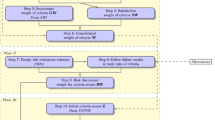
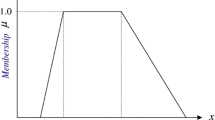
Abstract
Development of fuzzy compromised variable weight vector (VWV) and its application on fuzzy comprehensive decision making (FCDM) are studied specifically in this paper. Based on the definition of variable weight state vector (VWSV), a compromised VWSV is proposed and then further developed to obtain the fuzzy compromised VWSV. According to the algorithm of Hardarmard product, fuzzy compromised VWV is developed. A FCDM model with fuzzy compromised variable weights is developed accordingly. Fuzzy numbers and fuzzy operations are determined by using the fuzzy structured element, which is the essential part for the analytical algorithm of the FCDM model. The developed model was then applied as decision-making method on maintenance order for entries in underground coal mine. The research finding could also provide an alternative way for determination of weights and fuzzy operations in other fuzzy analysis models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalkey, N., Helmer, O.: An experimental application of the DELPHI method to the use of experts. Manag. Sci. 9, 458–467 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.9.3.458
Milholland, A.V., Wheeler, S.G., Heieck, J.J.: Medical assessment by a Delphi group opinion technic. N. Engl. J. Med. 288, 1272–1275 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197306142882405
Saaty, T.L.: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. McGraw-Hill, New York (1980)
Dadeviren, M., Yuksel, I.: Developing a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (AHP) model for behavior-based safety management. Inf. Sci. (Ny) 178, 1717–1733 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2007.10.016
Wang, Y.Y., Xu, Z.S.: Evaluation of the human settlement in Lhasa with intuitionistic fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 1–16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0422-y
Juang, C.H., Huang, X.H., Schiff, S.D.: Determination of weights of criteria for decision making by the fuzzy eigenvector method. Civ. Eng. Syst. 9, 1–16 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1080/02630259208970636
Xu, Y.J., Wang, H.M.: Eigenvector method, consistency test and inconsistency repairing for an incomplete fuzzy preference relation. Appl. Math. Model. 37, 5171–5183 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2012.10.008
Xu, Y.J., Chen, L., Rodríguez, R.M., Herrera, F., Wang, H.M.: Deriving the priority weights from incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations in group decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 99, 71–78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.01.047
Saaty, T.L.: The analytic network process. International 195, 1–26 (1996)
Saaty, T.L.: Decision making with dependence and feedback: The analytic network process. In: RWS Publications, 1996, ISBN 0-9620317-9-8. p. 370 (1996)
Erdoğmuş, Ş., Aras, H., Koç, E.: Evaluation of alternative fuels for residential heating in Turkey using analytic ne-twork process (ANP) with group decision-making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 10, 269–279 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2004.09.003
Moore, J.R., Baker, N.R.: An analytical approach to scoring model design—application to research and development project selection. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. EM-16, pp. 90–98 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1109/tem.1969.6447060
Nelson, C.A.: A scoring model for flexible manufacturing systems project selection. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 24, 346–359 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(86)90028-7
Huang, M.L., Xu, X.J., Tashnev, D.: A weighted linear quantile regression. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 85, 2596–2618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00949655.2014.938240
Wu, C., Yu, J.Z.: Evaluation of linear regression techniques for atmospheric applications: the importance of appropriate weighting. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 11, 1233–1250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-11-1233-2018
Aduol, F.W.O.: Robust geodetic parameter estimation under least squares through weighting on the basis of the mean square error. In Geodesy the Challenge of the 3rd Millennium. pp. 269–276 (2003)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27, 379–423 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1145/584091.584093
Soofi, E.: Generalized entropy-based weights for multiattribute value models. Oper. Res. 38, 362–363 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.38.2.362
Ng, D.K.W., Deng, J.: Contrasting grey system theory to probability and fuzzy. ACM Sigice Bull. 20, 3–9 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1145/202081.202082
Kao, P.S., Hocheng, H.: Optimization of electrochemical polishing of stainless steel by grey relational analysis. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 140, 255–259 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00747-7
Liang, D.C., Kobina, A.: Quan W (2017) Grey relational analysis method for probabilistic linguistic multi-criteria group decision-making based on geometric Bonferroni mean. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0374-2
Pawlak, Z.: Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 11, 341–356 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01001956
Son, C.S., Kim, Y.N., Kim, H.S., Park, H.S., Kim, M.S.: Decision-making model for early diagnosis of congestive heart failure using rough set and decision tree approach-es. J. Biomed. Inform. 45, 999–1008 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2012.04.013
Oztaysi, B.: A decision model for information technology selection using AHP integrated TOPSIS-Grey: the case of content management systems. Knowl. Based Syst. 70, 44–54 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.02.010
