Abstract
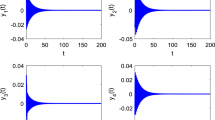
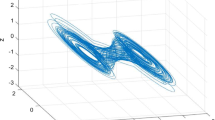
This paper is concerned with the secure synchronization and topology identification for fractional complex networks (FCNs) with multiple weight couplings under Denial-of-Service (DoS) jamming attacks, where DoS attacks are performed in the controller-to-actuator channels. First, an adaptive topology observer is designed to realize the secure synchronization and topology identification objective. Second, by Lyapunov stability theory and comparison principle, the secure synchronization conditions are achieved. Under the designed observer, the topology identification can be realized, as well. Finally, a numerical simulation is provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and the validity of theoretical results.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An XL, Zhang L, Li YZ, Zhang JG (2014) Synchronization analysis of complex networks with multi-weights and its application in public traffic network. Physica A: Stat Mech Appl 412:149–156
An XL, Li YZ, Zhang L, Zhang JG, Ma CX (2015) The research on multi-links complex networks and its application in urban public traffic. ICIC Express Lett Part B Appl Int J Res Surv 6:1613–1618
Chen X, Zhang J, Ma T (2016) Parameter estimation and topology identification of uncertain general fractional-order complex dynamical networks with time delay. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sin 9(3):295–303
Chen B, Ho DWC, Hu G, Yu L (2018) Secure fusion estimation for bandwidth constrained cyber-physical systems under replay attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(6):1862–1876
Cortes J (2008) Discontinuous dynamical systems. IEEE Control Syst Magn 28(3):36–73
DeLellis P, di Bernardo M, Russo G (2011) On QUAD. Lipschitz, and contracting vector fields for consensus and synchronization of networks, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I. 58(3):576–583
Ding D, Wang Z, Ho DWC, Wei G (2017) Observer-based eventtriggering consensus control for multiagent systems with lossy sensors and cyber-attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(8):1936–1947
Ding D, Wang Z, Han QL, Wei G (2018) Security control for discrete-time stochastic nonlinear systems subject to deception attacks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 48(99):779–789
Fan YH, Mei J, Liu HM, Fan YL, Liu FX, Zhang YJ (2020) Fast synchronization of complex networks via a periodically intermittent sliding mode control. Neural Process Lett 51:1331–1352
Gu Y, Yu Y, Wang H (2017) Synchronization-based parameter estimation of fractional-order neural networks. Phys A 483:351–361
Li RH, Wu HQ, Cao JD (2022) Impulsive exponential synchronization of fractional-order complex dynamical networks with derivative couplings via feedback control based on discrete time state observations. Acta Mathematica Scientia. 42B(2):737–754
Liu D, Ye D (2020) Pinning-observer-based secure synchronization control for complex dynamical networks subject to DoS attacks. IEEE Trans Circ Syst 67(12):5394–5404
Liu H, Li Y, Li ZY, Lu JA (2021) Topology identification of multilink complex dynamical networks via adaptive observers incorporating chaotic exosignals. IEEE Trans Cybern 99:267–281
Lu AY, Yang GH (2018) Input-to-state stabilizing control for cyberphysical systems with multiple transmission channels under denial of service. IEEE Trans Autom Control 63(6):1813–1820
Mannel A, Norelys, Javier A (2015) Using general quadratic Lyapunov functions to prove Lyapunov uniform stability for fractional order systems. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 22(3):650–659
Mei J, Jiang M, Wang J (2013) Finite-time structure identification and synchronization of drive-response systems with uncertain parameter. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(4):999–1015
Mirollo R, Strogatz S (1990) Synchronizayion of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM J Appl Math 50:1645–1662
Papadimitratos P, Fortelle ADL, Evenssen K, Brignolo R, Cosenza S (2009) Vehicular communication systems: enabling technologies, applications, and future outlook on intelligent transportation. Commun Magz IEEE 47(11):84–95
