Abstract
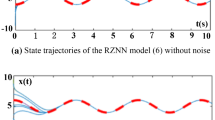
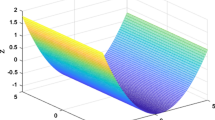
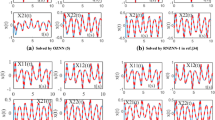
Zeroing neural network has proved its powerful abilities and efficiency in solving various time-varying problems, and its convergence and robustness have been deeply studied in recent years. To further enhance its convergent speed and robustness for time-varying linear matrix equation solving, a nonlinear zeroing neural network (NZNN) with a new activation function is proposed in this paper. The superiority of the proposed NZNN model is theoretically validated through rigorous mathematical analysis. Besides, the proposed NZNN model is applied to time-varying matrix inversion solving, static and dynamic voltage electronic circuit currents computing, which further verifies its practical abilities for engineering oriented applications.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen F, Li T (2021) Two-step AOR iteration method for the linear matrix equation AXB=C. Comput Appl Math 40:89
Dai J, Jia L, Xiao L (2020) Design and analysis of two prescribed-time and robust ZNN models with application to time-variant Stein matrix equation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32:1668–1677
Dai J, Li Y, Xiao L, Jia L (2021) Zeroing neural network for time-varying linear equations with application to dynamic positioning. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 18:1552–1561
Dehghan M, Shirilord A (2019) The double-step scale splitting method for solving complex Sylvester matrix equation. Comput Appl Math 38:146
Ding L, Xiao L, Zhou KQ, Lan YH, Zhang YS (2018) A new RNN model with a modified nonlinear activation function applied to complex-valued linear equations. IEEE Access 6:62954–62962
Ding L, Xiao L, Zhou K, Liao B, Peng C, Li J, Mo L (2020) A novel gradient neural network for tackling the complex-valued system of linear equations online. In: 10th International conference on information science and technology
Ding W, Li Y, Wang D (2021) Special least squares solutions of the reduced biquaternion matrix equation AX=B with applications. Comput Appl Math 40:279
Elsayed AAA, Ahmad N, Malkawi G (2020) On the solution of fully fuzzy Sylvester matrix equation with trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Comput Appl Math 39:278
Feng YY, Wu QBZ, Xie W (2021) Lopsided DSS iteration method for solving complex Sylvester matrix equation. Comput Appl Math 40:235
Gerontitis D, Behera R, Sahoo JK, Stanimirović PS (2021) Improved finite time zeroing neural network for time-varying division. Stud Appl Math 146:526–549
Gerontitis D, Behera R, Tzekis P, Stanimirović P (2022) A family of varying-parameter finite-time zeroing neural networks for solving time-varying Sylvester equation and its application. J Comput Appl Math 146:113826
Jin J (2021) An improved finite time convergence recurrent neural network with application to time-varying linear complex matrix equation solution. Neural Process Lett 53:777–786
Jin J, Gong J (2020) An interference-tolerant fast convergence zeroing neural network for dynamic matrix inversion and its application to mobile manipulator path tracking. Alex Eng J 60:659–669
Jin J, Gong J (2021a) A noise-tolerant fast convergence ZNN for dynamic matrix inversion. Int J Comput Math. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207160.2021.1881498
Jin J, Gong J (2021b) An interference-tolerant fast convergence zeroing neural network for dynamic matrix inversion and its application to mobile manipulator path tracking. Alex Eng J 60(1):659–669
Jin J, Qiu L (2022) A robust fast convergence zeroing neural network and its applications to dynamic Sylvester equation solving and robot trajectory tracking. J Franklin Inst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.02.022
Jin L, Zhang Y (2015) Discrete-time Zhang neural network for online time varying nonlinear optimization with application to manipulator motion generation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26:1525–1531
Jin J, Xiao L, Lu M, Li J (2019) Design and analysis of two FTRNN models with application to time-varying Sylvester equation. IEEE Access 7:58945–58950
Jin J, Zhao L, Li M, Yu F, Xi Z (2020) Improved zeroing neural networks for finite time solving nonlinear equations. Neural Comput Appl 32:4151–4160
Jin J, Zhu J, Gong J, Chen W (2022a) Novel activation functions-based ZNN models for fixed-time solving dynamic Sylvester equation. Neural Comput Appl 34:14297–14315
Jin J, Zhu J, Zhao L, Chen L, Chen L, Gong J (2022b) A robust predefined-time convergence zeroing neural network for dynamic matrix inversion. IEEE Trans Cybernet. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2022.3179312
Kong Y, Lu H, Xue Y, Xia HX (2016) Terminal neural computing: finite convergence and its applications. Neurocomputing 217:133–141
Li DP, Li DJ (2018) Adaptive neural tracking control for an uncertain state constrained robotic manipulator with unknown time-varying delays. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet Syst 48:2219–2228
Li S, Chen S, Liu B (2013) Accelerating a recurrent neural network to finite-time convergence for solving time-varying Sylvester equation by using a sign-bi-power activation function. Neural Process Lett 37:189–205
Li W, Xiao L, Liao B (2020) A finite-time convergent and noise-rejection recurrent neural network and its discretization for dynamic nonlinear equations solving. IEEE Trans Cybernet 50:3195–3207
Liu L, Liu YJ, Tong S (2019a) Neural networks-based adaptive finite time fault-tolerant control for a class of strict-feedback switched nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Cybernet 49:2536–2545
Liu L, Liu YJ, Tong S (2019b) Fuzzy based multi-error constraint control for switched nonlinear systems and its applications. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27:1519–1531
