Abstract
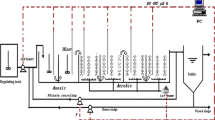
Dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration is a key variable in the operation of wastewater treatment processes (WWTPs). In this paper, an adaptive fuzzy neural network-based model predictive control (AFNN-MPC) is proposed for the control problem of DO concentration. The main contributions of AFNN-MPC are threefolds: First, an AFNN, based on a novel learning method with adaptive learning rate, is designed to model the unknown nonlinearities of WWTPs with high predicting performance. Second, a gradient method is used to solve the optimal control problem of AFNN-MPC to reduce the computational cost. Third, the convergence of AFNN, as well as the stability analysis of AFNN-MPC, has been given in detail. Finally, the proposed AFNN-MPC is applied to the benchmark simulation model No. 2. The promising results indicate that the proposed AFNN-MPC is a suitable solution to control DO concentration. Moreover, the comprehensive experiments clearly show the superiority and efficacy of the proposed AFNN-MPC.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behera, C.R., Srinivasan, B., Chandran, K., et al.: Model based predictive control for energy efficient biological nitrification process with minimal nitrous oxide production. Chem. Eng. J. 268, 300–310 (2015)
Nguyen, D., Gadhamshetty, V., Nitayavardhana, S., et al.: Automatic process control in anaerobic digestion technology: a critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 193, 513–522 (2015)
Mulas, M., Tronci, S., Corona, F., et al.: Predictive control of an activated sludge process: an application to the Viikinmäki wastewater treatment plant. J. Process Control 35, 89–100 (2015)
Adyel, T.M., Oldham, C.E., Hipsey, M.R.: Stormwater nutrient attenuation in a constructed wetland with alternating surface and subsurface flow pathways: event to annual dynamics. Water Res. 107, 66–82 (2016)
Diehl, S., Farås, S.: Control of an ideal activated sludge process in wastewater treatment via an ODE–PDE model. J. Process Control 23(3), 38–359 (2013)
Qiao, M., Qi, W., Liu, H., Qu, J.: Occurrence, behavior and removal of typical substituted and parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a biological wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 52, 11–19 (2014)
Kasmi, M., Hamdi, M., Trabelsi, I.: Ecofriendly process combining physical-chemical and biological technics for the fermented dairy products waste pretreatment and reuse. Water Sci. Technol. 75(1), 39–47 (2017)
Sweetapple, C., Fu, G., Butler, D.: Multi-objective optimisation of wastewater treatment plant control to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Water Res. 55, 52–62 (2014)
Santin, I., Pedret, C., Vilanova, R.: Applying variable dissolved oxygen set point in a two level hierarchical control structure to a wastewater treatment process. J. Process Control 28, 40–55 (2015)
Yang, T., Qiu, W., et al.: Fuzzy model-based predictive control of dissolved oxygen in activated sludge processes. Neurocomputing 136, 88–95 (2014)
Lee, C., Howe, K., Thomson, B.: Ozone and biofiltration as an alternative to reverse osmosis for removing PPCPs and micropollutants from treated wastewater. Water Res. 46(4), 1005–1014 (2012)
Aymerich, I., Rieger, L., et al.: The difference between energy consumption and energy cost: modelling energy tariff structures for water resource recovery facilities. Water Res. 81, 113–123 (2015)
Åmand, L., Carlsson, B.: The optimal dissolved oxygen profile in a nitrifying activated sludge process–comparisons with ammonium feedback control. Water Sci. Technol. 68(3), 641–649 (2013)
Alcntara, S., Pedret, C., Vilanova, R.: On the model matching approach to PID design: analytical perspective for robust servo/regulator trade off tuning. J. Process Control 20(5), 596–608 (2010)
Shen, W., Zhu, Y., Long, Z.: Two PID-combined controllers for dissolved oxygen concentration in wastewater treatment process of a paper mill—a simulation study. In: 2016 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). IEEE, pp. 8533–8538 (2016)
López-Pérez, P.A., Neria-González, M.I., Aguilar-López, R.: Improvement of activated sludge process using a nonlinear PI controller design via adaptive gain. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 14(1), 407–416 (2016)
Samsudin, S., Rahmat, M., et al.: Improvement of activated sludge process using enhanced nonlinear PI controller. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(8), 6575–6586 (2014)
Aouaouda, S., Chadli, M., Khadir, M.T., Bouarar, T.: Robust fault tolerant tracking controller design for unknown inputs T–S models with unmeasurable premise variables. J. Process Control 22(5), 861–872 (2012)
Ebadzadeh, M.M., SalimiBadr, A.: CFNN: correlated fuzzy neural network. Neurocomputing 148(1), 430–444 (2015)
Holenda, B., Domokos, E., Redey, A., Fazakas, J.: Dissolved oxygen control of the activated sludge wastewater treatment process using model predictive control. Comput. Chem. Eng. 32(6), 1270–1278 (2008)
Shen, W., Chen, X., Corriou, J.P.: Application of model predictive control to the BSM1 benchmark of wastewater treatment process. Comput. Chem. Eng. 32(12), 2849–2856 (2008)
