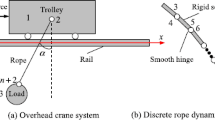
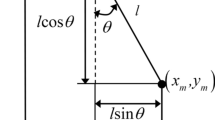
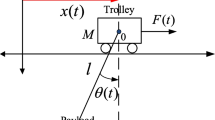
Abstract
In this paper, aiming at the under-actuated problem of the overhead crane systems, a fuzzy logic anti-swing controller is first designed according to operator experience. Moreover, for better configuring the parameters of the controller, an adaptive differential evolution with disturbance factor algorithm (ADE-D) is proposed by introducing the adaptive scaling factor, the dynamic crossover probability and disturbance factor. By implementing numeric experiment test, the results show that the adaptive differential evolution with disturbance factor algorithm outperforms the standard differential evolution algorithm and other improved differential evolution algorithms. Finally, the adaptive differential evolution with disturbance factor algorithm-based fuzzy logic anti-swing controller is simulated under different conditions and compared with other control methods; the results exhibit excellent robustness of control performance in positioning control and damping oscillation of payload.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singhose, W., Porter, L., Kenison, M., Kriikku, E.: Effects of hoisting on the input shaping control of gantry cranes. Control Eng. Pract. 8(10), 1159–1165 (2000)
Sorensen, K.L., Singhose, W.E.: Command-induced vibration analysis using input shaping principles. Automatica 44(9), 2392–2397 (2008)
Yoshida, Y., Tabata, H.: Visual feedback control of an overhead crane and its combination with time-optimal control. In: 2008 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, pp. 1114–1119 (2008)
Sun, Z., Wang, N., Bi, Y., Zhao, J.: A de based pid controller for two dimensional overhead crane. In: 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp. 2546–2550 (2015)
Sano, H., Sato, K., Ohishi, K., Miyazaki, T.: Robust design of vibration suppression control system for crane using sway angle observer considering friction disturbance. Electrical Eng. Japan 184(3), 36–46 (2013)
Sun, N., Fang, Y.: Nonlinear tracking control of underactuated cranes with load transferring and lowering: theory and experimentation. Automatica 50(9), 2350–2357 (2014)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Chen, H., Lu, B.: Amplitude-saturated nonlinear output feedback antiswing control for underactuated cranes with double-pendulum cargo dynamics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron 64(3), 2135–2146 (2017)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Chen, H.: Amplitude-saturated nonlinear output feedback antiswing control for underactuated cranes with double-pendulum cargo dynamics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron 64(3), 2135–2146 (2017)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Chen, H., He, B.: Adaptive nonlinear crane control with load hoisting/lowering and unknown parameters: design and experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 20(5), 2107–2119 (2015)
Wu, Y., Lu, R., Shi, P., Su, H., Wu, Z.: Analysis and design of synchronization for heterogeneous network. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(4), 1253–1262 (2018)
Du, C., Yang, C., Li, F., Gui, W.: A novel asynchronous control for artificial delayed markovian jump systems via output feedback sliding mode approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(2), 364–374 (2019)
Xie, X., Yue, D., Zhang, H., Peng, C.: Control synthesis of discrete-time t-s fuzzy systems: reducing the conservatism whilst alleviating the computational burden. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(9), 2480–2491 (2017)
Xie, X., Yue, D., Park, J.H., Li, H.: Relaxed fuzzy observer design of discrete-time nonlinear systems via two effective technical measures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(5), 2833–2845 (2018)
Zhai, D., An, L., Dong, J., Zhang, Q.: Switched adaptive fuzzy tracking control for a class of switched nonlinear systems under arbitrary switching. IEEE Tran. Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 585–597 (2018)
Wang, Y., Yang, X., Yan, H.: Reliable fuzzy tracking control of near-space hypersonic vehicle using aperiodic measurement information. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(12), 9439–9447 (2019)
Wang, Y., Karimi, H.R., Lam, H., Yan, H.: Fuzzy output tracking control and filtering for nonlinear discrete-time descriptor systems under unreliable communication links. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, pp. 1–11 (2019)
Wang, Y., Zhou, W., Luo, J., Yan, H., Pu, H., Peng, Y.: Reliable intelligent path following control for a robotic airship against sensor faults. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 24 (6), 2572–2582 (2019)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Shi, P., Wu, L.: A piecewise-markovian lyapunov approach to reliable output feedback control for fuzzy-affine systems with time-delays and actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(9), 2723–2735 (2018)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Lam, H.K.: A novel approach to reliable output feedback control of fuzzy-affine systems with time delays and sensor faults. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst.25(6), 1808–1823 (2017)
