Abstract
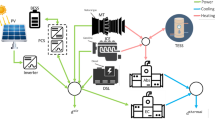
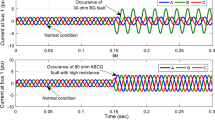
The modern smart grid involves two distinct and intricate cyber-power networks. Cyber networks are employed to protect, monitor and control different types of physical systems. Various topologies of the cyber network affect reliability of the power grid. In conventional methods, it is supposed that the cyber components are failure free, but this simplification has errors and is not precise. So, in this paper, a novel analytical method is proposed to evaluate the reliability indices considering cyber-power interdependencies. The introduced method evaluates the smart grid reliability under failure of power and cyber elements and uncertainties of renewable resources such as wind distributed generation. Also, a new procedure is proposed based on changing structure of cyber topology. The proposed method is applied to a realistic distribution network in Iran. The reliability indices of each configuration are calculated. The test results indicate that it is vital to consider cyber effects on power grid in reliability assessment of smart grid as well as power effects. Cyber network properties and topologies which are important are investigated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SAA, Tarek HME, Magdy MAS (2014) Optimal ESS allocation and load shedding for improving distribution system reliability. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 99:1–11
Amirreza HA, Hossein AA, Gevork BG (2015) Negative effects of cyber network (control, monitoring, and protection) on reliability of smart grids based on DG penetration. Comput Knowl Eng 5:54–60
Atwa YM, El-Saadany EF, Guise AC (2010) Supply adequacy assessment of distribution system including wind-based DG during different modes of operation. IEEE Trans Power Syst 25:78–86
Atwa YM, El-Saadany EF, Salama MMA, Seethapathy R, Assam M, Conti S (2011) Adequacy evaluation of distribution system including wind/solar DG during different modes of operation. IEEE Trans Power Syst 26:1945–1952
Bamdad F, Yong F (2012) A study on interdependencies of cyber-power networks in smart grid applications. In: Innovative smart grid technologies (ISGT). IEEE PES, pp 1–8
Bamdad F, Yong F (2014a) Faults and failures in cyber-power interdependent networks. In: T&D conference and exposition. IEEE PES, pp 1–5
Bamdad F, Yong F (2014b) Reliability assessment of smart grids considering indirect cyber-power interdependencies. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 5:677–1685
Bamdad F, Yong F, Lei W (2012) Reliability assessment of smart grid considering direct cyber-power interdependencies. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 3:1515–1524
Debomita G, Ghose T, Mohanta DK (2013) Communication feasibility analysis for smart grid with phasor measurement units. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 9:1486–1496
Hassan F (2014) A road map to integration: perspectives on smart grid development. IEEE Power Energy Mag 12:52–66
IEEE Reliability Test System (1979) A report prepared by the reliability test system task force of the application of probability methods subcommittee. IEEE Trans Power Appl Syst 98:2047–2054
Lucian ID, Mihail A, Dorin B (2014) Distributed generation and virtual power plants. In: 49th international universities power engineering conference (UPEC), pp 1–5
Murtadha NA, Nathan J, Kamlesh AJ, Sahra SS (2014) Analysis of reliability and resilience for smart grids. In: IEEE 38th annual computer software and applications conference (COMPSAC), pp 529–534
Nouredine H, Carolina T, Benoit R, Maria V, Raphael C (2009) Modeling cyber and physical interdependencies—application in ICT and power grids. In: Power systems conference and exposition. IEEE/PES, pp 1–6
Pravin PV, Felix FW, Janusz WB (2011) Smart operation of smart grid: risk-limiting dispatch. Proc IEEE 99:40–57
Roy B, Bipul K (2011) Well-being analysis of wind integrated power systems. IEEE Trans Power Syst 26:2101–2108
Seyed Ali A, Yasser AIM, Tarek HME (2012) Supply-adequacy-based optimal construction of microgrids in smart distribution systems. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 3:1491–1502
Shahram K, Matti L, Mahmud F (2012) Impacts of fault diagnosis schemes on distribution system reliability. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 3:720–727
Shengjie X, Yi Q, Rose QH (2015) On reliability of smart grid neighborhood area networks. IEEE Access 3:2352–2365
Vijay VV, Oddbjorn G, Gerd K (2013) Dependability and security-based failure considerations in protection system reliability studies. In: 2013 4th innovative smart grid technologies Europe (ISGT EUROPE). IEEE/PES, pp 1–5
Wei-Liang S, Chung-Shiuan C, Kate CJL, Kien AH (2014) Autonomous mobile mesh networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 13:364–376
Weixiao M, Ruofei M, Hsiao-Hwa C (2014) Smart grid neighborhood area networks: a survey. IEEE Netw 28:24–32
Xi F, Satyajayant M, Guoliang X, Dejun Y (2012) Smart grid—the new and improved power grid: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 14:944–980
Ye Y, Yi Q, Hamid S, David T (2013) A survey on smart grid communication infrastructures: motivations, requirements and challenges. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15:5–20
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassani Ahangar, A., Vahidi, B. & Askarian Abyaneh, H. Evaluating smart grid reliability based on impacts of cyber (control, monitoring and protection) network and its different topologies. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 9, 1047–1056 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-018-0730-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-018-0730-0