Zeng, J., Liu, J.: Economic model predictive control of wastewater treatment processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54(21), 5710–5721 (2015)
O’Brien, M., Mack, J., et al.: Model predictive control of an activated sludge process: a case study. Control Eng. Pract. 19(1), 54–61 (2011)
Han, H.G., Qiao, J.F.: Nonlinear model-predictive control for industrial processes: an application to wastewater treatment process. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(4), 1970–1982 (2014)
Rashid, M.M., Mhaskar, P., Swartz, C.L.E.: Multi-rate modeling and economic model predictive control of the electric arc furnace. J. Process Control 40, 50–61 (2016)
Rojas, J.D., Flores-Alsina, X., et al.: Application of multivariate virtual reference feedback tuning for wastewater treatment plant control. Control Eng. Pract. 20(5), 499–510 (2012)
Santin, I., Pedret, C., Vilanova, R.: Applying variable dissolved oxygen set point in a two level hierarchical control structure to a wastewater treatment process. J. Process Contr. 28, 40–55 (2015)
Patan, K.: Neural network-based model predictive control: fault tolerance and stability. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 23(3), 1147–1155 (2015)
Han, H.G., Qiao, J.F., Chen, Q.L.: Model predictive control of dissolved oxygen concentration based on a self-organizing RBF neural network. Control Eng. Pract. 20(4), 465–476 (2012)
Hagras, H., Alghazzawi, D., Aldabbagh, G.: Employing type-2 fuzzy logic systems in the efforts to realize ambient intelligent environments. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 10(1), 44–51 (2015)
Castro, J.R., Castillo, O., Sanchez, M.A., Mendoza, O., Rodríguez-Diaz, A., Melin, P.: Method for higher order polynomial sugeno fuzzy inference systems. Inf. Sci. 351, 76–89 (2016)
Castillo, O., Cervantes, L., Soria, J., Sanchez, M., Castro, J.R.: A generalized type-2 fuzzy granular approach with applications to aerospace. Inf. Sci. 354, 165–177 (2016)
Starkey, A., Hagras, H., Shakya, S., Owusu, G.: iPatch: a many-objective type-2 fuzzy logic system for field workforce optimization. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 27(3), 502–514 (2019)
Rubaai, A., Young, P.: Hardware/software implementation of fuzzy-neural-network self-learning control methods for brushless DC motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 52(1), 414–424 (2016)
Lin, C.M., Le, T.L.: PSO-self-organizing interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for antilock braking systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(5), 1–13 (2017)
Pratama, M., Lu, J., Lughofer, E., Zhang, G., Er, M.J.: An incremental learning of concept drifts using evolving type-2 recurrent fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(5), 1175–1192 (2017)
Han, H.G., Lin, Z.L., Qiao, J.F.: Modeling of nonlinear systems using the self-organizing fuzzy neural network with adaptive gradient algorithm. Neurocomputing 266(29), 566–578 (2017)
Ebadzadeh, M.M., Salimi-Badr, A.: IC-FNN: a novel fuzzy neural network with interpretable, intuitive, and correlated-contours fuzzy rules for function approximation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(3), 1288–1302 (2018)
Han, H.G., Qian, H.H., Qiao, J.F.: Nonlinear multiobjective model-predictive control scheme for wastewater treatment process. J. Process Control 24(3), 47–59 (2014)
Han, H.G., Zhang, L., Hou, Y., Qiao, J.F.: Nonlinear model predictive control based on a self-organizing recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(2), 402–415 (2016)
Jeppsson, U., Pons, M.N.: The COST benchmark simulation model-current state and future perspective. Control Eng. Pract. 12(4), 299–304 (2004)
Wu, X.J., Zhu, X.J., Cao, G.Y., Tu, H.Y.: Predictive control of SOFC based on a GA-RBF neural network model. J. Power Sources 179(1), 232–239 (2008)
Hagan, M.T., Menhaj, M.B.: Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5(6), 989–993 (1994)
Ampazis, N., Perantonis, S.J.: Two highly efficient second-order algorithms for training feedforward networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 13(5), 1064–1074 (2002)
Lu, C.H.: Wavelet fuzzy neural networks for identification and predictive control of dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(7), 3046–3058 (2011)
Jeppsson, U., Rosen, C., et al.: Vanrolleghem, Towards a benchmark simulation model for plant-wide control strategy performance evaluation of WWTPs. Water Sci. Technol. 53(1), 287–295 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Project under Grants 2018YFC1900800-5, National Science Foundation of China under Grants 61890930-5 and 61622301, Beijing Natural Science Foundation under Grant 4172005 and Major National Science and Technology Project under Grant 2017ZX07104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, HG., Liu, Z. & Qiao, JF. Fuzzy Neural Network-Based Model Predictive Control for Dissolved Oxygen Concentration of WWTPs. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1497–1510 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00644-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00644-8