Peng X, Wu HQ (2020) Non-fragile robust finite-time stabilization and H infinity performance analysis for fractional-order delayed neural networks with discontinuous activations under the asynchronous switching. Neural Comput Appl 32(8):4045–4071
Peng X, Wu HQ, Cao JD (2019) Global nonfragile synchronization in finite time for fractional-order discontinuous neural networks with nonlinear growth activations. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(7):2123–2137
Podlubny I (1999) Fractional Differential Equations. Academic, San Diego, CA
Saeedian M, Khalighi M, Azimi-Tafreshi N, Jafari GR, Ausloos M (2017) Memory effects on epidemic evolution: the susceptible-infected-recovered epidemic model. Phys Rev E 95:022409
Shisheh Foroush H, Martnez S (2016) On triggering control of single-input linear systems under pulse-width modulated DoS signals. SIAM J Control Optim 54(6):3084–3105
Si G, Sun Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y (2012) Parameter estimation and topology identification of uncertain fractional order complex networks. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17(12):5158–5171
Strogatz SH (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature 410:268–276
Wang XH, Wu HQ, Cao JD (2020) Global leader-following consensus in finite time for fractional-order multiagent systems with discontinuous inherent dynamics subject to nonlinear growth. Nonlinear Anal-Hybrid Syst 37:100888
Wang LH, Mo ZK, Han QL (2020) Secure impulsive Synchronization in lipschitz-type multi-agent systems subject to deception attacks. IEEE J Autom Sin 7(5):1326–1334
Wu X (2008) Synchronization-based topology identification of weighted general complex dynamical networks with time-varying coupling delay. Phys A 387(4):997–1008
Wu XJ, Lu HT (2010) Outer synchronization between two different fractional-order general complex dynamical networks. Chin Phys B 19(7):129–140
Wu HY, Wang L, Zhao LH, Wang JL (2012) Topology identification of coupled neural networks with multiple weights. Neurocomputing 457(2):254–264
Xu LZ (2010) Applied inequalities, Shandong Science and Technology Press
Yu D, Righero M, Kocarev L (2006) Estinating topology of networks. Phys Rev Lett 97:31–34
Yu J, Cheng H, Jiang HJ (2012) \(\alpha \)-stability and \(\alpha \)-synchronization for fractional-order neural networks. Neural Netw 35:82–87
Zhang YQ, Wu HQ, Cao JD (2020) Group consensus in finite time for fractional multiagent systems with discontinuous inherent dynamics subject to Holder growth. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3023704
Zhang TY, Ye D (2020) Distributed secure control against denial-of-service attacks in cyber-physical systems based on K-connected communication topology. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(7):3094–3103
Zhang XM, Han QL, Ge X, Ding L (2020) Resilient control design based on a sampled-date model for a class of networked control systems under denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(8):3616–3626
Zhang YQ, Wu HQ, Cao JD (2021) Global Mittag–Leffler consensus for fractional singularly perturbed multiagent systems with discontinuous inherent dynamics via event-triggered control strategy. J Frankl Inst 358(3):2086–2114
Zhao J, Aziz-Alaoui MA, Bertelle C, Corson N (2016) Sinusoidal disturbance induced topology identification of Hindmarsh–Rose neural networks. Sci Chin Inf Sci 59(11):112205
Zhao W, Wu HQ (2018) Fixed-time synchronization of semi-Markovian jumping neural networks with time-verying delays. Adv Differ Equ 2018 (1):213
Zheng Y, Wu XQ, Fan ZY, Wang W (2022) Identifying topology and system parameters of fractional-order complex dynamical networks. Appl Math Comput 414:126666
Zhu S, Zhou J, Chen G, Lu JA (2019) A new method for topology identification of complex dynamical networks. IEEE Trans Cybern 51(4):2224–2231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Fabio Durastante.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61833005) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. A12171416)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Wu, H. & Cao, J. Secure synchronization and identification for fractional complex networks with multiple weight couplings under DoS attacks. Comp. Appl. Math. 41, 187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-022-01895-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-022-01895-2