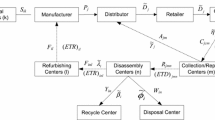
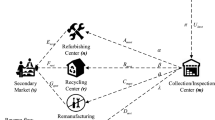
Abstract
The substantial impact of environmental and social issues on business performance highlights the significant role of sustainability in supply chain network design problems. The innate uncertainty of the problem factors such as customer demand and return rates requires an integrated approach to deal with the problem. This paper aims to design a closed-loop supply chain (CLSC) network considering both sustainability and uncertainty issues. Fuzzy programming is used to address the uncertainty in this study. A fuzzy multi-objective mixed-integer linear programming is developed to simultaneously optimize a sustainable CLSC network. The objectives are considered to be the total costs and the environmental impacts minimization and social benefits maximization. Three pillars of sustainability (cost, environmental, and social) are taken into account in network design. A three-phased fuzzy solution approach is developed to solve this model. To examine the significance of the proposed model and the solution approach, a computational experiment is conducted. The results approve the applicability of the proposed approach and the feasibility of the solution methodology. Results also show that the proposed model presents a systematic framework that enables the management to obtain a satisfactory solution by adjusting the search direction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Wahed, W.F.: Interactive fuzzy goal programming for multi-objective transportation problems. Omega 34(2), 158–166 (2006)
Alshamsi, A., Diabat, A.: A reverse logistics network design. J. Manuf. Syst. 37(3), 589–598 (2015)
Amin, S.H., Zhang, G.: A multi-objective facility location model for closed-loop supply chain network under uncertain demand and return. Appl. Math. Model. 37(6), 4165–4176 (2013)
Chaabane, A., Ramudhin, A., Paquet, M.: Design of sustainable supply chains under the emission trading scheme. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 135(1), 37–49 (2012)
Dai, Z., Li, Z.: Design of a dynamic closed-loop supply chain network using fuzzy bi-objective linear programming approach. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 34(5), 330–343 (2017)
Diabat, A., Theodorou, E.: A location–inventory supply chain problem: reformulation and piecewise linearization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 90, 381–389 (2015)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.M.: Fuzzy Sets and Systems: Theory and Applications. Academic Press, New York (1980)
El-Sayed, M., Afia, N., El-Kharbotly, A.: A stochastic model for forward–reverse logistics network design under risk. Comput. Ind. Eng. 58(3), 423–431 (2010)
Francas, D., Minner, S.: Manufacturing network configuration in supply chains with product recovery. Omega 37(4), 757–769 (2009)
Gholamian, N., Mahdavi, I., Tavakoli-Moghaddam, R., Mahdavi-amiri, N.: Comprehensive fuzzy multi-objective multi-product multi-site aggregate production planning decisions in a supply chain under uncertainty. Appl. Soft Comput. 37, 585–607 (2015)
Gaur, J., Amini, M., Rao, A.K.: Closed-loop supply chain configuration for new and reconditioned products: an integrated optimization model. Omega 66, 212–223 (2017)
Guide Jr., V.D.R., Van Wassenhove, L.N.: The evolution of closed-loop supply chain research. Oper. Res. 57(1), 10–18 (2009)
Hasani, A., Zegordi, S.H., Nikbakhsh, E.: Robust closed-loop supply chain network design for perishable goods in agile manufacturing under uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Res. 50(16), 4649–4669 (2012)
Hannan, E.L.: Linear programming with multiple fuzzy goals. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 6(3), 235–248 (1981)
Hwang, C.L., Yoon, K.: Multiple Attribute Decision Making –Methods and Applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg (1981)
Jamalnia, A., Soukhakian, M.A.: A hybrid fuzzy goal programming pproach with different goal priorities to aggregate production planning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 56, 1474–1486 (2009)
Kannan, D., Diabat, A., Alrefaei, M., Govindan, K., Yong, G.: A carbon footprint based reverse logistics network design model. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 67, 75–79 (2012)
Keramydas, C., Mallidis, I., Dekker, R., Vlachos, D., Iakovou, E.: Cost and environmental trade-offs in supply chain network design and planning: the merit of a simulation-based approach. J. Simul. 11(1), 20–29 (2017)
Kerachian, R., Karamouz, M.: A stochastic conflict resolution model for water quality management in reservoir–river systems. Adv. Water Resour. 30(4), 866–882 (2007)
Keyvanshokooh, E., Ryan, S.M., Kabir, E.: Hybrid robust and stochastic optimization for closed-loop supply chain network design using accelerated Benders decomposition. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 249(1), 76–92 (2016)
Kenne, J.-P., Dejax, P., Gharbi, A.: Production planning of a hybrid manufacturing–remanufacturing system under uncertainty within a closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 135(1), 81–93 (2012)
Klibi, W., Martel, A., Guitouni, A.: The design of robust value-creating supply chain networks: a critical review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 203(2), 283–293 (2010)
Lee, D.H., Dong, M.: A heuristic approach to logistics network design for end-of-lease computer products recovery. Transp. Res. E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 44(3), 455–474 (2008)
Lai, Y.J., Hwang, C.L.: A new approach to some possibilistic linear programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 49(2), 121–133 (1992)
Lai, Y.J., Hwang, C.L.: Fuzzy Multiple Objective Decision Making, Methods and Applications. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Li, X.Q., Zhang, B., Li, H.: Computing efficient solutions to fuzzy multiple objective linear programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 157(11), 1328–1332 (2006)
Liang, T.F.: Distribution planning decisions using interactive fuzzy multi-objective linear programming. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 157(10), 1303–1316 (2006)
Liang, T.F., Cheng, H.W.: Application of fuzzy sets to manufacturing/distribution planning decisions with multi-product and multi-time period in supply chains. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(2), 3367–3377 (2009)
