Abstract
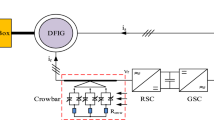
This paper investigates a comprehensive analysis of the dynamic behavior of a typical 2 mw grid-connected double fed induction generator-based wind turbine during a symmetrical grid voltage dip scenario. The stator flux dynamics and the induced rotor electromotive force have been investigated aiming to undertake an accurate assessment of the DFIG behavior. Furthermore, without any complication of the DFIG vector control scheme, the paper offers a comparative study between the use of the stator flux reference frame orientation approach and the grid voltage reference frame orientation approach, this, in order to accurately assess the appropriate choice regarding the stability of the vector control scheme and hence, to have a good background about the LVRT capability of the DFIG during the studied grid fault. The simulation results have been performed through Matlab/Simulink environment.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{\text{V}}_{\text{g}}\) :
-
Grid rms value
- \({\hat{\text{V}}}_{\text{g}}\) :
-
Grid maximum value
- \(\uptheta_{\text{g}}\) :
-
Grid voltage angle
- \(\uptheta_{\text{s}}\) :
-
Stator voltage angle
- \(\uptheta_{\text{r}}\) :
-
Rotor voltage angle
- \(\uptheta_{\text{m}}\) :
-
Rotor mechanical angle
- \(\upsigma\) :
-
Leakage coefficient
- s:
-
Slip
- (s):
-
Stator reference frame
- (r):
-
Rotor reference frame
- \({\vec{\upphi }}_{\text{sn}}\) :
-
Natural stator flux
- \({\vec{\upphi }}_{\text{sf}}\) :
-
Forced stator flux
- EMF:
-
Electromotive force
- GVO:
-
Grid voltage orientation
- SFO:
-
Stator flux orientation
References
Abad G, Iwanski G, Lopez J (2011) Doubly fed induction machine: modeling and control for wind energy generation, 1st edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Abdelbasset MM, Drid S, Sid MA, Cheikh R (2017) Sliding mode control of grid connected brushless doubly fed induction generator driven by wind turbine in variable speed. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8(2):788–798
Akel F, Ghennam T, Berkouk EM, Laour M (2014) An improved sensorless decoupled power control scheme of grid connected variable speed wind turbine generator. Energy Convers Manag 78:584–594
Athanasios DG, Safacas N (2015) Quantitative and qualitative behavior analysis of a DFIG wind energy conversion system by a wind gust and converter faults. Wind Energy 19(3):527–546
Bekakra Y, Attous DB (2014) Direct control of doubly fed induction generator fed by PWM converter with a variable structure control based on a sliding mode control. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 5(3):213–218
Boshell F (2017) Grid codes as enablers of energy transition. Scaling up variable renewable power. World future energy summit 2017, Abu Dhabi, UAE
Camblong H (2003) Minimisation de l’impact des perturbations d’origine éolienne dans la génération d’électricité par des aérogénérateurs à vitesse variable PhD Thesis, École Nationale Supérieure d’Arts et Métiers. Bordeaux, France
Datta R, Ranganathan VT (1999) Decoupled control of active and reactive power for a grid-connected doubly-fed wound rotor induction machine without position sensors. In: Proceedings of IEEE industry applications conference, vol 4. Phoenix, USA, pp 2623–28
Datta R, Ranganathan VT (2002) Variable-speed wind power generation using doubly fed wound rotor induction machine-a comparison with alternative schemes. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 17(3):414–421
Dida A, Attous DB (2017) Fuzzy logic control of grid connected DFIG system using back-to-back converters. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-014-0309-3
Dirksen J (2013) LVRT low voltage ride through. DEWI Mag 43:56–60
Ekanayake JB, Holdsworth L, Xue Guang W, Jenkins N (2003) Dynamic modeling of doubly fed induction generator wind turbines. IEEE Trans Power Syst 18(2):803–809
El-Kharashi E, Farid AW (2015) Accurate assessment of the output energy from the doubly fed induction generators. Energy 93(Part 1):406–415
El-Sattar AA, Saad NH, Shams El-Dein MZ (2008) Dynamic response of doubly fed induction generator variable speed wind turbine under fault. Int J Electr Power Syst Res 78(3):1240–1246
Gayen PK, Chatterjee D, Goswami SK (2016) An improved low-voltage ride-through performance of DFIG based wind plant using stator dynamic composite fault current limiter. ISA Trans 62:333–348
Geng H, Yang G, Dewei X, Bin W (2011) Unified power control for PMSG based WECS during different grid situations. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 26(3):822–830
Geng H, Liu C, Yang G (2013) LVRT capability of DFIG-based WECS under asymmetrical grid fault condition. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(6):2495–2509
Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC) (2018) Global wind statistics. Report 2018. www.gwec.net. Accessed Apr 2019
