Abstract
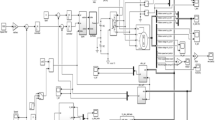
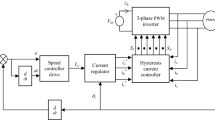
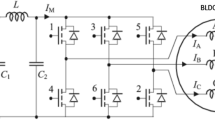
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) is one of the most viable motion control products due to the inherent benefits of low rotor inertia, high efficiency and high-power density in industrial applications. The speed control for PMSM is a significant task. Many researchers carried out their research for improving performance of PMSM through speed control. But, the performance and efficiency of PMSM are reduced due to the external load disturbances and parameter deviation like nonlinear, time-varying, strong coupling of PMSM. In order to address these problems, Particle Swarm Maxpooling Fully Connective Deep Convolutional Neural Learnt Sugeno-Takagi Fuzzy Controller (PSMFCDCNLSTFC) model is introduced. The key objective of PSMFCDCNLSTFC model is to regulate the speed of PMSM for obtaining the highest current value. PSMFCDCNLSTFC model comprises two processes, namely Particle Swarm Weight and Hidden Neuron Optimization process and Maxpooling Fully Connective Deep Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network-based Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Controller process. In the former process, weight parameters and number of hidden neurons are optimized to design efficient deep convolutional neural network. In the latter process, four layers are used to regulate the speed of PMSM through Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Controller. After that, the soft sign activation function is used to find the minimum mean square error for attaining the rated current value of PMSM. Finally, the performance of PMSM gets improved. The performance of PSMFCDCNLSTFC model is performed with PMSM data and measured in terms of rise time, peak time, peak value, peak overshoot and settling time. The simulation results show that the PSMFCDCNLSTFC model increases the performance of PMSM with higher output current value when compared to state-of-the-art works.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, Y., Dong, L.: Robust current and speed control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor using SMC and ADRC. Control Theory Technol. 17, 190–199 (2019)
Gao, P., Zhang, G., Ouyang, H., Mei, L.: An adaptive super twisting nonlinear fractional order PID sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor speed regulation system based on extended state observer. IEEE Access 8, 53498–53510 (2020)
Szczepanski, R., Tarczewski, T., Grzesiak, L.M.: Adaptive state feedback speed controller for PMSM based on Artificial Bee Colony algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 83, 1–12 (2019)
Chaoui, H., Khayamy, M., Okoye, O., Gualous, H.: Simplified speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motors using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(4), 3563–3574 (2019)
Lu, E., Li, W., Yang, X., Liu, Y.: Anti-disturbance speed control of low-speed high-torque PMSM based on second-order non-singular terminal sliding mode load observer. ISA Trans. 88, 142–152 (2019)
Yiguang, C., Chenghan, L., Zhenmao, B., Xiaobin, Z.: Modified super-twisting algorithm with an anti-windup coefficient adopted in PMSM speed loop control. Energy Procedia 158, 2637–2642 (2019)
Djerioui, A., Houari, A., Ait-Ahmed, M., Benkhoris, M.-F., Chouder, A., Machmoum, M.: Grey Wolf based control for speed ripple reduction at low-speed operation of PMSM drives. ISA Trans. 74, 111–119 (2018)
Jon, R., Wang, Z., Luo, C., Jong, M.: Adaptive robust speed control based on recurrent Elman neural network for sensorless PMSM servo drives. Neurocomputing 227, 131–141 (2017)
Apte, A.A., Joshi, V.A., Walambe, R.A., Godbole, A.A.: Speed control of PMSM using disturbance observer. IFAC-Papers Online 49(1), 308–313 (2016)
Tang, M., Zhuang, S.: On speed control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor with current predictive compensation. Energies 12(65), 1–15 (2019)
Kim, S.-K., Lee, J.-S., Lee, K.-B.: Robust speed control algorithm with disturbance observer for uncertain PMSM. Int. J. Electron. 105(8), 1300–1318 (2018)
Zhang, H., Liu, Q., Zhang, J., Chen, S., Zhang, C.: Speed regulation of permanent magnet synchronous motor using event triggered sliding mode control. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 1–11 (2018)
Wang, M.-S., Syamsiana, I.N., Lin, F.-C.: Sensorless speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motors by neural network algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 1–7 (2014)
Mendoza-Mondragon, F., Hernandez-Guzman, V.M., Rodriguez-Resendiz, J.: Robust speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motors using two-degrees-of-freedom control. IEEE Tran. Ind. Electron. 65(8), 6099–6108 (2018)
Choi, H.H., Kim, E.K., Yu, D.Y., Jung, J.W., Kim, T.H.: Precise PI speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motor with a simple learning feedforward compensation. Electr. Eng. 99, 133–139 (2017)
Ciabattoni, L., Ferracuti, F., Foresi, G., Freddi, A., Monteriù, A., Pagnotta, D.P.: A robust and self-tuning speed control for permanent magnet synchronous motors via meta-heuristic optimization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 96, 1283–1292 (2018)
Xia, X., Zhang, B., Li, X.: High precision low-speed control for permanent magnet synchronous motor. Sensors 20(5), 15–26 (2020)
Rumana Farheen, N., Bharathi Dasan, S.G.: State feedback speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motor for an electric vehicle. Int. J. Sci. Dev. Res. 5(7), 133–146 (2020)
Younesi, A., Tohidi, S., Feyzi, M.R., Baradarannia, M.: An improved nonlinear model predictive direct speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 28(5), 25–35 (2018)
Altaey, A., Kulaksiz, A.A.: Stability analysis of sensorless speed control of IPMSM. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 12(2), 101–112 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest in publishing this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, F.V.A., Kannan, V.K. Particle Swarm Optimized Deep Convolutional Neural Sugeno-Takagi Fuzzy PID Controller in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 180–201 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01126-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01126-6