Wang, Y.S., Jin, Z.X., Deng, C.B., Wang, X.Y.: Comprehensive decision-making with fuzzy combined weighting and its application on the order of gob management. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 34, 2641–2649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-17700
Liu, B.S., Huo, T.F., Liao, P.C., Yuan, J.F., Sun, J., Hu, X.: A special Partial Least Squares (PLS) path decision modeling for bid evaluation of large construction projects. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 21, 579–592 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0702-3
Liu, B.S., Shen, Y.H., Chen, X.H., Sun, H., Chen, Y.: A complex multi-attribute large-group PLS decision-making method in the interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Appl. Math. Model. 38, 4512–4527 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.02.023
Xu, Y.J., Patnayakuni, R., Wang, H.M.: Logarithmic least squares method to priority for group decision making with incomplete fuzzy preference relations. Appl. Math. Model. 37, 2139–2152 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2012.05.010
Li, H.X.: Multifactorial functions in fuzzy sets theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 35, 69–84 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(90)90019-3
Wang, P.Z.: Fuzzy sets and the falling shadow of random sets. Beijing Normal University Press, Beijing (1985)
Li, H.X., Yen, V.C.: Fuzzy sets and fuzzy decision-making. Crc Press. (1995)
Li, H.X., Li, L.X., Wang, J.Y., Mo, Z.W., Li, Y.D.: Fuzzy decision making based on variable weights. Math. Comput. Model. 39, 163–179 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7177(04)90005-2
Zeng, W.Y., Li, D.Q., Wang, P.Z.: Variable weight decision making and balance function analysis based on factor space. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 15, 999–1014 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S021962201650022X
Li, D.Q., Zeng, W.Y., Li, J.H.: Balance function analysis in variable weight decision making. In: Proceedings—2014 10th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, CIS 2014 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/cis.2014.61
Li, D.Q., Hao, F.L.: Weights transferring effect of state variable weight vector. Syst. Eng. Pract. 29, 127–131 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1874-8651(10)60054-3
Wu, Q., Li, B., Chen, Y.L.: Vulnerability assessment of groundwater inrush from underlying aquifers based on variable weight model and its application. Water Resour. Manag. 30, 3331–3345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1352-4
Nagurney, A., Ke, K.: Financial networks with intermediation: risk management with variable weights. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 172, 40–63 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2004.09.035
Zeng, X.Z., Fang, Z.F.: Comprehensive evaluation of blasting effects based on variable weight method and research on fuzzy decision. Adv. Mater. Res. 402, 610–616 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.402.610
Zhang, J.H., Tian, C.F., Fang, W., Zhang, N.N.: Assessment on operational risk in power grid enterprises based on variable weight fuzzy evaluation. In: 2009 International Conference on Energy and Environment Technology, ICEET 2009. pp. 92–95 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/iceet.2009.259
Li, L., Xie, L.J., Zhang, D., Yu, B., Ge, Y.F., Lin, F.C.: Condition assessment of power transformers using a synthetic analysis method based on association rule and variable weight coefficients. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 20, 2052–2060 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2013.6678853
Liu, C.: Research on safety assessment method for bridge structure based on variable weight synthesis method. Perspect. Sci. 7, 200–203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pisc.2015.11.033
Zhang, R.F., Huang, L.F., Xiao, M.B.: Security evaluation for wireless network based on fuzzy-AHP with variable weight. In: 2010 Second International Conference on Networks Security, Wireless Communications and Trusted Computing. pp. 490–493 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/nswctc.2010.122
Zhang, S.Z., Zeng, Q.D., Zhang, G.: A new approach for prioritization of failure mode in FMECA using encouragement variable weight AHP. Appl. Mech. Mater. 289, 93–98 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.289.93
Hu, J.H., Yang, Y., Guo, S.Z.: Fuzzy number intuitionist-ic fuzzy set and its representation of structured element. Presented at the (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/iita.workshops.2008.131
Guo, S.Z.: Comparison and ordering of fuzzy numbers b-ased on method of structured element. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 29, 106–111 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1874-8651(10)60013-0
Guo, S.C., Zhao, Y.: Transform group of monotonic functions with the same monotonicity on [− 1, 1] and operations of fuzzy numbers. Ann. Data Sci. 2, 281–291 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-015-0055-7
Wang, H.D., Guo, S.C., Bamakan, S.M.H., Shi, Y.: Homeomorphism problems of fuzzy real number space and the space of bounded functions with same monotonicity on [− 1,1]. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 10, 889–903 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24474-7_11
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to appreciate editors and reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions. The research described in this paper was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51704145 and 51604144). The authors would like also to thank for all the supports to publish this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Jin, Z., Deng, C. et al. Comprehensive Decision Making with Fuzzy Compromised Variable Weights and its Application on Maintenance Order for Entries in Underground Coal Mine. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1379–1388 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00638-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00638-6