Abstract
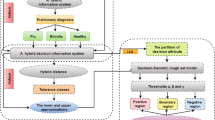
Three-way decision models and their relative applications have received a great deal of research attention. Most of these models were constructed on the basis of decision-theoretic rough sets (DTRSs) and Bayesian decision theory, both of which ignore the risk preferences of decision-makers. To address this shortcoming, this paper constructs a novel TODIM method-based three-way decision model and demonstrates its use in the context of online diagnosis and medical treatment selection. This model combines information systems and DTRSs together to construct a hybrid information system. And it solves the problems in aggregating cost-loss information with different levels of importance by utilizing the power average operator. Furthermore, an extension of the TODIM method is proposed based on the novel possibility degree measurement considering the probability distribution of loss functions. To validate the reasonableness and effectiveness of our model, we give a series of simulation experiments related to treatment selection for a Good Doctor Online user infected with the common cold.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao, Y.Y.: The superiority of three-way decisions in probabilistic rough set models. Inf. Sci. 181(6), 1080–1096 (2011)
Liu, D., Yao, Y.Y., Li, T.R.: Three-way investment decisions with decision-theoretic rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 4(1), 66–74 (2011)
Li, H.X., Zhou, X.Z.: Risk decision making based on decision-theoretic rough set: a three-way view decision model. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 4(1), 1–11 (2011)
Yao, Y.Y.: Three-way decision: an interpretation of rules in rough set theory. In: International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology 2009, pp. 642–649
Pawlak, Z.: Rough set theory and its applications to data analysis. Cybern. Syst. 29(7), 661–688 (1998)
Yao, J.T., Azam, N.: Web-based medical decision support systems for three-way medical decision making with game-theoretic rough sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(1), 3–15 (2015)
Liu, D., Liang, D.C., Wang, C.C.: A novel three-way decision model based on incomplete information system. Knowl.-Based Syst. 91, 32–45 (2016)
Yao, Y.Y.: An outline of a theory of three-way decisions. In: International Conference on Rough Sets and Current Trends in Computing 2012, pp. 1–17. Springer
Yao, Y.Y., Zhou, B.: Naive Bayesian rough sets. In: International Conference on Rough Set and Knowledge Technology 2010, pp. 719–726
Pawlak, Z.: Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inform. Sci. 11(5), 341–356 (1982)
Ma, M.: Advances in three-way decisions and granular computing. Knowl.-Based Syst. 91, 1–3 (2016)
Goudey, R.: Do statistical inferences allowing three alternative decisions give better feedback for environmentally precautionary decision-making? J. Environ. Manage. 85(2), 338–344 (2007)
Peters, J.F., Ramanna, S.: Proximal three-way decisions: theory and applications in social networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 91, 4–15 (2016)
Jia, X.Y., Zheng, K., Li, W.W., Liu, T.T., Shang, L.: Three-way decisions solution to filter spam email: an empirical study. In: International Conference on Rough Sets and Current Trends in Computing 2012, pp. 287–296. Springer
Zhou, B., Yao, Y.Y., Luo, J.G.: Cost-sensitive three-way email spam filtering. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 42(1), 19–45 (2014)
Liu, D., Li, T.R., Liang, D.C.: Three-way government decision analysis with decision-theoretic rough sets. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzz. Knowl.-Based Syst. 20(01), 119–132 (2012)
Zhang, H.R., Min, F.: Three-way recommender systems based on random forests. Knowl.-Based Syst. 91, 275–286 (2016)
Zhang, H.R., Min, F., Shi, B.: Regression-based three-way recommendation. Inf. Sci. 378, 444–461 (2017)
Hu, B.Q.: Three-way decision spaces based on partially ordered sets and three-way decisions based on hesitant fuzzy sets. Knowl.-Based Syst. 91, 16–31 (2016)
Liang, D.C., Liu, D.: Deriving three-way decisions from intuitionistic fuzzy decision-theoretic rough sets. Inf. Sci. 300, 28–48 (2015)
Sayadi, M.K., Heydari, M., Shahanaghi, K.: Extension of VIKOR method for decision making problem with interval numbers. Appl. Math. Model. 33(5), 2257–2262 (2009)
Liu, J.S., Wang, X.Z., Zhang, B.Y.: The ranking of interval numbers. Chin. J. Eng. Math. 18(4), 103–109 (2001)
Li, D., Gu, Y.: Method for ranking interval numbers based on possibility degree. J. Syst. Eng. 23(2), 243 (2008)
Xu, Z.S., Da, Q.L.: Possibility degree method for ranking interval numbers and its application. J. Syst. Eng. 18(1), 67–70 (2003)
Hu, J.H., Zhang, Y., Chen, X.H., Liu, Y.M.: Multi-criteria decision making method based on possibility degree of interval type-2 fuzzy number. Knowl.-Based Syst. 43, 21–29 (2013)
Liang, D.C., Liu, D.: Systematic studies on three-way decisions with interval-valued decision-theoretic rough sets. Inf. Sci. 276, 186–203 (2014)
Liang, D.C., Pedrycz, W., Liu, D., Hu, P.: Three-way decisions based on decision-theoretic rough sets under linguistic assessment with the aid of group decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 29, 256–269 (2015)
