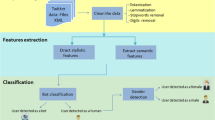
Abstract
Recently, author profiling on social media and on online platforms, characterized by a huge volumes of data, has become more than a critical issue. This issue is of increasing interest in various fields related to forensic medicine, security, marketing, education, etc. The main objective of author profiling is to identify the type of writer of the messages, whether it is a human or a bot with a very strong presence. These bots have the task of drawing the attention of browsers to specific events, often used to disseminate incorrect and/or false information. In this work, we offer a new approach to detect these bots and the kind of anonymous perpetrators on these social networks. Our approach, purely statistical, is based on digital features (APSF), extracted from users’ tweets, and on the technique of random forests. A total of 17 stylometry-based features were used to train the model. To assess the performance of our approach, we considered different standard measures, namely accuracy, precision, recall and F1-score. The results obtained show that our approach gives the best performance for both English and Spanish languages. For the English dataset, we achieved an accuracy of 92.45% for the bot detection task and 90.36% for the gender classification; similarly, we obtained accuracy values of 89.68% and 88.88% for the Spanish dataset.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akar Ö, Güngör O (2012) Classification of multispectral images using random forest algorithm. J Geod Geoinf 1(2):105–112
Alarifi A, Alsaleh M, Al-Salman A (2016) Twitter turing test: identifying social machines. Inf Sci 372:332–346
Ashraf S, Iqbal HR, Nawab RMA (2016) Cross-genre author profile prediction using stylometry-based approach. In: CLEF (Working Notes), Citeseer, pp 992–999
Ashraf S, Javed O, Adeel M, Iqbal H, Nawab RMA (2019) Bots and gender prediction using language independent stylometry-based approach. In: CLEF (Working Notes)
Basil M, Gaikwad S, Salim AS (2019) Deep learning approach based dominant age group based classification for social network. In: International conference on applied computing to support industry: innovation and technology, Springer, pp 148–156
Bessi A, Ferrara E (2016) Social bots distort the 2016 us presidential election online discussion. First Monday 21:7–11
Boukhari K, Omri MN (2020) Approximate matching-based unsupervised document indexing approach: application to biomedical domain. Scientometrics 124:903–924
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Cai C, Li L, Zengi D (2017) Behavior enhanced deep bot detection in social media. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on intelligence and security informatics (ISI). IEEE, pp 128–130
Chu Z, Gianvecchio S, Wang H, Jajodia S (2012) Detecting automation of twitter accounts: Are you a human, bot, or cyborg? IEEE Trans Depend Secure Comput 9(6):811–824
Daneshvar S, Inkpen D (2018a) Gender identification in twitter using n-grams and lsa. In: Proceedings of the ninth international conference of the CLEF Association (CLEF 2018)
Daneshvar S, Inkpen D (2018b) Gender identification in twitter using n-grams and LSA: notebook for PAN at CLEF 2018. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2018-Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Avignon, France, September 10–14, 2018, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 2125
Davis CA, Varol O, Ferrara E, Flammini A, Menczer F (2016) Botornot: a system to evaluate social bots. In: Proceedings of the 25th international conference companion on world wide web, pp 273–274
Dickerson JP, Kagan V, Subrahmanian VS (2014) Using sentiment to detect bots on twitter: Are humans more opinionated than bots? In: 2014 IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM 2014). IEEE, pp 620–627
Dong R, Schaal M, O’Mahony MP, Smyth B (2013) Topic extraction from online reviews for classification and recommendation. In: Twenty-third international joint conference on artificial intelligence
Fatima M, Hasan K, Anwar S, Nawab RMA (2017) Multilingual author profiling on Facebook. Inf Process Manag 53(4):886–904
Fernquist J, Kaati L, Schroeder R (2018) Political bots and the Swedish general election. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on intelligence and security informatics (ISI). IEEE, pp 124–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44564-9_9
Fkih F, Omri MN (2013) Estimation of a priori decision threshold for collocations extraction: an empirical study. Int J Inf Technol Web Eng 8(3):34–49. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijitwe.2013070103
Fkih F, Omri MN (2020) Hidden data states-based complex terminology extraction from textual web data model. Appl Intell 50(6):1813–1831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01568-4
