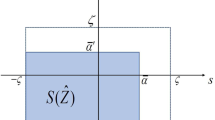Abstract
The probabilistic linguistic term set has been proposed to deal with the probabilistic distribution in providing linguistic assessments. However, because of various subjective and objective situations, it is usually hard for the decision makers to provide the probabilities of linguistic assessments exactly. The existing methods still have some shortcomings in dealing with ignorance. In this paper, we propose the concept of uncertain probabilistic linguistic term set (UPLTS) to serve as an extension of the existing tools. First, some basic operational laws and aggregation operators for the UPLTS are presented. Then, we develop an aggregation-based method and present the application of the UPLTSs in multiple attribute group decision making. Finally, a practical case is shown to illustrate the UPLTS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975)
Xu, Z.S.: Linguistic Decision Making: Theory and Methods. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Herrera, F., Verdegay, J.L.: Linguistic assessments in group decision. In: Proceedings of the First European Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Technologies, pp. 941–948. Aachen (1993)
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Verdegay, J.L.: A model of consensus in group decision making under linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 78, 73–87 (1996)
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Verdegay, J.L.: A rational consensus model in group decision making using linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 88, 31–49 (1997)
Herrera, F., Martinez, L.: A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 8(6), 746–752 (2000)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy logic equals computing with words. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 4, 103–111 (1996)
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Martínez, L.: Computing with words for decision making versus linguistic decision making: a reflection on both scenarios. Stud. Fuzziness Soft Comput 322, 245–260 (2015)
Mendel, J.M., Zadeh, L.A., Trillas, E., Yager, R.R., Lawry, J., Hagras, H., Guadarrama, S.: What computing with words means to me: discussion forum. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 5(1), 20–26 (2010)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy logic = computing with words. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 4, 103–111 (1996)
Xu, Z.S.: A method based on linguistic aggregation operators for group decision making with linguistic preference relations. Inf. Sci. 166, 19–30 (2004)
Xu, Z.S., Wang, H.: On the syntax and semantics of virtual linguistic terms for information fusion in decision making. Inf. Fusion 34, 43–48 (2017)
Wang, J.H., Hao, J.: A new version of 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 14(3), 435–445 (2006)
Zhangm, G., Dong, Y., Xu, Y.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17(1), 46–55 (2014)
Rodriguez, R.M., Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision-making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(1), 109–119 (2012)
Torra, V.: Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 25(6), 529–539 (2010)
Zhu, B., Xu, Z.S.: Consistency measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 35–45 (2014)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J., Merigó, J.M.: Qualitative decision-making with correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Knowl.-Based Syst. 76(1), 127–138 (2015)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Herrera-Viedma, E., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application in decision-making: a state-of-the-artsurvey. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12, 1–27 (2017)
Xia, M.M., Xu, Z.S.: Hesitant fuzzy information aggregation in decision-making. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 52(3), 395–407 (2011)
Xu, Z.S., Xia, M.M.: Hesitant fuzzy entropy and cross-entropy and their use in multiattribute decision-making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 27(9), 799–822 (2012)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic VIKOR method and its application in qualitative multiple criteria decision-making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(5), 1343–1355 (2015)
Zhang, F.Y., Luo, L., Liao, H.C., Zhu, T., Shi, Y.: Inpatient admission assessment in West China Hospital based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic VIKOR method. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 30(6), 3143–3154 (2016)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Herrera-Viedma, E., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application in decision-making: a state-of-the-artsurvey. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12, 1–27 (2017)
Malik, A., Bashir, Z., Rashid, T., Ali, J.: Probabilistic hesitant intuitionistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Symmetry 10(9), 392 (2018)
