Abstract
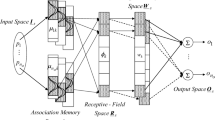
An interval-valued fuzzy cerebellar model neural network (IV-FCMNN) is proposed for the identification and control of uncertain systems. It is a more general model that uses the framework of a cerebellar model neural network (CMNN) and Atanassov intuitionistic fuzzy sets (AIFSs), so that the mathematical representation of a fuzzy event is more complete and the fuzzy neural network is more general. In some special cases, this neural network can be reduced to an interval-valued fuzzy neural network (IV-FNN), a fuzzy neural network (FNN), a fuzzy cerebellar model neural network (FCMNN) or a CMNN. Since the interval-type input data are used to realize this algorithm, the IV-FCMNN copes better with uncertainty and allows greater freedom of design. Therefore, the ability to learn, the approximation precision and the fuzzy semantic description of this network are much better than those of other models. In the proposed IV-FCMNN, a training algorithm that uses a gradient descent method is proposed to adjust the parameters and convergence is proved using the Lyapunov stability theorem. The variable learning rates are analyzed and the optimal learning rates are also determined. For demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed IV-FCMNN, three types of applications, including multiple functions approximation, multi-dimensional classification and nonlinear dynamic system feedback control, are performed and the comparison with other models are also provided.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, Y., Liu, S.: A historical introduction to grey systems theory. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pp. 2403–2408 (2004)
Albus, J.S.: A new approach to manipulator control: the cerebellar model articulation controller (CMAC). J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 97, 220–227 (1975)
Chiang, C.T., Lin, H.S.: CMAC with general basis functions. Neural Netw. 9(7), 1199–1211 (1996)
Lin, C.M., Chen, L.Y., Yeung, D.S.: Adaptive filter design using recurrent cerebellar model articulation controller. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 21(7), 1149–1157 (2010)
Lin, C.M., Li, H.Y.: A novel adaptive wavelet fuzzy cerebellar model articulation control system design for voice coil motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(4), 2024–2033 (2012)
Lin, C.M., Li, H.Y.: TSK fuzzy CMAC-based robust adaptive back stepping control for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(6), 1147–1154 (2012)
Lin, C.M., Hou, Y.L., Chen, T.Y., Chen, K.H.: Breast nodules computer-aided diagnostic systems design using fuzzy cerebellar model neural network. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(3), 693–699 (2014)
Almedia, P.E.M., Simoes, M.G.: Parametric CMAC networks fundamentals and applications of a fast convergence neural structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 39(5), 1551–1557 (2003)
Lin, C.M., Chen, L.Y., Chen, C.H.: RCMAC hybrid control for MIMO uncertain nonlinear systems using sliding-mode technology. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 18(3), 708–720 (2007)
Mendel, J.M.: Computing derivatives in interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 12(1), 84–98 (2004)
Straszecka, E.: Combining uncertainty and imprecision in models of medical diagnosis. Inf. Sci. 176(20), 3026–3059 (2006)
Han, J.W., Kamber, M.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Morgan, San Mateo (2006)
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-1. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975)
Bustince, H., Barrenechea, E., Pagola, M., Fernandez, J., Xu, Z., Bedregal, B., Montero, J., Hagras, H., Herrera, F., De Baets, B.: A historical account of types of fuzzy sets and their relationships. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 24(1), 179–194 (2016)
Hu, X., Pedrycz, W., Castillo, O., Melin, P.: Fuzzy rule-based models with interactive rules and their granular generalization. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 307, 1–28 (2017)
Sanchez, M.A., Castillo, O., Castro, J.R.: Information granule formation via the concept of uncertainty-based information with interval type-2 fuzzy sets representation and Takagi-Sugeno-Kang consequents optimized with cuckoo search. Appl. Soft Comput. 27, 602–609 (2015)
Hernandez, M.D.L.A., Melin, P., Méndez, G.M., Castillo, O., López-Juarez, I.: A hybrid learning method composed by the orthogonal least-squares and the back-propagation learning algorithms for interval A2-C1 type-1 non-singleton type-2 TSK fuzzy logic systems. Soft. Comput. 19(3), 661–678 (2015)
Abiyev, R.H., Kaynak, O.: Type 2 fuzzy neural structure for identification and control of time-varying plants. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(12), 4147–4159 (2010)
Castillo, O., Melin, P.: A review on the design and optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy controllers. Appl. Soft Comput. 12(4), 1267–1278 (2012)
Castillo, O., Castro, J.R., Melin, P., Rodríguez-Díaz, A.: Application of interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks in non-linear identification and time series prediction. Soft. Comput. 18(6), 1213–1224 (2014)
Castillo, O., Castro, J.R., Melin, P., Rodríguez-Díaz, A.: Universal approximation of a class of interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks in nonlinear identification. Adv. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 1–16 (2013)