Liang, T.-F.: Fuzzy multi objective production/distribution planning decisions with multi product and multi time period in a supply chain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 55(3), 676–694 (2008)
Luhandjula, M.K.: Fuzzy optimization: an appraisal. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 30, 257–282 (1989)
Millet, D.: Designing a sustainable reverse logistics channel: the 18 generic structures framework. J. Clean. Prod. 19(6), 588–597 (2011)
Mula, J., Peidro, D., Madronero, M.D., Vicens, E.: Mathematical programming models for supply chain production and transport planning. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 204(3), 377–390 (2010)
Özceylan, E., Paksoy, T.: A mixed integer programming model for a closed-loop supply-chain network. Int. J. Prod. Res. 51(3), 718–734 (2013)
Paksoy, T., Bektas, T., O¨zceylan, E.: Operational and environmental performance measures in a multi-product closed-loop supply chain. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 47(4), 532–546 (2011)
Paksoy, T., Özceylan, E., Weber, G.W.: A multi objective model for optimization of a green supply chain network. In: Barsoum N., Weber G.W., Vasant, P. (eds.) AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1239, no. 1, pp. 311–320. AIP (2010)
Pishvaee, M.S., Torabi, S.A.: A possibilistic programming approach for closed-loop supply chain network design under uncertainty. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 161(20), 2668–2683 (2010)
Pishvaee, M.S., Rabbani, M., Torabi, S.A.: A robust optimization approach to closed-loop supply chain network design under uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 35(2), 637–649 (2011)
Pishvaee, M.S., Razmi, J.: Environmental supply chain network design using multi-objective fuzzy mathematical programming. Appl. Math. Model. 36(8), 3433–3446 (2012)
Pishvaee, M.S., Torabi, S.A., Razmi, J.: Credibility-based fuzzy mathematical programming model for green logistics design under uncertainty. Comput. Ind. Eng. 62(2), 624–632 (2012)
Phuc, P.N.K., Yu, V.F., Chou, S.Y.: Optimizing the fuzzy closed-loop supply chain for electrical and electronic equipments. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 15(1), 9–21 (2013)
Ramezani, M., Bashiri, M., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.: A new multi-objective stochastic model for a forward/reverse logistic network design with responsiveness and quality level. Appl. Math. Model. 37(1–2), 328–344 (2013)
Ramezani, M., Kimiagari, A.M., Karimiz, B.: Closed-loop supply chain network design: a financial approach. Appl. Math. Model. 38(15–16), 4099–4119 (2014)
Rommelfanger, H.: Fuzzy linear programming and applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 92(3), 512–527 (1996)
Sakawa, M., Yano, H.: Interactive fuzzy satisficing method for multi-objective nonlinear programming problems with fuzzy parameters. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 30, 221–238 (1989)
Sakawa, M.: An interactive fuzzy satisficing method for multiobjective linear fractional programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 28(2), 129–144 (1988)
Selim, H., Ozkarahan, I.: A supply chain distribution network design model: an interactive fuzzy goal programming-based solution approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 36(3), 401–418 (2008)
Seuring, S.: A review of modeling approaches for sustainable supply chain management. Decis. Support Syst. 54(4), 1513–1520 (2013)
Sherafati, M., Bashiri, M.: Closed loop supply chain network design with fuzzy tactical decisions. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 12(3), 255–269 (2016)
Subulan, K., Tasan, A.S., Baykaso˘glu, A.: Fuzzy mixed integer programming model for medium-term planning in a closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing option. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 23(6), 345–368 (2012)
Tang, C.S., Zhou, S.: Research advances in environmentally and socially sustainable operations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 223(3), 585–594 (2012)
Tanaka, H., Asai, K.: Fuzzy linear programming with fuzzy numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 13, 1–10 (1984)
Tanaka, H., Ichihashi, H., Asai, K.: A formulation of fuzzy linear programming problem based on comparison of fuzzy numbers. Control Cybern. 13(3), 185–194 (1984)
Torabi, S.A., Hassini, E.: An interactive possibilistic programming approach for multiple objective supply chain master planning. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 159(2), 193–214 (2008)
Vahdani, B., Jolai, F., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R., Mousavi, S.M.: Two fuzzy possibilistic bi-objective zero-one programming models for outsourcing the equipment maintenance problem. Eng. Optim. 44(7), 801–820 (2012)
Wang, R.C., Liang, T.F.: Applying possibilistic linear programming to aggregate production planning. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 98(3), 328–341 (2005)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Zailani, S., Jeyaraman, K., Vengadasan, G., Premkumar, R.: Sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) in Malaysia: a survey. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 140(1), 330–340 (2012)
Zeballos, L., Gomes, M., Barbosa-Povoa, A.P., Novais, A.Q.: Addressing theuncertain quality and quantity of returns in closed-loop supply chains. Comput. Chem. Eng. 47, 237–247 (2012)
Zhou, Z., Cheng, S., Hua, B.: Supply chain optimization of continuous process industries with sustainability considerations. Comput. Chem. Eng. 24(2–7), 1151–1158 (2000)
Zhang, Y.M., Huang, G.H., He, L.: An inexact reverse logistics model for municipal solid waste management systems. J. Environ. Manage. 92(3), 522–530 (2011)
Zimmermann, H.-J.: Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1(1), 45–56 (1978)
Zimmermann, H.-J.: Fuzzy Set Theory and Its Applications. Kluwer Academic Publications, Boston (1996)
Acknowledgements
This paper research has been supported by a grant (No 155147-2013) from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourjavad, E., Mayorga, R.V. Multi-objective Fuzzy Programming of Closed-Loop Supply Chain Considering Sustainable Measures. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 655–673 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0551-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0551-y