Pour HN, Goughery HS (2015) New hermitian and skew-hermitian splitting methods for non-Hermitian positive-definite linear systems. Numer Algorithms 69:207–225
Rodriguez G, Seatzu S, Theis D (2003) A new technique for ill-conditioned linear systems. Numer Algorithms 33:433–442
Stanimirović P, Gerontitis D, Tzekis P, Behera R, Sahoo JK (2021) Simulation of varying parameter recurrent neural network with application to matrix inversion. Math Comput Simul 185:614–628
Sun H, Wu A, Liu W (2020) Gradient-based neural networks for online solutions of coupled Lyapunov matrix equations. Neurocomputing 453:599–609
Tan Z, Hu Y, Chen K (2020) On the investigation of activation functions in gradient neural network for online solving linear matrix equation. Neurocomputing 413:185–192
Xiao L (2016) A new design formula exploited for accelerating Zhang neural network and its application to time-varying matrix inversion. Theor Comput Sci 647:50–58
Xiao L, Zhang Y (2014) From different Zhang functions to various ZNN models accelerated to finite-time convergence for time-varying linear matrix equation. Neural Process Lett 39:309–326
Xiao L, Liao B, Luo J, Ding L (2017a) A convergence-enhanced gradient neural network for solving Sylvester equation. In: IEEE 2017 36th Chinese control conference (CCC). https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2017.8027968
Xiao L, Liao B, Li S, Zhang Z, Ding L, Jin L (2017b) Design and analysis of FTZNN applied to the real-time solution of a nonstationary Lyapunov equation and tracking control of a wheeled mobile manipulator. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 14:98–105
Xiao L, Yi Q, Dai J, Li K, Hu Z (2019a) Design and analysis of new complex zeroing neural network for a set of dynamic complex linear equations. Neurocomputing 363:171–181
Xiao L, Zhang Y, Li K, Liao B, Tan Z (2019b) A novel recurrent neural network and its finite-time solution to time-varying complex matrix inversion. Neurocomputing 331:483–492
Xiao L, Dai J, Jin L, Li W, Li S, Hou J (2021) A noise-enduring and finite-time zeroing neural network for equality-constrained time-varying nonlinear optimization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet Syst 51:4729–4740
Xiao L, He Y, Dai J, Liu X, Liao B, Tan H (2022) A variable-parameter noise-tolerant zeroing neural network for time-variant matrix inversion with guaranteed robustness. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 33:1535–1545
Yan X, Liu M, Jin L, Li S, Hu B, Zhang X, Huang Z (2019) New zeroing neural network models for solving nonstationary Sylvester equation with verifications on mobile manipulators. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15:5011–5022
Zhang Y, Ge S (2003) A general recurrent neural network model for time-varying matrix inversion. In: Proceedings of 42nd IEEE conference on decision and control, vol 6, pp 6169–6174
Zhang Y, Ge S (2005) Design and analysis of a general recurrent neural network model for time-varying matrix inversion. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16:1477–1490
Zhang Z, Zheng L (2019) A complex varying-parameter convergent-differential neural-network for solving online time-varying complex Sylvester equation. IEEE Trans Cybernet 49:3627–3639
Zhang Y, Jiang D, Wang J (2002) A recurrent neural network for solving Sylvester equation with time-varying coefficients. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13:1053–1063
Zhang Y, Ma W, Cai B (2008) From Zhang neural network to Newton iteration for matrix inversion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I(56):1405–1415
Zhang Y, Yi C, Ma W (2009) Simulation and verification of Zhang neural network for online time-varying matrix inversion. Simul Model Pract Theory 17:1603–1617
Zhang Y, Li Z, Li K (2011) Complex-valued Zhang neural network for online complex-valued time-varying matrix inversion. Appl Math Comput 217:10066–10073
Zhang Z, Fu T, Yan Z, Jin L, Xiao L, Sun Y, Yu Z, Li Y (2018a) A varying-parameter convergent-differential neural network for solving joint-angular-drift problems of redundant robot manipulators. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 23:679–689
Zhang Z, Deng X, Qu X, Liao B, Kong LD, Li L (2018b) A varying-gain recurrent neural network and its application to solving online time-varying matrix equation. IEEE Access 6:77940–77952
Zhang Z, Zheng L, Weng J, Mao Y, Lu W, Xiao L (2018c) A new varying-parameter recurrent neural-network for online solution of time-varying Sylvester equation. IEEE Trans Cybernet 48:3135–3148
Zhang Z, Zheng L, Qiu T, Deng F (2020) Varying-parameter convergent-differential neural solution to time-varying overdetermined system of linear equations. IEEE Trans Autom Control 65:874–881
Zhao L, Jin J, Gong J (2021) Robust zeroing neural network for fixed-time kinematic control of wheeled mobile robot in noise-polluted environment. Math Comput Simul 185:289–307
Zhu J, Jin J, Chen W, Gong J (2022) A combined power activation function based convergent factor-variable ZNN model for solving dynamic matrix inversion. Math Comput Simul 197:291–307
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62273141 and 61875054), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2020JJ4315, No. 2020JJ5199), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Grant No. 20B216, No. 20C0786, No. 18C0296).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Marcos Eduardo Valle.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Chen, W., Zhao, L. et al. A nonlinear zeroing neural network and its applications on time-varying linear matrix equations solving, electronic circuit currents computing and robotic manipulator trajectory tracking. Comp. Appl. Math. 41, 319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-022-02031-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-022-02031-w