Abstract
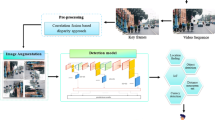
Automatic re-identification of people entering the camera network is an important and challenging task. Multiple frames of the same person will be easily available in surveillance videos for re-identification. Dealing with pose variations of the person in the image and partial occlusion issues is major challenge in single-frame re-identification process. The use of more frames from the surveillance videos can generate robust descriptor to tackle issues of pose variations and occlusion. In this paper, we have emphasized on using multiple frames from the same video to generate a multi-frame twin-channel descriptor. The work deals with building a spatial-temporal descriptor which takes advantage of the twin paths to extract features of the person image. Mahalanobis distance metric learning algorithms is used for matching and evaluation. Our descriptor is evaluated on two benchmark datasets and found to surpass the performance of the existing methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bak S, Corvee E, Bremond F, Thonnat M (2010) Person re-identification using haar-based and dcd-based signature. In: Proceedings of 7th IEEE international confernce on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS), pp 1–8
Bazzani L, Cristani M, Perina A, Farenzena M, Murino V (2010) Multiple-shot person re-identification by HPE signature. In: 20th international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR)
Bazzani L, Cristani M, Perina A, Murino V (2012) Multipleshot person re-identification by chromatic and epitomic analyses. Pattern Recogn Lett 33:898–903
Bingpeng MA, Su Y, Jurie F (2012) Bicov: A novel image representation for person re-identification and face verification. In: British machine vision conference
Cheng DS, Cristani M, Stoppa M, Bazzani L, Murino V (2011) Custom pictorial structures for re-identification. In: British machine vision conference
Cho Y-J, Yoon K-J (2016) Improving person re-identification via pose-aware multi-shot matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1354–1362
Davis JV, Kulis B, Jain PS, Dhillon IS (2007) Information-theoretic metric learning. In: Proceedings of international conference on machine learning
Farenzena M, Bazzani L, Perina A, Murino V, Cristani M (2010) Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Gray D, Tao H (2008) Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In: European Conference on computer vision. Marseille, France, pp 262–275
Hamdoun O, Moutarde F, Stanciulescu B, Steux B (2008) Person re-identification in multi-camera system by signature based on in-terest point descriptors collected on short video sequences. In: ACM international conference on distributed smart cameras, pp 1–6
Hirzer M, Beleznai C, Roth PM, Bischof H (2011) Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. In: Proceedings of Scandinavian conference on image analysis (SCIA)
Hirzer M, Roth PM, Bischof H (2012) Person re-identification by efficient metric learning. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal-based surveillance
Ijiri Y, Lao S (2012) Human re-identification through distance metric learning based on Jensen-Shannon Kernel. In: Visapp, (c), pp 603–612
Köostinger M, Hirzer M, Wohlhart P, Roth P M, Bischof H (2012) Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Lowe D (2004) Distinctive image features from scale invariant features. Int J Comput Vis 60:91–110
Leng Q, Hu R, Liang C, Wang Y, Chen J (2015) Person re-identification with content and context re-ranking. Multimed Tool Appl 74(17):6989–7014
Liao S, Hu Y, Zhu X, Li SZ (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: CVPR, IEEE
Pedagadi S, Orwell J, Velastin S, Boghossian B (2013) Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3318–3325
Roth PM, Hirzer M, Kstinger M, Beleznai C, Bischof H (2014) Mahalanobis distance learning for person re-identification. Springer, Berlin, pp 247–267
Schölkopf B, Smola A, Mller K-R (1998) Nonlinear component analysis as a Kernel eigenvalue problem. Neural Comput 10(5):1299–1319
Schwartz W, Davis LS (2009) Learning discriminative appearance-based models using partial least squares. In: Brazilian symposium on computer graphics and image processing
Štruc V, Pavešic N (2009) Gabor-based Kernel partial-least-squares discrimination features for face recognition. Informatica (Vilnius) 20(1):115–138
Štruc V, Pavešic N (2010) The complete Gabor-Fisher classifier for robust face recognition, EURASIP Adv Signal Process 26
Vedaldi A, Fulkerson B (2008) VLFeat: an open and portable library of computer vision algorithms. http://www.vlfeat.org
Wang T, Gong S, Zhu X, Wang S (2014) Person re-identification by video ranking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, pp 688–703
Weber M, Buml M, Stiefelhagen R (2011) Part-based clothing segmentation for person retrieval. In: 2011 8th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance, AVSS, pp 361–366
Weinberger KQ, Saul LK (2008) Fast solvers and efficient implementations for distance metric learning. In: Proceedings of international conference on machine learning
Xiang ZJ, Chen Q, Liu Y (2014) Person re-identification by fuzzy space colour histogram. Multimed Tool Appl 73(1):91–107
Zheng WS, Gong S, Xiang T (2009) Associating groups of people. In: BMVC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathish, P.K., Balaji, S. Multi-frame twin-channel descriptor for person re-identification in real-time surveillance videos. Int J Multimed Info Retr 6, 289–294 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-017-0136-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-017-0136-9