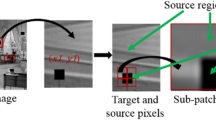
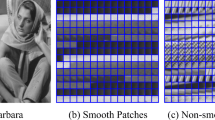
Abstract
Ancient murals have been haunted by various problems such as color fading, surface layer turning crisp and even large-area peeling off. Virtually inpainting technologies are widely used to restore these damages. In general, when structure information are blurred or completely missing within a large region, the image inpainting would be more thorny. In this paper, we study mural image inpainting by incorporating structure information collected from the limners guidance or the line drawings, and propose a global and local feature weighted method based on structure guidance to repair the damaged murals of Yulin Grottoes and Mogao Grottoes, Gansu. Unlike traditional methods, a novel sparse representation model with elastic net regularization based on similarity-preserving overcomplete dictionary is formulated to enhance the global feature consistency, and then an estimated method of neighborhood similarity is presented to guarantee local feature consistency, finally, we apply a global feature patch and local feature patch weighted method to obtain the target patch. Experimental results on damaged murals demonstrate the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art inpainting methods.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertalmio M, Sapiro G, Caselles V, Ballester C (2000) Image inpainting. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH ’00, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, pp 417–424. https://doi.org/10.1145/344779.344972
Roth S, Black MJ (2005) Fields of experts: a framework for learning image priors. In: 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), Vol. 2, pp 860–867 vol. 2. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.160
Criminisi A, Perez P, Toyama K (2004) Region filling and object removal by examplar-based image inpainting. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(9):1200–1212. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2004.833105
Xu Z, Sun J (2010) Image inpainting by patch propagation using patch sparsity. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(5):1153–1165. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2042098
Wang J, Lu K, Pan D, He N, Bao BK (2014) Letters: robust object removal with an examplar-based image inpainting approach. Neurocomputing 123:150–155
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E (1992) Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D Nonlinear Phenomena 60:259–268
Komodakis N, Tziritas G (2007) Image completion using efficient belief propagation via priority scheduling and dynamic pruning. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(11):2649–2661
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) K-svd: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322
Mairal J, Elad M, Sapiro G (2007) Sparse representation for color image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(1):53–69
Pathak D, Krähenbühl P, Donahue J, Darrell T, Efros AA, Context encoders: feature learning by inpainting, CoRR arXiv:abs/1604.07379
Zou Q, Cao Y, Li Q, Mao Q, Wang S (2014) Automatic inpainting by removing fence-like structures in rgbd images. Mach Vis Appl 25(7):1841–1858
D. G. E. S. Connelly Barnes, Ivan Belaunde, Adobe systems inc, www.adobe.com/ technology/ graphics/ content_aware_fill.html
Chan TF, Shen J (2001) Nontexture inpainting by curvature-driven diffusions. J Vis Commun Image Rep. 12(4):436–449
Bornemann F, März T (2007) Fast image inpainting based on coherence transport. J Math Imaging Vis 28(3):259–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-007-0017-6
Shen J, Chan TF (2002) Mathematical models for local nontexture inpaintings. SIAM J Appl Math 62(3):1019–1043
Masnou S (2002) Disocclusion: a variational approach using level lines. IEEE Trans Image Process 11(2):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/83.982815
Efros AA, Leung TK (1999) Texture synthesis by non-parametric sampling. In: Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vol. 2, pp 1033–1038 vol. 2. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.1999.790383
Wei L-Y, Levoy M (2000) Fast texture synthesis using tree-structured vector quantization, in: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH ’00, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, pp 479–488. https://doi.org/10.1145/344779.345009
Zontak M, Irani M (2011) Internal statistics of a single natural image. In: CVPR 2011, pp 977–984. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995401
Bornard R, Lecan E, Laborelli L, Chenot J-H (2002) Missing data correction in still images and image sequences. In: Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MULTIMEDIA ’02, ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 355–361. https://doi.org/10.1145/641007.641084
Drori I, Cohen-Or D, Yeshurun H (2003) Fragment-based image completion. ACM Trans Graph 22(3):303–312. https://doi.org/10.1145/882262.882267
Patel AG, Kumar S, Prajapati AD (2014) Improved examplar based image inpainting using structure tensor. Int J Comput Appl 96(15):9–14
Strobel M, Diebold J, Cremers D (2014) Flow and color inpainting for video completion. In: Jiang X, Hornegger J, Koch R (eds) Pattern recognition. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 293–304
Siadati SZ, Yaghmaee F, Mahdavi P (2016) A new examplar-based image inpainting algorithm using image structure tensors, in: Electrical Engineering, pp 995–1001
Xiao M, Li G, Tan Y, Qin J (2015) Image completion using similarity analysis and transformation. Int J Multimedia Ubiquitous Eng 10(4):193–204
Li Z, He H, Yin Z, Chen F (2014) A color-gradient patch sparsity based image inpainting algorithm with structure coherence and neighborhood consistency. Signal Process 99(6):116–128
Li Z, He H, Tai H, Yin Z, Chen F (2015) Color-direction patch-sparsity-based image inpainting using multidirection features. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(3):1138–1152
Meur OL, Gautier J, Guillemot C (2011) Examplar-based inpainting based on local geometry, In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 3401–3404
