Abstract
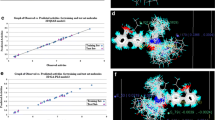
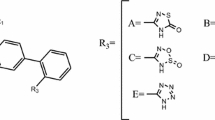
2D quantitative structure–activity relationships (2D QSAR) studies were performed on a series of diarylcyclopentene derivatives as prostaglandin EP1 receptor antagonist. To establish the relationship between Prostaglandin EP1 receptor and diarylcyclopentene derivatives, a 2D-QSAR model based on individual, estate numbers, structural, electro topological and baumann alignment descriptors parameters was developed. The best model-1 correlation coefficient with r 2 = 0.8101, significant cross validated correlation coefficient (q 2 = 0.7491) and for external test set pred_r 2 = 0.7812 developed by Partial Least Squares method. The QSAR model reveals that hydroxyl and methoxy group at R position on the diarylcyclopentene moiety is responsible for improving the prostaglandin EP1 receptor activity. The results of 2D QSAR studies were used to design new molecules and to predict their prostaglandin EP1 receptor activity using the developed models.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann K (2002) an alignment-independent versatile structure descriptor for QSAR and QSPR based on the distribution of molecular features. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 42:26–35
Bhattacharya M, Peri KG, Almazan G, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Shichi H, Durocher Y, Abramovitz M, Hou X, Varma DR, Chemtob S (1998) Nuclear localization of prostaglandin E2 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15792–15797
Bianchi M, Broggini MA (2003) randomised, double-blind, clinical trial comparing the efficacy of nimesulide, celecoxib and rofecoxib in osteoarthritis of the knee. Drugs 63(1):37–46
Boie Y, Stocco R, Sawyer N, Slipetz DM, Ungrin MD, Neuschafer-Rube F, Puschel G, Metters KM, Abramovitz M (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of the four rat prostaglandin E2 prostanoid receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol 340:227–247
Breyer MD, Breyer RM (2000) Prostaglandin E receptors and the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F12–F23
Camu F, Shi L, Vanlersberghe C (2003) The role of COX-2 inhibitors in pain modulation. Drugs 63(Suppl 1):1–7
Coleman RA, Kennedy I, Humphrey PPA, Bunce K, Lumley P (1990) In comprehensive medicinal chemistry; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, vol 3, pp 643–714
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Funk CD (2001) Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science 294:1871–1875
Giblin GMP, Bit RA, Brown SH, Chaignot HM, Chowdhury A, Chessell Iain P, Clayton Nicholas M, Coleman T, Hall A, Hammond B, Hurst David N, Michel Anton D, Naylor A, Novelli R, Scoccitti T, Spalding D, Tang Sac P, Wilson Alex W, Wilson R (2007) The discovery of 6-[2-(5-chloro-2-{[(2,4-difluorophenyl)- methyl]oxy}phenyl)-1-cyclopenten-1-yl]-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid, GW848687X, a potent and selective prostaglandin EP1 receptor antagonist for the treatment of inflammatory pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:385–389
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Predictive QSAR modeling based on diversity sampling of experimental datasets for the training and test set selection. J Comput Aided Mol Des 16:357–369
Gupta SP, Mathur AN, Naggapa AN, Kumar D, Kumaran S (2003) A quantitative structure-activity relationship study on a novel class of calcium entry blockers:1-[{4-(aminoalkoxy)phenylsulfonyl] indolizines. Eur J Med Chem 38:867–873
Kiriyama M, Ushikubi F, Kobayashi T, Hirata M, Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S (1997) Ligand binding specificities of the eight types and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol 122(2):217–224
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Patacchini R, Conte B, Furio M, Santicioli P, Meli P, Gragnani L, Meli A (1988) The effect of SC-19220, a prostaglandin antagonist, on the micturition reflex in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 152(3):273–279
Minami T, Nishihara I, Uda R, Ito S, Hyodo M, Hayaishi O (1994) Characterization of EP-receptor subtypes involved in allodynia and hyperalgesia induced by intrathecal administration of prostaglandin E2 to mice. Br J Pharmacol 112(3):735–740
Minami T, Nakano H, Kobayashi T, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S, Ito S (2001) Characterization of EP receptor subtypes responsible for prostaglandin E2-induced pain responses by use of EP1 and EP3 receptor knockout mice. Br J Pharmacol 133(3):438–444
Namba T, Sugimoto Y, Negishi M, Namba T, Sugimoto Y, Negishi M, Irie A, Ushikubi F, Kakizuka A, Ito S, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S et al (1993) Alternative splicing of C-terminal tail of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP3 determines G-protein specificity. Nature 365:166–170
Narumiya S, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F (1999) Prostanoid receptors: structures, properties, and functions. Physiol Rev 79(4):1193–1226
Sharma BK, Pilania P, Prithvi Singh P (2010) QSAR rationales for the 1,2-diarylcyclopentenes as prostaglandin EP1 receptor antagonists: potentially useful in the treatment of inflammatory pain. Euro J Chem 1(4):325–334
Sheen CL, MacDonald TM (2002) Gastrointestinal side effects of NSAIDs—pharmacoeconomic implications. Exp Opin Pharmacother 3:265–269
Takeda H, Sonoshita M, Oshima H, Sugihara K, Chulada PC, Langenbach R, Oshima M, Taketo MM (2003) Cooperation of cyclooxygenase 1 and cyclooxygenase 2 in intestinal polyposis. Cancer Res 63:4872–4877
VLife MDS 3.5 (2010) Molecular design suite. Vlife Sciences Technologies Pvt. Ltd., Pune. https://www.vlifesciences.com
Wibberley A (2005) Overactive bladder: targeting prostaglandins in sensory pathways. Drug Discov Today: Therap Strateg 2:7–13
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank VLife Sciences Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Pune for providing software facility and Journal referees for their valuable suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M.C., Sharma, S. & Sharma, S. Computational study of diarylcyclopentene derivatives as selective prostaglandin EP1 receptor antagonist: QSAR approach. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 5, 14 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-016-0120-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-016-0120-y