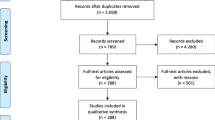
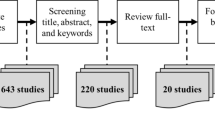
Abstract
In order to adapt to a continuously changing environment, organizations are evolving their business objectives, processes, and operations through various strategic initiatives. In this context, it is imperative for organizations to continuously monitor their performance and adjust when there is a need or an opportunity to do so. The cluster of technologies that delivers this monitoring capability is called business intelligence (BI), and over the years it has come to play a central role in business operations and governance. Unfortunately, there is a huge cognitive gap between a requirements view of a strategic initiative articulated in terms of business goals, processes, and performance on one hand, and an implementation view of BI monitoring articulated in terms of databases, networks, and computational processing. In this paper, we present a model-based performance management framework for managing strategic initiatives across their complete lifecycle of analysis, modeling, implementation, and evaluation to bridge this cognitive gap. We demonstrate its usefulness through a case study at a major teaching hospital, which is implementing a strategic initiative to reduce antibiotic-resistant infections.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adya A, Blakeley JA, Melnik S, Muralidhar S (2007) Anatomy of the ado.net entity framework. In: Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data. SIGMOD ’07ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 877–888
Amyot D, Horkoff J, Gross D, Mussbacher G (2009) A lightweight GRL profile for i* modeling. In: ER Workshops, vol 5833, lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 254–264
Andersson B, Johannesson P, Zdravkovic J (2009) Aligning goals and services through goal and business modelling. Inf Syst E-Bus Manag 7(2):143–169
Barone D, Jiang L, Amyot D, Mylopoulos J (2011) Strategic models for business intelligence. In: Conceptual modeling—ER 2011, 30th International Conference on conceptual modeling, lecture notes in computer science, vol 6998. Springer, pp 429–439
Barone D, Mylopoulos J, Jiang L, Amyot D (2010) Business intelligence model, version 1.0. Tech. Rep. CSRG-607, University of Toronto, Canada. ftp://ftp.cs.toronto.edu/csri-technical-reports/INDEX.html
Barone D, Peyton L, Rizzolo F, Amyot D, Mylopoulos J (2011) Towards model-based support for managing organizational transformation. In: Babin G, Stanoevska-Slabeva K, Kropf P (eds) MCETECH, lecture notes in business information processing, vol 78. Springer, pp 17–31
Barone D, Topaloglou T, Mylopoulos J (2012) Business intelligence modeling in action: a hospital case study. In: CAiSE 2012–24th Int. Conf. on advanced information aystems engineering, lecture notes in computer science, vol 7328. Springer, pp 502–517
Barone D, Yu ESK, Won J, Jiang L, Mylopoulos J (2010) Enterprise modeling for business intelligence. In: van Bommel P, Hoppenbrouwers S, Overbeek S, Proper E, Barjis J (eds) PoEM 2010—Third IFIP WG8.1 Working Conference on the practice of enterprise modelling, lecture notes in business information processing, vol 68. Springer, pp 31–45
Bell D, Cesare SD, Iacovelli N, Lycett M, Merico A (2007) A framework for deriving semantic web services. Inf Syst Front 9(1):69–84
Bititci U, Turner T, Begemann C (2000) Dynamics of performance measurement systems. Int J Oper Prod Manag 20(6):692–704
Bose R (2006) Understanding management data systems for enterprise performance management. Ind Manag Data Syst 106(1):43–59
Burgin AL, Koss E (1993) Transformation to high performance—a journey in organizational learning. Tech. Rep. No. 823, SRI International, USA
Business Rules Group (2007) The business motivation model: business governance in a volatile world. Ver. 1.3. http://www.businessrulesgroup.org/bmm.shtml
Chen PPS (1976) The entity-relationship model—toward a unified view of data. ACM Trans Database Syst 1(1):9–36
Cheung W, Babin G (2006) A metadatabase-enabled executive information system (part A): a flexible and adaptable architecture. DSS 42:1589–1598
Creech B (1994) The five pillars of TQM. Truman Talley Books/Dutton, New York
Dalpiaz F, Barone D, Horkoff J, Jiang L, Mylopoulos J (2013) Bim-tool: modeling and reasoning support for strategic business models. In: Proceedings of the 6th International i* Workshop 2013 (iStar 2013), CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 978, pp 134–137
Dealtry TR (1994) Dynamic SWOT analysis. Dynamic SWOT Associates, Birmingam
Dixon J, Nanni A, Vollmann T (1990) The new performance challenge—measuring operations for world-class competition. Dow Jones-Irwin, Homewood
Galipeau J, Garritty C, Moher D (2010) What is known about the characteristics of antimicrobial stewardship programs and their implementation and effectiveness? Tech. rep, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Canada
Galliers RD, Baets WRJ (eds) (1998) Information technology and organizational transformation: innovation for the 21st century organization. John Wiley Series in Information Systems
Gangemi A, Guarino N, Masolo C, Oltramari A, Schneider L (2002) Sweetening ontologies with DOLCE. In: EKAW 2002, vol 2473, lecture notes in computer science. Springer, London, pp 166–181