Martnez-Noriega R, Roumy A, Blanchard G (2012) Examplar-based image inpainting: fast priority and coherent nearest neighbor search. In: IEEE international workshop on machine learning for signal processing, pp 1–6
Daisy M, Buyssens P, Tschumperl D, Lzoray O (2015) A smarter examplar-based inpainting algorithm using local and global heuristics for more geometric coherence, In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 4622–4626
Patel J, Sarode TK (2014) Examplar based image inpainting with reduced search region. Int J Comput Appl 92(12):27–33
Cornelis B, Ruić T, Gezels E, Dooms A, Piurica A, Platića L, Cornelis J, Martens M, De Mey M, Daubechies I (2013) Crack detection and inpainting for virtual restoration of paintings: the case of the ghent altarpiece. Signal Process 93(3):605–619
Prez-Careta E, Torres-Cisneros M, Manzano OGI, Aguilera-Corts LA, Snchez-Mondragn JJ (2001) Oscillating patterns in image processing and nonlinear evolution equations. American Mathematical Society
Bertalmio M, Vese L, Sapiro G, Osher S (2003) Simultaneous structure and texture image inpainting. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(8):882–889
Cao F, Gousseau Y, Masnou S, Prez P (2009) Geometrically guided examplar-based inpainting. SIAM J Imaging Sci 4(4):1143–1179
Du X, Cho D, Bui TD (2011) Image segmentation and inpainting using hierarchical level set and texture mapping. Singla Process 91:852–863
Chen XW, Zhou B, Yu G, Fang XU, Zhao QP (2014) Structure guided texture inpainting through multi-scale patches and global optimization for image completion. Sci China Inf Sci 57(1):1–16
Wexler Y, Shechtman E, Irani M (2007) Space-time completion of video. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(3):463–476
Szeliski R, Zabih R, Scharstein D, Veksler O, Kolmogorov V, Agarwala A, Tappen M, Rother C (2008) A comparative study of energy minimization methods for markov random fields with smoothness-based priors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(6):1068–1080
Barnes C, Shechtman E, Finkelstein A, Dan BG (2009) Patchmatch: a randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing, In: SIGGRAPH, pp 1–11
Darabi S, Shechtman E, Barnes C, Goldman DB, Sen P (2012) Image melding: combining inconsistent images using patch-based synthesis. ACM Trans Graph 31(4):82:1–82:10
He K, Sun J (2014) Image completion approaches using the statistics of similar patches. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(12):2423–2435
Ge S, Xie K, Li S, Yang R (2016) Global image completion with joint sparse patch selection and optimal seam synthesis. Signal Process 124(C):147–155
Elad M, Aharon M (2006) Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(12):3736–3745
Trkan M, Guillemot C (2013) Locally linear embedding based texture synthesis for image prediction and error concealment. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 3009–3012
Guillemot C, Turkan M, Meur OL, Ebdelli M (2013) Object removal and loss concealment using neighbor embedding methods. Image Commun 28(10):1405–1419
Takahashi T, Konishi K, Furukawa T (2012) Structured matrix rank minimization approach to image inpainting. Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp 860–863
Guleryuz OG (2006) Nonlinear approximation based image recovery using adaptive sparse reconstructions and iterated denoising-part I: theory. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(3):555–571
Fadili M, Starck J-L, Murtagh F (2009) Inpainting and zooming using sparse representations. Comput J 52(1):64–79. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxm055
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G (2010) Online learning for matrix factorization and sparse coding. J Mach Learn Res 11: 19–60. URL http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1756006.1756008
Shen B, Hu W, Zhang Y, Zhang YJ (2009) Image inpainting via sparse representation, In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp 697–700
Peyr Gabriel (2009) Sparse modeling of textures. J Math Imaging Vis 34(1):17–31
Yang C, Lu X, Lin Z, Shechtman E, Wang O, Li H, High-resolution image inpainting using multi-scale neural patch synthesis. CoRR arXiv:abs/1611.09969
Li C, Wand M, Combining markov random fields and convolutional neural networks for image synthesis. CoRR arXiv:abs/1601.04589
Iizuka S, Simo-Serra E, Ishikawa H (2017) Globally and Locally Consistent Image Completion, ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH 2017) 36 (4), 107:1–107:14
Song Y, Yang C, Lin Z, Li H, Huang Q, Kuo CJ, Image inpainting using multi-scale feature image translation. CoRR arXiv:abs/1711.08590
Yu J, Lin Z, Yang J, Shen X, Lu X, Huang TS, Generative image inpainting with contextual attention. CoRR arXiv:1801.07892
Liu G, Reda FA, Shih KJ, Wang T, Tao A, Catanzaro B, Image inpainting for irregular holes using partial convolutions. CoRR arXiv:abs/1804.07723
Li Q, Zou Q, Ma D, Wang Q, Wang S (2018) Dating ancient paintings of mogao grottoes using deeply learnt visual codes. Sci China Inf Sci 15(6):1–13
Wang H, Li Q, Zou Q (2019) Inpainting of dunhuang murals by sparsely modeling the texture similarity and structure continuity. ACM J Comput Cult Herit 12(3):17. https://doi.org/10.1145/3280790
Hastie Hui T (2005) Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Statistical Methodology) 67(2): 301–320. URL http://www.jstor.org/stable/3647580
M. Elad, Elad, m.: Sparse and redundant representations. From theory to applications in signal and image processing. springer
Mallat S (2008) A wavelet tour of signal processing, 3rd edn. The Sparse Way, Academic Press
Mairal J, Spams: sparse modeling software. http://spams-devel.gforge.inria.fr/
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Basic Research Program of China under Grant No. 2012CB725303, National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants No. 91546106, No. 61872277, No. 41571437, No. 41971300 and No. 61671307, in part by the Shenzhen Scientific Research and Development Funding Program under Grant JCYJ20180305124802421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Li, Q. & Jia, S. A global and local feature weighted method for ancient murals inpainting. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 11, 1197–1216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-01032-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-01032-2