Wang, H., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for linguistic decision making: current developments, issues and challenges. Inf. Fusion 43, 1–12 (2018)
Li, C.C., Rodríguez, R.M., Martinez, L., Dong, Y.C., Herrera, F.: Personalized individual semantics based on consistency in hesitant linguistic group decision making with comparative linguistic expressions. Knowl.-Based Syst. 145, 156–165 (2018)
Xu, Z.S., Xia, M.M.: Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 181(11), 2128–2138 (2011)
Chen, N., Xu, Z.S., Xia, M.M.: Correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy sets and their applications to clustering analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 37(4), 2197–2211 (2013)
Riera, J.V., Massanet, S., Herrera-Viedma, E., Torrens, J.: Some interesting properties of the fuzzy linguistic model based on discrete fuzzy numbers to manage hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Appl. Soft Comput. 36, 383–391 (2015)
Wei, C.P., Liao, H.C.: A Multigranularity linguistic group decision-making method based on hesitant 2-tuple sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 31(6), 612–634 (2016)
Pang, Q., Wang, H., Xu, Z.S.: Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision-making. Inf. Sci. 369, 128–143 (2016)
Lin, M.W., Xu, Z.S., Zhai, Y.L., Yao, Z.: Multi-attribute group decision-making under probabilistic uncertain linguistic environment. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 22, 1–15 (2017)
Zhai, Y.L., Xu, Z.S., Liao, H.C.: Probabilistic linguistic vector-term set and its application in group decision-making with multi-granular linguistic information. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 801–816 (2016)
Peng, H.G., Zhang, H.Y., Wang, J.Q.: Cloud decision support model for selecting hotels on TripAdvisor. com with probabilistic linguistic information. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 68, 124–138 (2018)
Bai, C.Z., Zhang, R., Qian, L.X., Wu, Y.N.: Comparisons of probabilistic linguistic term sets for multi-criteria decision making. Knowl.-Based Syst. 119, 284–291 (2017)
Liu, P.D., Teng, F.: Some Muirhead mean operators for probabilistic linguistic term sets and their applications to multiple attribute decision-making. Appl. Soft Comput. 68, 396–431 (2018)
Kobina, A., Liang, D.C., He, X.: Probabilistic linguistic power aggregation operators for multi-criteria group decision making. Symmetry 9(12), 320–321 (2017)
Tang, J., Meng, F.Y., Zhang, S.L., An, Q.X.: Group decision making with interval linguistic hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 119, 231–246 (2018)
Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Yu, S.: Computing the numerical scale of the linguistic term set for the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17(6), 1366–1378 (2009)
Wang, Y.M.: Using the method of maximizing deviation to make decision for multiindices. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 8(3), 21–26 (1997)
Kim, S.H., Ahn, B.S.: Interactive group decision making procedure under incomplete information. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 116(3), 498–507 (1999)
Kim, S.H., Choi, S.H., Kim, J.K.: An interactive procedure for multiple attribute group decision making with incomplete information: range-based approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 118(1), 139–152 (1999)
Xu, Z.S.: An interactive procedure for linguistic multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Making 6(1), 17–27 (2007)
Jiang, Y.P., Fan, Z.P., Ma, J.: A method for group decision making with multi-granularity linguistic assessment information. Inf. Sci. 178, 1098–1109 (2008)
Herrera, F., Herrera, V.E., Martinez, L.: A fuzzy linguistic methodology to deal with unbalanced linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 16(2), 354–370 (2008)
Dong, Y.C., Wu, Y.Z., Zhang, H.J., Zhang, G.Q.: Multi-granular unbalanced linguistic distribution assessments with interval symbolic proportions. Knowl.-Based Syst. 82, 139–151 (2015)
Li, C.C., Dong, Y.C., Herrera, F., Herrera, V.E., Martinez, L.: Personalized individual semantics in computing with words for supporting linguistic group decision making: an application on consensus reaching. Inf. Fusion 33, 29–40 (2017)
Zhu, B., Xu, Z.S.: Extended hesitant fuzzy sets. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 22(1), 100–121 (2015)
Hai, W., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Linguistic terms with weakened hedges: a model for qualitative decision making under uncertainty. Inf. Sci. 433–434, 37–54 (2018)
Zhang, G.Q., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17, 46–55 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71571123, 71771155) and the Major Program of the National Social Science Fund of China (Grant No. 17ZDA092).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, C., Wang, H. & Xu, Z. Uncertain Probabilistic Linguistic Term Sets in Group Decision Making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1241–1258 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00619-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00619-9