Flekova L, Preoţiuc-Pietro D, Ungar L (2016) Exploring stylistic variation with age and income on twitter. In: Proceedings of the 54th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (volume 2: Short Papers), pp 313–319
Garibay AP, Camacho-González AT, Fierro-Villaneda RA, Hernandez-Farias I, Buscaldi D, Ruíz IVM (2015) A random forest approach for authorship profiling. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2015—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Toulouse, France, September 8–11, 2015, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 1391. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1391/72-CR.pdf
Goubin R, Lefeuvre D, Alhamzeh A, Mitrovic J, Egyed-Zsigmond E, Fossi LG (2019) Bots and gender profiling using a multi-layer architecture. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2019—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 9–12, 2019, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 2380. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2380/paper_235.pdf
Guimaraes RG, Rosa RL, De Gaetano D, Rodriguez DZ, Bressan G (2017) Age groups classification in social network using deep learning. IEEE Access 5:10805–10816
Hall A, Terveen L, Halfaker A (2018) Bot detection in wikidata using behavioral and other informal cues. In: Proceedings of the ACM on human–computer interaction, vol 2 (no CSCW), pp 1–18
Inuwa-Dutse I, Liptrott M, Korkontzelos I (2018) Detection of spam-posting accounts on twitter. Neurocomputing 315:496–511
Isbister T, Kaati L, Cohen K (2017) Gender classification with data independent features in multiple languages. In: 2017 European intelligence and security informatics conference (EISIC). IEEE, pp 54–60
Juola P (2015) Industrial uses for authorship analysis. Math Comput Sci Ind 66:21–25
Kudugunta S, Ferrara E (2018) Deep neural networks for bot detection. Inf Sci 467:312–322
Kyebambe MN, Cheng G, Huang Y, He C, Zhang Z (2017) Forecasting emerging technologies: a supervised learning approach through patent analysis. Technol Forecast Soc Change 125:236–244
Lee K, Eoff B, Caverlee J (2011) Seven months with the devils: a long-term study of content polluters on twitter. In: Proceedings of the international AAAI conference on web and social media, vol 5
Li H, Zhang C, Zhang S, Atkinson PM (2020) Crop classification from full-year fully-polarimetric l-band uavsar time-series using the random forest algorithm. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 87:66
López-Monroy AP, González FA, Solorio T (2020) Early author profiling on twitter using profile features with multi-resolution. Expert Syst Appl 140:66
Mabrouk O, Hlaoua L, Omri MN (2020) Exploiting ontology information in fuzzy SVM social media profile classification. Appl lntell 66:23
Mac Kim S, Xu Q, Qu L, Wan S, Paris C (2017) Demographic inference on twitter using recursive neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 55th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pp 471–477
Maitra P, Ghosh S, Das D (2016) Authorship verification—an approach based on random forest. arXiv preprint arXiv:160708885
Mehrotra R, Sanner S, Buntine W, Xie L (2013) Improving lda topic models for microblogs via tweet pooling and automatic labeling. In: Proceedings of the 36th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pp 889–892
Najib F, Cheema WA, Nawab RMA (2015) Author’s traits prediction on twitter data using content based approach. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2015-conference and labs of the evaluation forum, Toulouse, France, September 8–11, 2015, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 1391. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1391/96-CR.pdf
Naouar F, Hlaoua L, Omri MN (2017) Information retrieval model using uncertain confidence’s network. Int J Inf Retrieval Res 7(2):34–50
Nieuwenhuis M, Wilkens J (2018) Twitter text and image gender classification with a logistic regression n-gram model: notebook for PAN at CLEF 2018. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2018-Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Avignon, France, September 10–14, 2018, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop Proceedings. vol 2125. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2125/paper_183.pdf
Oentaryo RJ, Murdopo A, Prasetyo PK, Lim EP (2016) On profiling bots in social media. In: International conference on social informatics, Springer, pp 92–109
Omri M (2004a) Possibilistic pertinence feedback and semantic networks for goal’s extraction. Asian J Inf Technol 3(4):258–265
Omri M (2004b) Relevance feedback for goal’s extraction from fuzzy semantic networks. Asian J Inf Technol 3(6):434–440
