 10(1):178–85
Xu Z, Yang Q (2012) Analyzing user retweet behavior on twitter. In: Proceedings of the 2012 international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM 2012), IEEE Computer Society, pp 46–50
Yang Z, Guo J, Cai K, Tang J, Li J, Zhang L, Su Z (2010) Understanding retweeting behaviors in social networks. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management 2010, ACM, pp 1633–1636
Zhao WX, Jiang J, Weng J, He J, Lim EP, Yan H, Li X (2011) Comparing twitter and traditional media using topic models. European conference on information retrieval 2011. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 338–349
Zhao XW, Guo Y, He Y, Jiang H, Wu Y, Li X (2014) We know what you want to buy: a demographic-based system for product recommendation on microblogs. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining 2014 Aug 24, ACM, pp 1935–1944
Acknowledgements
This work was made possible by the facilities of the Shared Hierarchical Academic Research Computing Network (SHARCNET: www.sharcnet.ca) and Compute/Calcul Canada.This work is partially sponsored by Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Grant 2015-05555).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firdaus, S.N., Ding, C. & Sadeghian, A. Topic specific emotion detection for retweet prediction. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 10, 2071–2083 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0798-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0798-5