Abstract
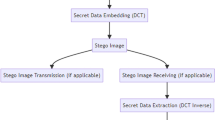
Information security is one of the most important processes and methodologies which have to be considered when any information is communicated secretly between two parties. Cryptography and steganography are the two important practices used for this purpose. Cryptography changes the secret message into unintelligible text; however, it reveals the existence of the secret message. Steganography technique on the other hand hides the secret message such that no one can notice the presence of it. Current paper presents an image steganographic technique exploiting fuzzy logic edge detection and chaotic method. The fuzzy logic approach for image processing allows defining the degree to which a pixel belongs to an edge. Least significant bit substitution approach is used for data hiding in the carrier image. The combination of chaotic theory with steganography is emerging and gets attracted by researchers. Chaotic method is applied to the original message to generate the random sequence of binary equivalent secret message which prevents the secret message from attackers. The proposed method hides large amount of data with good quality of stage image of the human visual system and guarantees the confidentiality in the communication. The experimental results shows better peak signal-to-noise ratio, image quality index and payload for evaluating the stego image compared to the existing methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox, I., Miller, M., Bloom, J., Fridrich, J., Kalker, T.: Digital Watermarking and Steganography. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Burlington (2007)
Johnson, N.F., Duric, Z., Jajodia, S., Memon, N.: Information hiding: steganography and watermarking—attacks and counter measures. J. Electron. Imaging 10, 825–826 (2001)
Ziou, D., Reza, J.: Efficient steganalysis of images: learning is good for anticipation. Pattern Anal. Appl. 17, 279–289 (2014)
Wang, R.-Z., Lin, C.-F., Lin, J.-C.: Hiding data in images by optimal moderately significant-bit replacement. IEEE Electron. Lett. 36, 2069–2070 (2000)
Pareek, N.K., Vinod, P., Sud, K.K.: Image encryption using chaotic logistic map. Image Vis. Comput. 24, 926–934 (2006)
Dachselt, F., Schwarz, W.: Chaos and cryptography. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 48, 1498–1501 (2001)
Ornstein, D.S., Weiss, B.: Statistical properties of chaotic systems. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 24, 11–116 (1991)
Parker, S., Chua, L.O.: Chaos a tutorial for engineers. Proc. IEEE. 75, 982–1008 (1995)
Bandyopadhyay, D., Dasgupta, K., Mandal, J.K., Dutta, P.: A novel secure image steganography method based on chaos theory in spatial domain. Int. J. Secur. Priv. Trust Manag. (IJSPTM) 3, 11–22 (2014)
Wu, W., Rulkov, N.F.: Studying chaos via 1-D maps—a tutorial. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 40, 707–721 (1993)
Guan, Z.H., Huang, F., Guan, W.: Chaos-based image encryption algorithm. Phys. Lett. 346, 153–157 (2005)
Yang, C.Y., Zhang, Q.L., Zhou, L.N.: Lur’e Lyapunov functions and absolute stability criteria for Lur’e systems with multiple nonlinearities. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 17, 829–841 (2007)
Wang, X.-Y., Sheng-Xian, G.: New chaotic encryption algorithm based on chaotic sequence and plain text. IET Inf. Secur. 8, 213–216 (2014)
Kanopoulos, N., Vasanthavada, N., Baker, R.L.: Design of an image edge detection filter using the Sobel operator. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 23, 358–367 (1988)
Bassil, Y.: Image steganography based on a parameterized canny edge detection algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.6259 (2012)
Canny, J.: A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 6, 679–698 (1986)
Moghaddamzadeh, A., Bourbaki, N.: A fuzzy region growing approach for segmentation of color images. Pattern Recogn. 30, 867–881 (1997)
El-Khamy, S.E., Lotfy, M., El-Yamany, N.: A modified fuzzy Sobel edge detector. In: Radio Science Conference, pp. C32-1. IEEE (2000)
Zhao, M., Fu, A.M., Yan, H.: A technique of three-level thresholding based on probability partition and fuzzy 3-partition. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 9, 469–479 (2001)
Russo, F., Ramponi, G.: Edge extraction by FIRE operators. In: Proceedings of the Third IEEE Conference on Fuzzy Systems. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, pp. 249–253. (1994)
Aborisade, D.O.: Novel fuzzy logic based edge detection technique. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 29, 75–82 (2011)
See, J., Madasu, H., Shantaram, V.: Fuzzy-based parameterized gaussian edge detector using global and local properties. In: International Conference on Information Technology: Coding and Computing, ITCC, vol. 2. IEEE (2005)
Kaur, E.K., Mutenja, V., Gill, E.I.S.: Fuzzy logic based image edge detection algorithm in MATLAB. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 22, 55–58 (2010)
Amarunnishad, T.M., Govindan, V.K., Mathew, T.: Improving BTC image compression using a fuzzy complement edge operator. Sig. Process. 88, 2989–2997 (2008)
Chen, W.J., Chang, C.C., Le, T.H.: High payload steganography mechanism using hybrid edge detector. Expert Syst. Appl. 37, 3292–3301 (2010)
Yu, J.G., Yoon, E.J., Shin, S.H., Yoo, K.Y.: A new image steganography based on 2 k correction and edge-detection. In: Information Technology: New Generations, pp. 563–568. IEEE (2008)
Sun, S.: A novel edge based image steganography with 2 k correction and Huffman encoding. Inf. Process. Lett. 116, 93–99 (2016)
Wang, Z.: A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9, 81–84 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanmathi, C., Prabu, S. Image Steganography Using Fuzzy Logic and Chaotic for Large Payload and High Imperceptibility. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 460–473 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0420-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0420-0