Hevner AR, March ST, Park J, Ram S (2004) Design science in information systems research. MIS Quart 28(1):75–105
Horkoff J, Barone D, Jiang L, Yu E, Amyot D, Borgida A, Mylopoulos J (2012) Strategic business modeling: representation and reasoning. Softw Syst Model :1–27. doi:10.1007/s10270-012-0290-8
Horkoff J, Borgida A, Mylopoulos J, Barone D, Jiang L, Yu E, Amyot D (2012) Making data meaningful: the business intelligence model and its formal semantics in description logics. In: Proceedings of 11th Int. Conf. on Ontologies, DataBases, and applications of semantics (ODBASE 2012), lecture notes in computer science, vol 7565. Springer, pp 700–717
Howard RA, Matheson JE (2005) Influence diagrams. Decis Anal 2(3):127–143
Howson C (2006) BusinessObjects XI (release 2): the complete reference. McGraw-Hill, London
Institute for Safe Medication Practices (2011) Ontario antimicrobial stewardship project. http://www.ismp-canada.org/abx/
International Telecommunication Union: Recommendation Z.151 (10/12) (2012) User requirements notation (URN)—language definition. http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Z.151/en
Kaplan RS, Norton DP (1996) Balanced Scorecard: translating strategy into action. Harvard Business School Press, Cambridge
Kaplan RS (2004) Strategy maps: converting intangible assets into tangible outcomes. Harvard Business School Press, Cambridge
Krishnapillai A (2009) Understanding key performance indicators through driver measures. Master’s thesis, SITE, University of Ottawa
Kronz A (2006) Managing of process key performance indicators as part of the ARIS methodology. In: Corporate performance management. Springer, New York, pp 31–44
Lenzerini M (2002) Data integration: a theoretical perspective. In: Popa L (ed) 21st principles of database systems (PODS). ACM, London, pp 233–246
Malinowski E, Zimányi E (2004) OLAP hierarchies: a conceptual perspective. In: Persson A, Stirna J (eds) CAiSE, lecture notes in computer science, vol 3084. Springer, London, pp 477–491
Malinowski E, Zimányi E (2008) Advanced data warehouse design: from coventional to spatial and temporal applications. Springer, Berlin
Mazzeo F, Capuano A, Avolio A, Filippelli A, Rossi F (2005) Hospital-based intensive monitoring of antibiotic-induced adverse events in a university hospital. Pharmacol Res 51(3):269–274
Melnik S, Adya A, Bernstein PA (2007) Compiling mappings to bridge applications and databases. In: SIGMOD. ACM, New York, pp 461–472
Nadler DA, Shaw RB, Walton AE (1994) Associates: discontinuous change: leading organizational transformation. Jossey-Bass, An Imprint of Wiley, New York
Nargesian F (2011) Bridging decision applications and multidimensional databases. Master’s thesis, SITE, University of Ottawa
Neely A, Adams C, Crowe P (2001) The performance prism in practice. Meas Bus Excell 5(2):6–12
Negash S (2004) Business intelligence. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 13(15):177–195
Otley D (1999) Performance management: a framework for management control system research. Manag Acc Res 10:363–382
Porter L, Oakland J, Gadd K (1998) Unlocking business performance with self-assessment. Manag Acc 76(8):35–37
Pourshahid A, Amyot D, Peyton L, Ghanavati S, Chen P, Weiss M, Forster AJ (2009) Business process management with the user requirements notation. Electron Commer Res 9(4):269–316
Rizzolo F, Kiringa I, Pottinger R, Wong K (2010) The conceptual integration modeling framework: abstracting from the multidimensional. In: CoRR abs/1009.0255, p 18
Salama S, Rotstein C, Mandell L (1996) A multidisciplinary hospital-based antimicrobial use program: impact on hospital pharmacy expenditures and drug use. Can J Infect Dis 7(2):104–109
van Solingen R, Basili V et al (2002) Goal question metric (gqm) approach. Encycl Softw Eng. doi:10.1002/0471028959.sof142
Villar C (2011) A goal-driven methodology for developing health care quality metrics. Master’s thesis, SITE, University of Ottawa
Volitich D (2008) IBM Cognos 8 business intelligence: the official guide. McGraw-Hill, New York
Vonderheide-Liem DN, Pate B (2004) Applying quality methodologies to improve healthcare: six sigma, lean thinking, balanced scorecard, and more. HCPro, Inc., London
Watson HJ, Wixom BH (2007) The current state of business intelligence. Computer 40:96–99
Wongrassamee S, Simmons J, Gardiner P (2003) Performance measurement tools: the balanced scorecard and the efqm excellence model. Meas Bus Excell 7(1):14–29
Yu E (1997) Towards modelling and reasoning support for early-phase requirements engineering. In: 3rd IEEE Int., Symposium on requirements engineering, RE ’97IEEE Computer Society, Washington, USA, pp 226–235
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the business intelligence network (BIN), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. We are grateful to Eric Yu, Iluju Kiringa, Lei Jiang, Gary Garber, Alan J. Forster, and many other colleagues for useful discussions and suggestions that helped shape this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barone, D., Peyton, L., Rizzolo, F. et al. Model-Based Management of Strategic Initiatives. J Data Semant 4, 149–165 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13740-014-0042-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13740-014-0042-8