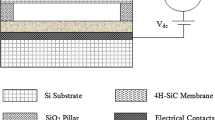
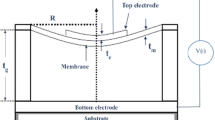
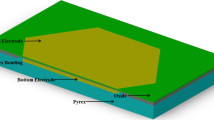
Abstract
Background For ultrasonic signal generation and detection, the Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (CMUTs), constructed using semiconductor fabrication processes are basically Microelectromechanical Systems based structures. Utilizing the semiconductor technology, the CMUTs can provide improved bandwidth, high transduction efficiency, ease of batch production etc. in contrast to piezoelectric transducers. Objective The CMUTs can be constructed in various possible geometries like square, rectangular, circular, and hexagonal. It has been found that CMUT with circular geometry provides optimum performance but has the disadvantage of area wastage in array construction due to voids in between the devices. Hence, the hexagonal CMUT is modelled and analyzed with circular CMUT. Method The Kirchhoff’s thin plate theory is employed for novel analytical model of hexagonal CMUT. Result The results comparison is found similar with the circular CMUT with 13.42% of more wafer area utilization. Conclusion The proposed analytical model provides a cheaper design tool for the researchers with highly reduced simulation time.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad B, Pratap R (2010) The effect of evacuated backside cavity on the dynamic characteristics of a capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer. Int J Adv Eng 2:50–54
Averkiou MA, Roundhill DN (1997) Powers JE. A new imaging technique based on the nonlinear properties of tissues. Ultrasonic Symposium IEEE, 1561–1566.
Babar A, Rudra P (2010) Elasto-electrostatic analysis of circular microplates used in capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers. IEEE Sens J 10(11):1767–1773
Bang JH, Suslick KS (2010) Applications of ultrasound to the synthesis of nanostructured materials. Adv Mater 22(10):1039–1059
Calkins Smith Flatau FTRCAB (2000) An energy-based hysteresis model for magnetostrictive transducers. IEEE Trans Magn 36(2):429–439
Caronti A, Savoia A, G., Caliano and M., Pappalardo. (2005) Acoustic coupling in capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducers: modelling and experiments. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 52(12):2220–2234
Carovac A, Smajlovic F, Junuzovic D (2011) Application of ultrasound in medicine. J Acad Med Sci Bosnia Herzeg 19(3):168–171
Chemat F, Huma Z, Khan MK (2011) Applications of ultrasound in food technology: processing, preservation, and extraction. Ultrason Sonochem 18(4):813–835
Chen JK, Cheng XY, Chen CC, Li PC, Liu JH, Cheng YT (2008) A capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer array for minimally invasive medical diagnosis. J Microelectromechical Syst 17(3):599–610
Cheng X (2009). CMUT-in-CMOS ultrasonic transducer arrays with on-chip electronics. in Proceedings Transducers, 1222–1225.
Coppa A, Cianci E, Foglietti V, Caliano G, Pappalardo M (2007) Building CMUTs for imaging applications from top to bottom. Microelectron Eng 84(5–8):1312–1315
Doody CB, Cheng XY, Rich CA, Lemmerhirt DF, White RD (2011) Modeling and characterization of CMOS-fabricated Capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers. J Microelectromechical Syst 20(1):104–118
Eccardt PC, Niederer K, Scheiter T, Hierold C (1996). Surface micromachined ultrasound transducers in CMOS technology. In: Proceedings IEEE Ultrasononics Symposium, 959–962.
Ergun AS, Huang YL, Zhuang XF, Oralkan O et al (2005) Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers: fabrication technology. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 52(12):2242–2258
Haller Khuri-Yakub MIBT (1994) A surface micromachined electrostatic ultrasonic air transducer. Ultrason Symp IEEE 2:1241–1244
Haller Khuri-Yakub MIBT (1996) A surface micromachined electrostatic ultrasonic air transducer. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 43(1):1–6
Hansen ST, Mossawir BJ, Ergun AS et al. (1999). Air-coupled nondestructive evaluation using micromachined ultrasonic transducers. Ultrasonic Symposium IEEE, 1037–1040.
Helin P, Czarnecki P, Verbist A, Bryce G, Rottenberg X, Severi S (2012). Poly-SiGe-based cMUT array with high acoustical pressure. In: Proceedings of IEEE 25th International Conference on MEMS, 305–308.