Pardo FMR, Rosso P (2019) Overview of the 7th author profiling task at PAN 2019: Bots and gender profiling in twitter. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2019-Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 9–12, 2019, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 2380. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2380/paper_263.pdf
Pardo FMR, Celli F, Rosso P, Potthast M, Stein B, Daelemans W (2015) Overview of the 3rd author profiling task at PAN 2015. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2015—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Toulouse, France, September 8–11, 2015, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 1391. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1391/inv-pap12-CR.pdf
Patra BG, Das KG, Das D (2018) Multimodal author profiling for twitter: Notebook for PAN at CLEF 2018. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2018-conference and labs of the evaluation forum, Avignon, France, September 10–14, 2018, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 2125. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2125/paper_115.pdf
Pennebaker JW, Francis ME, Booth RJ (2001) Linguistic inquiry and word count: Liwc 2001. Lawrence, Mahway, p 71
Puertas E, Moreno-Sandoval LG, Arco F, Alvarado-Valencia JA, Quimbaya AP, López L (2019) Bots and gender profiling on twitter using sociolinguistic features. In: CLEF
Rangel F, Rosso P (2016) On the impact of emotions on author profiling. Inf Process Manag 52(1):73–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2015.06.003
Rangel F, Rosso P, Koppel M, Stamatatos E, Inches G (2013) Overview of the author profiling task at pan 2013. In: CLEF conference on multilingual and multimodal information access evaluation. CELCT, pp 352–365
Rangel F, Rosso P, Potthast M, Trenkmann M, Stein B, Verhoeven B, Daelemans W et al (2014) Overview of the 2nd author profiling task at pan 2014. In: CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 1180, pp 898–927
Rangel F, Rosso P, Montes-y Gómez M, Potthast M, Stein B (2018) Overview of the 6th author profiling task at pan 2018: multimodal gender identification in twitter. Working Notes Papers of the CLEF
Safara F, Mohammed AS, Potrus MY, Ali S, Tho QT, Souri A, Janenia F, Hosseinzadeh M (2020) An author gender detection method using whale optimization algorithm and artificial neural network. IEEE Access 8:48428–48437. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2973509
Sendi M, Omri MN, Abed M (2017) Possibilistic interest discovery from uncertain information in social networks. Intell Data Anal 21(6):1425–1442
Sendi M, Omri MN, Abed M (2019) Discovery and tracking of temporal topics of interest based on belief-function and aging theories. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 10(9):3409–3425
Singh M, Bansal D, Sofat S (2018) Who is who on twitter-spammer, fake or compromised account? A tool to reveal true identity in real-time. Cybern Syst 49(1):1–25
Subrahmanian V, Azaria A, Durst S, Kagan V, Galstyan A, Lerman K, Zhu L, Ferrara E, Flammini A, Menczer F (2016) The Darpa twitter bot challenge. Computer 49(6):38–46
Surendran K, Gressel G, S T, Hrudya P, Ashok A, Poornachandran P (2014) Ensemble learning approach for author profiling. In: Working Notes for CLEF 2014 conference, Sheffield, UK, September 15–18, 2014, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop proceedings, vol 1180, pp 1148–1156. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1180/CLEF2014wn-Pan-SurendranEt2014.pdf
Takahashi T, Tahara T, Nagatani K, Miura Y, Taniguchi T, Ohkuma T (2018) Text and image synergy with feature cross technique for gender identification: Notebook for PAN at CLEF 2018. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2018-Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Avignon, France, September 10–14, 2018, CEUR-WS.org, CEUR Workshop proceedings, vol 2125. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2125/paper_83.pdf
Varol O, Ferrara E, Davis C, Menczer F, Flammini A (2017) Online human-bot interactions: Detection, estimation, and characterization. In: Proceedings of the international AAAI conference on web and social media, vol 11
Wei F, Nguyen UT (2019) Twitter bot detection using bidirectional long short-term memory neural networks and word embeddings. In: 2019 First IEEE international conference on trust. Privacy and security in intelligent systems and applications (TPS-ISA). IEEE, pp 101–109
Yang KC, Varol O, Davis CA, Ferrara E, Flammini A, Menczer F (2019) Arming the public with artificial intelligence to counter social bots. Hum Behav Emerg Technol 1(1):48–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouni, S., Fkih, F. & Omri, M.N. Toward a new approach to author profiling based on the extraction of statistical features. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 11, 59 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-021-00768-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-021-00768-6