Guediri AK, Attous DB (2017) Modeling and fuzzy control of a wind energy system based on double-fed asynchronous machine for supply of power to the electrical network. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8(1):353–360
Jadhav HT, Ranjit Roy A (2013) Comprehensive review on the grid integration of doubly fed induction generator. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 49:8–18
Justo JJ, Mwasilu F, Jung J-W (2015) Doubly-fed induction generator based wind turbines: a comprehensive review of fault ride-through strategies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 45:447–467
Krause PC, Wasynczuk O, Sudhoff SD (2002) Analysis of electric machinery and drive systems, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Lindholm FA, Fossum JG, Burgess EL (1979) Application of the superposition principle to solar-cell analysis. IEEE Trans Electron Dev 26(3):165–171
Lopez J, Pablo Sanchis P, Roboam X, Marroyo L (2007) Dynamic behavior of the doubly fed induction generator during three-phase voltage dips. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 22(3):709–717
Lopez J, Gubıa E, Sanchis P, Marroyo XRL (2008) Wind turbines based on DFIG under asymmetrical voltage dips. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 23(1):321–330
Nielsen JG (2004) Method for controlling a power-grid connected wind turbine generator during grid faults and apparatus for implementing said method. Vestas, worldwide patent no. WO2004070936
Özsoy EE, Golubovic E, Sabanovic A, Bogosyan S, Gokasan M (2016) Modeling and control of a doubly fed induction generator with a disturbance observer: a stator voltage oriented approach. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 24:961–972
Pena R, Clare JC, Asher GM (1996) Doubly fed induction generator using back-to-back PWM converters and its application to variable-speed wind-energy generation. IEE Proc Electr Power Appl 143(3):231–241
Perdana A, Carlson O, Persson J (2004) Dynamic response of grid-connected wind turbine with doubly fed induction generator during disturbances. In Nordic workshop on power and industrial electronics. Trondheim, Norway
Petersson A, Harnefors L, Thiringer T (2004) Comparison between stator-flux and grid-flux-oriented rotor current control of doubly-fed induction generators. In: Proceedings of the 35th annual IEEE power electronics specialists conference. Aachen, Germany
Petersson A, Thiringer T, Harnefors L, Petru T (2005) Modeling and experimental verification of grid interaction of a DFIG wind turbine. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 20(4):878–886
Rahimi M, Parniani M (2010) Dynamic behavior analysis of doubly-fed induction generator wind turbines—the influence of rotor and speed controller parameters. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 32(5):464–477
Rahimi M, Masoum Mohammad AS, Islam SM (2011) Low and high voltage ride-through of DFIG wind turbines using hybrid current controlled converters. Int J Electr Power Syst Res 81:1456–1465
Rodriguez M, Abad G, Sarasola I, Gilabert A (2005) Crowbar control algorithms for doubly fed induction generator during voltage dips. In European power electronics and applications conference. Dresden, Germany, pp 1–10
Shuai X, Hong Z (2013) An LVRT control strategy based on flux linkage tracking for DFIG-based WECS. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(7):2820–2832
Thiringer T, Petersson A, Petru T (2003) Grid disturbance response of wind turbines equipped with induction generator and doubly-fed induction generator. Power engineering society general meeting, vol 3. IEEE
Tohidi S, Mohammadi-ivatloo B (2016) A comprehensive review of low voltage ride through of doubly fed induction wind generators. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 57:412–419
Xiang D, Li Ran PJ, Tavner S Yang (2006) Control of a doubly fed induction generator in a wind turbine during grid fault ride through. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 21(3):652–662
Yu L, Cai Z (2013) Rotor current dynamics of doubly fed induction generators during grid voltage dip and rise. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 44(1):17–24
Zou J, Peng C, Yan Y, Zheng H, Li Y (2014) A survey of dynamic equivalent modeling for wind farm. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 40:956–963
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheikh, R., Belmili, H., Menacer, A. et al. Dynamic behavior analysis under a grid fault scenario of a 2 MW double fed induction generator-based wind turbine: comparative study of the reference frame orientation approach. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 10, 632–643 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00790-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00790-0