Abstract
Changing trends and globalization has given rise to various challenges to the software industry. Today the repute of any software engineering is related to its quality and timely delivery of product. The repute also depends on how the industry keeps in pace with the new expertise and changing market situation. The factors like transparency, recognition, work life balance etc. play an imperative part in preserving the reasonable edge. The ISM is a methodology for interactive learning process. In this method the factors that affect the system directly or indirectly are outlined into a complete structure model. The major advantage of the ISM model is its graphical representations of identified factors in a structured manner is indeed the subject in consideration. As a tool, it organizes the elements affecting the system’s credibility. It also highlights the hierarchical complexity among the factors of the system. The ultimate necessity is to analyze the performance of these factors for their operative application in the execution of software development process. The main objective of this paper is to identify the shared communication of these factors and identify the driving and dependent factors. In this work an ISM model has been prepared to recognize significant factors and their administrative consequences from software release time point of view.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcade J, Godet M, Meunier F, Roubelat F (2003) Structural analysis, “Structural analysis with the MICMAC method and Actors’ strategy with MACTOR method”, CD ROM, the Millennium Project, Laboratory for Investigation in Prospective and Strategy (LIPS)
Attri R, Dev N, Sharma V (2013) Interpretive structural modelling (ISM) approach: an overview. Res J Manag Sci 2(2):3–8
Balzer RM (1975) Imprecise program specification. DTIC Document
Borade AV, Bansod SV (2011) Interpretive structural modeling-based framework for VMI adoption in Indian industries. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58(9–12):1227–1242
Chand M, Singh RK (2010) Study of select issues of supply chain management: a case study. Int J Adv Manuf Syst 1(2):151–155
Chand M, Raj T, Shankar R (2014) Analysing the operational risks in supply chain by using weighted interpretive structural modeling (W-ISM) technique. Int J Serv Oper Manag 18(4):378–403
Chand M, Raj T, Shankar R (2015) Weighted-ISM technique for analysing the competitiveness of uncertainty and risk measures in supply chain. Int J Logist Syst Manag 21(2):181–198
Chhokar KB (2010) Higher education and curriculum innovation for sustainable development in India. Int J Sustain High Educ 11(2):141–152
Dhillon BS (2007) Human reliability and error in transportation systems, Springer series in reliability engineering. Springer, London, p 182
Hagen EW (1976) Human reliability analysis. Nucl Saf 17:315–326
Jain V, Raj T (2015) A hybrid approach using ISM and modified TOPSIS for the evaluation of flexibility in FMS. Int J Ind Syst Eng 19(3):389–406
Jayant A, Azhar M (2014) Analysis of the barriers for implementing green supply chain management (GSCM) practices: an interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. In: Procedia Engineering “12th global congress on manufacturing and management” GCMM—2014, volume 97, pp 2157–2166
Omrana AM, Khorshidb M (2014) Intelligent environmental scanning approach (a case study: the Egyptian wheat crop production). In: International conference on applied computing, computer science, and computer engineering (ICACC 2013), volume 7, pp 28–34
Ravi V, Shankar R (2005) Analysis of interactions among the barriers of reverse logistics. Technol Forecast Soc Change 72(8):1011–1029
Raj T, Shankar R, Suhaib M (2008) An ISM approach for modelling the enablers of flexible manufacturing system: the case for India. Int J Prod Res 46(24):6883–6912
Sage AP (1977) Interpretive structural modeling: methodology for large-scale systems. McGrawHill, NewYork, USA, pp 91–164
Singh MD, Shankar R, Narain R, Agarwal A (2003) An interpretive structural modeling of knowledgemanagement in engineering industries. J Adv Manag Res 1(1):28–40
Singh S, Kumar R, Kumar U (2015) Modelling factors affecting human operator failure probability in railway maintenance task: an ISM based analysis. Inst J Syst Assur Eng Manag 6(2):129–138
Warfield JW (1974) Developing interconnected matrices in structural modelling. IEEE TransSyst Men Cyberne 4(1):51–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
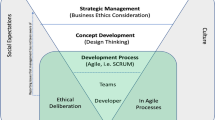
Appendix: Hierarchy structure with relationship amongst factors
Appendix: Hierarchy structure with relationship amongst factors

In the Diagraph Top Level factors are placed Top, second Level factors at second and so on.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majumdar, R., Kapur, P.K. & Khatri, S.K. Assessment of environmental factors affecting software development process using ISM & MICMAC analysis. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 7, 435–441 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0477-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0477-4