Yager, R.R.: The power average operator. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-A: Syst. Hum. 31(6), 724–731 (2001)
Peng, H.G., Wang, J.Q.: Hesitant uncertain linguistic Z-numbers and their application in multi-criteria group decision-making problems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 1–17 (2016). doi:10.1007/s40815-016-0257-y
Peng, J.J., Wang, J.Q., Wu, X.H., Tian, C.: Hesitant intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators based on the Archimedean t-norms and t-conorms. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 1–13 (2017). doi:10.1007/s40815-017-0303-4
Wan, S.P.: Power average operators of trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and application to multi-attribute group decision making. Appl. Math. Model. 37(6), 4112–4126 (2013)
Xu, Z.S., Cai, X.Q.: Uncertain power average operators for aggregating interval fuzzy preference relations. Group Decis. Negot. 21(3), 381–397 (2012)
Peng, J.J., Wang, J.Q., Wu, X.H., Wang, J., Chen, X.H.: Multi-valued neutrosophic sets and power aggregation operators with their applications in multi-criteria group decision-making problems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 8(2), 345–363 (2015)
Zhang, Z.M.: Some hesitant multiplicative aggregation operators and their application in group decision making with hesitant multiplicative preference relations. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18(2), 177–197 (2016)
Jiang, L., Liu, H.B., Cai, J.F.: The power average operator for unbalanced linguistic term sets. Inf. Fusion 22, 85–94 (2015)
Yao, Y.Y.: Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf. Sci. 180(3), 341–353 (2010)
Yu, S.M., Wang, J., Wang, J.Q.: An extended TODIM approach with intuitionistic linguistic numbers. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. (2016). doi:10.1111/itor.12363
Wang, J., Wang, J.Q., Zhang, H.Y.: A likelihood-based TODIM approach based on multi-hesitant fuzzy linguistic information for evaluation in logistics outsourcing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 99C, 287–299 (2016)
Gomes, L., Lima, M.: From modeling individual preferences to multicriteria ranking of discrete alternatives: a look at Prospect Theory and the additive difference model. Found. Comput. Decis. Sci. 17(3), 171–184 (1992)
Gomes, L.F.A.M., Lima, M.M.P.P.: Todim: Basic and application to multicriteria ranking of projects with environmental impacts. Paris 16(4), 113–127 (1991)
Kahneman, D., Tversky, A.: Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econom.: J. Econom. Soc. 47(2), 263–291 (1979)
Liu, P.D., Teng, F.: An extended TODIM method for multiple attribute group decision-making based on 2-dimension uncertain linguistic Variable. Complexity 21(5), 20–30 (2014)
Gomes, L.F.A.M., Rangel, L.S.A.D.: An application of the TODIM method to the multicriteria rental evaluation of residential properties. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 193(1), 204–211 (2009)
Lourenzutti, R., Krohling, R.A.: A study of TODIM in a intuitionistic fuzzy and random environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 40(16), 6459–6468 (2013)
Tseng, M.-L., Lin, Y.H., Tan, K., Chen, R.H., Chen, Y.H.: Using TODIM to evaluate green supply chain practices under uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 38(11), 2983–2995 (2014)
Ji, P., Zhang, H.Y., Wang, J.Q.: A projection-based TODIM method under multi-valued neutrosophic environments and its application in personnel selection. Neural Comput. Appl. (2016). doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2436-z
Whitehead, J., Brunier, H.: Bayesian decision procedures for dose determining experiments. Stat. Med. 14(9), 885–893 (1995)
Gomes, L., Lima, M.: TODIM: Basics and application to multicriteria ranking of projects with environmental impacts. Found. Comput. Decis. Sci. 16(4), 113–127 (1992)
Jiang, Y.P., Liang, X., Liang, H.M.: An I-TODIM method for multi-attribute decision making with interval numbers. Soft Comput. 1–18 (2016). doi:10.1007/s00500-016-2139-5
Nehi, H.M.: A new ranking method for intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12(1), 80–86 (2010)
Sun, H.L., Yao, W.X.: Comments on methods for ranking interval numbers. J. Syst. Eng. 3, 005 (2010)
Xu, Z.S., Da, Q.L.: The uncertain OWA operator. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 17(6), 569–575 (2002)
Qian, W.Y., Zeng, Z.: Method for ranking interval rough numbers based on possibility degree. Oper. Res. Manage. Sci. 22(1), 71–76 (2013)
Gao, F.J.: Possibility degree and comprehensive priority of interval numbers. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 33(8), 2033–2040 (2013)
Tao, Z.F., Liu, X., Chen, H.Y., Zhou, L.G.: Ranking interval-valued fuzzy numbers with intuitionistic fuzzy possibility degree and its application to fuzzy multi-attribute decision making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 1–13 (2016). doi:10.1007/s40815-016-0193-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71371196 and 71210003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Yang, Y. & Chen, X. A Novel TODIM Method-Based Three-Way Decision Model for Medical Treatment Selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 1240–1255 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0320-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0320-3