Wang, L., Zhang, H., Kong, Z.: Anti-swing control of overhead crane based on double fuzzy controllers. In: The 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2015 CCDC), pp. 981–986 (2015)
Zhang, L., Chen, W., Cui, T., Tong, X.: An online secondary path modeling algorithm based on gradient descent for active noise control. Noise Vibration Control 38(3), 15–19 (2018)
Han, X., Dong, Y., Yue, L., Xu, Q.: State transition simulated annealing algorithm for discrete-continuous optimization problems. IEEE Access 7, 44391–44403 (2019)
Gao, X.M., Yang, Y., Wu, Z.H.: Genetic algorithm for scheduling double different size crane system with different truck ready times. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), pp. 447–451 (2016)
Smoczek, J., Szpytko, J.: Particle swarm optimization-based multivariable generalized predictive control for an overhead crane. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 22(1), 258–268 (2017)
Juang, C., Jeng, T., Chang, Y.: An interpretable fuzzy system learned through online rule generation and multiobjective aco with a mobile robot control application. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(12), 2706–2718 (2016)
Reynoso-Meza, G., Sanchis, J., Blasco, X. Design of continuous controllers using a multiobjective differential evolution algorithm with spherical pruning. In: International Conference on Applications of Evolutionary Computation, pp. 532–541 (2010)
Das, S., Mandal, A., Mukherjee, R.: An adaptive differential evolution algorithm for global optimization in dynamic environments. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(6), 966–978 (2014)
Fan, Q., Yan, X.: Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm with zoning evolution of control parameters and adaptive mutation strategies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(1), 219–232 (2016)
Sarker, R.A., Elsayed, S.M., Ray, T.: Differential evolution with dynamic parameters selection for optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 18(5), 689–707 (2014)
Sun, Z., Wang, N., Srinivasan, D., Bi, Y.: Optimal tunning of type-2 fuzzy logic power system stabilizer based on differential evolution algorithm. Int. J. Electrical Power Energy Syst.62, 19–28 (2014)
Do, D.T., Lee, S., Lee, J.: A modified differential evolution algorithm for tensegrity structures. Composite Struct. 158(Supplement C), 11–19 (2016)
Fu, C., Jiang, C., Chen, G., Liu, Q.: An adaptive differential evolution algorithm with an aging leader and challengers mechanism. Appl. Soft Comput.57(Supplement C), 60–73 (2017)
Suganthi, S., Devaraj, D., Ramar, K., Thilagar, S.H.: An improved differential evolution algorithm for congestion management in the presence of wind turbine generators. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 81(Part 1), 635–642 (2018)
Cui, L., Li, G., Zhu, Z., Lin, Q., Wong, K.C., Chen, J., et al.: Adaptive multiple-elites-guided composite differential evolution algorithm with a shift mechanism. Inform. Sci. 422(Supplement C), 122–143 (2018)
Brest, J., Greiner, S., Boskovic, B., Mernik, M., Zumer, V.: Self-adapting control parameters in differential evolution: a comparative study on numerical benchmark problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 10(6), 646–657 (2006)
Sun, Z., Wang, N., Bi, Y., Srinivasan, D.: Parameter identification of pemfc model based on hybrid adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Energy 90, 1334–1341 (2015)
Chellaswamy, C., Ramesh, R.: Parameter extraction of solar cell models based on adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Renew. Energy 97, 823–837 (2016)
Wang, X., Liu, H., Lai, X., Xu, Z., Jiang, R.: A new approach of anti-swing control system based on run-to-run control and fuzzy control for overhead crane. In: 2017 13th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), pp. 1264–1270 (2017)
Liu, J., Zheng, S., Tan, Y.: Analysis on global convergence and time complexity of fireworks algorithm. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, New York, 2014, pp. 3207–3213 (2014)
Sun, Z., Bi, Y., Chen, S., Hu, B., Xiang, F., Ling, Y., et al.: Designing and optimization of fuzzy sliding mode controller for nonlinear systems. Comput. Mater. Continua 61(1), 119–128 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61672299, No. 61972208,No. 61602259, No. 61701251, No. 61803213 and 61972211), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 18KJB520035, No. 18KJB510016) and National Engineering Laboratory for Logistics Information Technology, YuanTong Express Co. LTD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Ling, Y., Qu, H. et al. An Adaptive DE Algorithm Based Fuzzy Logic Anti-swing Controller for Overhead Crane Systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 1905–1921 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00883-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00883-0