Hunt FV (1982) The analysis of transduction, and its historical background: electroacoustics, 2nd edn. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Hunt FV (1982) The analysis of transduction, and its historical background: electroacoustic, 2nd edn. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Hussain A, Akhtar S (2017) Evaluation of Historic Masonry and Concrete Structures. Arab J Sci Eng 42:925–940
Jiles DC (1995) Theory of the magneto mechanical effect. J Phys D Appl Phys 28:1537–1546
Kamlah M (2001) Ferroelectric and ferroelastic piezoceramics-modeling of electromechanical hysteresis phenomena. Continuum Mech Thermodyn 13:219–268
Katzir S (2003) The discovery of the piezoelectric effect. Arch Hist Exact Sci 57:61–91
Knight J, McLean J, Degertekin FL (2004) Low temperature fabrication of immersion capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers on silicon and dielectric substrates. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 51(10):1324–1333
Liu J, Oakley C, Shandas R (2009) Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers using commercial multi-user MUMPs process: capability and limitations. Ultrasonics 49:765–773
Mitragotri S (2005) Healing sound the use of ultrasound in drug delivery and other therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:255–260
Niezrecki C, Balakrishnan BD, Moskalik S (2001) Piezoelectric actuation state of the art. Shock Vibrat Digest 33:269–280
Noble Jones Robertson RAADRTJDA, Hutchins Billson DR (2001) Novel wide bandwidth, micromachined ultrasonic transducers. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 48(6):1495–1507
Oralkan O et al (2006) Experimental characterization of collapse-mode CMUT operation. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 53(8):1513–1523
Park Lee Kupnik Khuri-Yakub. KKHJMBT (2011) Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers via local oxidation and direct wafer bonding. J Microelectromechical Syst 20(1):95–103
Preumont A (2006) Mechatronics. Springer, Dynamics of Electromechanical and Piezoelectric Systems
Rashmi S, Rekha A, Arora A (2016) Evaluation of ultrasonic transducer with divergent membrane materials and geometries. Smart Com CCIS 628:779–787
Reshmi Maity Guha MNPK et al (2018) A new compact analytical model of nanoelectromechanical systems-based capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers for pulse echo imaging. J Comput Electron 17:1334–1342
Reshmi M, Maity NP, Guha K, et. al. (2019). Study of 3D Hexagonal Membrane Structure for MEMS-Based Ultrasonic Transducer Using Finite Element Method. proceedings of ICDMC, 199–209.
Schindel D, Hutchins Zou Sayer WDAL (1995) The design and characterization of micromachined air-coupled capacitance transducers. IEEE TransUltrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 42(1):42–50
Serena Wong Kupnik Zhuang HMX et al (2009) Evaluation of wafer bonded CMUTs with rectangular membranes featuring high fill factor. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 55(9):2053–2065
Shuai N, Zhenhao L, Lawrence LP et al (2017) An Optimization and Comparative Study of Air-Coupled CMUT Cells with Circular and Annular Geometries. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectron Freq Control 64(11):1723–1734
Timoshenko Krieger SPSW (1959) Theory of plates and shells. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 52–55
Tiwari Satyanarayana Pai Trivedi SKBSAGKK (2009) Circular capacitance micromachined ultrasonic transducer. Def Sci J 59(6):627–633
Wei Y, Cretu E, Rohling R (2011) Analytical modeling of CMUTs in coupled electro-mechano-acoustic domains using plate vibration theory. IEEE Sensors 11(9):2159–2168
Yang J (2005) An introduction to the theory of piezoelectricity. Springer, New York, USA
Yaralioglu Ergun Bayram GGASB et al (2001) Residual stress and Young’s modulus measurement of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer membranes. IEEE Ultrason Symp Proc Int Symp 2:953–956
Zhuang Lin Oralkan Khuri-Yakub XFDSOBT (2008) Fabrication of flexible transducer arrays with through-wafer electrical interconnects based on trench refilling with PDMS. J Microelectromechical Syst 17(2):446–452
Acknowledgment
The simulation on ANSYS software is done at Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amity School of Engineering & Technology, Amity University, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India. Authors thank Amity University, Noida, for providing the opportunity to carry out research simulations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, R., Agarwal, R., Dubey, A.K. et al. Analytical Modelling of Hexagonal Shaped Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 12, 252–262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-020-01046-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-020-01046-y