Castro, J.R., Castillo, O.: A class of interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks illustrated with application to non-linear identification. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1–6 (2013)
Soto, J., Melin, P., Castillo, O.: Particle swarm optimization of the fuzzy integrators for time series prediction using ensemble of IT2FNN architectures. In: Nature-Inspired Design of Hybrid Intelligent Systems. Springer, pp. 141–158 (2017)
Gaxiola, F., Melin, P., Valdez, F., Castro, J.R., Castillo, O.: Optimization of type-2 fuzzy weights in backpropagation learning for neural networks using GAs and PSO. Appl. Soft Comput. 38, 860–871 (2016)
Li, H., Sun, X., Wu, L., Lam, H.K.: State and output feedback control of interval type-2 fuzzy systems with mismatched membership functions. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(6), 1943–1957 (2015)
Sanz, J.A., Bernardo, D., Herrera, F., Bustince, H.: A compact evolutionary interval-valued fuzzy rule-based classification system for the modeling and prediction of real-world financial applications with imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 973–990 (2015)
Kumbasar, T.: Robust stability analysis and systematic design of single-input interval type-2 fuzzy logic controllers. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 24(3), 675–694 (2016)
Karnik, N.N., Mendel, J.M.: Centroid of a type-2 fuzzy set. Inf. Sci. 132(1–4), 195–220 (2001)
Mendel, J.M.: Uncertain Rule-Based Fuzzy Logic Systems: Introduction and New Directions. Prentice-Hall, Prentice (2001)
Melgarejo, M.A., Garcia, R.A., Pena-Reyes, C.A.: Pro-two: a hardware based platform for real time type-2 fuzzy inference. IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 977–982 (2004)
Lynch, C., Hagras, H., Callaghan, V.: Embedded type-2 FLC for real-time speed control of marine and traction diesel engines. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 347–352 (2005)
Wu, H., Mendel, J.M.: Uncertainty bounds and their use in the design of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 10(5), 622–639 (2002)
Atanassov, K.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20(1), 87–96 (1986)
Bustince, H., Burillo, P.: Vague sets are intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 79(3), 403–405 (1996)
Wu, D.: Approaches for reducing the computational cost of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: overview and comparisons. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 21(1), 80–99 (2013)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(1), 338–353 (1965)
Huang, H.P., Yan, J.L., Cheng, T.H.: Development and fuzzy control of a pipe inspection robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 57(3), 1088–1095 (2010)
Badaloni, S., Falda, M.: Temporal-based medical diagnoses using a fuzzy temporal reasoning system. J. Intell. Manuf. 21(1), 145–153 (2010)
Louverdis, G., Andreadis, I., Tsalides, P.: New fuzzy model for morphological colour image processing. IEE Proc. Vision Image Signal Process. 149(3), 129–139 (2002)
Atanassov, K.: Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets, Theory and Applications. Physica-Verlag, Wurzburg (1999)
Ye, J.: Cosine similarity measures for intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications. Math. Comput. Model. 53(1–2), 91–97 (2011)
Keleş, A., Yavuz, U.: Expert system based on neuro-fuzzy rules for diagnosis breast cancer. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(5), 5719–5726 (2011)
Own, C.M.: Switching between type-2 fuzzy sets and intuitionistic fuzzy sets: an application in medical diagnosis. Appl. Intell. 31(3), 283–291 (2009)
Badaloni, S., Falda, M.: Temporal-based medical diagnoses using a fuzzy temporal reasoning system. J. Intell. Manuf. 21(1), 145–153 (2010)
Turksen, I.B.: Interval valued fuzzy sets based on normal forms. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20(2), 191–210 (1986)
Gau, W.L., Buehrer, D.J.: Vague sets. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(2), 610–614 (1993)
Xu, Z., Yager, R.R.: Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int. J. Gen Syst. 35(4), 417–433 (2006)
Mandic, D.P.: A generalized normalized gradient descent algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. Lett. 11(2), 115–118 (2004)
Li, Q.J., Wang, Y., Li, Z.X., Wang, X.: ISODATA algorithm based on intuitionistic fuzzy. Comput. Eng. Appl. 48(9), 176–177 (2012)
Khatibi, V., Montazer, G.A.: A new evidential distance measure based on belief intervals. Sci. Iran. Trans. D Comput. Sci. Eng. Electr. Eng. 17(2), 119–132 (2010)
Cha, S.H.: Comprehensive survey on distance similarity measures between probability density functions. Int. J. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 1(4), 300–307 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and based on which the presentation of this paper has been greatly improved. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation (2015J01275) of Science and Technology agency, Fujian, and the Science and Technology-Planned Project (3502Z20143034) of Xiamen, and the Foreign Science and Technology Special Cooperation (E201401400) of Xiamen University of Technology, and the National Science Council of the Republic of China under Grant NSC 98-2221-E-155-058-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Lin, CM. An Interval-Valued Fuzzy Cerebellar Model Neural Network Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19, 881–894 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0321-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0321-2