Abstract
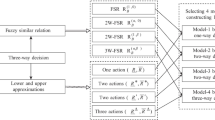
The decision-theoretic rough set model based on Bayesian decision theory proposes a framework for studying rough set approximations using probabilistic theory, it has become an important research direction of rough set theory. In order to extend the theory of decision-theoretic rough set, this article is devoted to studying the fuzzy decision-theoretic rough set model in type-2 fuzzy conditional information systems. The type-2 fuzzy similarity relations are induced though computing the measure of similarity between objects for each attribute. Then, we use intersection operation of type-2 fuzzy sets to aggregate the multiple induced fuzzy similarity relations. Next, a fuzzy decision-theoretic rough set approach for type-2 fuzzy conditional information systems is proposed by means of inclusion degree of type-2 fuzzy sets. Finally, an example is considered to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which is helpful for applying these theories to deal with practical issues.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pawlak, Z.: Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 11(5), 341–356 (1982)
Pawlak, Z.: Rough sets: theoretical aspect of reasoning about data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York (1991)
Dai, J.H., Wei, B.J., Zhang, X.H., Zhang, Q.L.: Uncertainty measurement for incomplete interval-valued information systems based on \(\alpha\)-weak similarity. Knowl. Based Syst. 136, 159–171 (2017)
Du, Y., Hu, Q.H., Zhu, P.F., Ma, P.J.: Rule learning for classification based on neighborhood covering reduction. Inf. Sci. 181(24), 5457–5467 (2011)
Dai, J.H., Tian, H.W., Wang, W.T., Liu, L.: Decision rule mining using classification consistency rate. Knowl. Based Syst. 43, 95–102 (2013)
Wei, J.M., Wang, S.Q., Yuan, X.J.: Ensemble rough hypercuboid approach for classifying cancers. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 22(3), 381–391 (2010)
Dai, J.H., Hu, Q.H., Zhang, J.H., Hu, H., Zheng, N.G.: Attribute selection for partially labeled categorical data by rough set approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(9), 2460–2471 (2017)
Dai, J.H., Hu, H., Wu, W.Z., Qian, Y.H., Huang, D.B.: Maximal-discernibility-pair-based approach to attribute reduction in fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(4), 2174–2187 (2018)
Dai, J.H., Hu, Q.H., Hu, H., Huang, D.B.: Neighbor inconsistent pair selection for attribute reduction by rough set approach. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 937–950 (2018)
Wang, C.Z., Shi, Y.P., Fan, X.D., Shao, M.W.: Attribute reduction based on \(k\)-nearest neighborhood rough sets. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 106, 18–31 (2019)
Dai, J.H., Xu, Q.: Attribute selection based on information gain ratio in fuzzy rough set theory with application to tumor classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 13(1), 211–221 (2013)
Dai, J.H., Chen, J.L.: Feature selection via normative fuzzy information weight with application into tumor classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 92, 106299 (2020)
Qian, Y.H., Liang, J.Y., Wu, W.Z., Dang, C.Y.: Information granularity in fuzzy binary GrC model. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 19(2), 253–264 (2011)
Chen, H.M., Li, T.R., Luo, C., Horng, S.-J., Wang, G.Y.: A decision-theoretic rough set approach for dynamic data mining. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(6), 1958–1970 (2015)
Zhang, K., Zhan, J.M., Yao, Y.Y.: TOPSIS method based on a fuzzy covering approximation space: an application to biological nano-materials selection. Inf. Sci. 502, 297–329 (2019)
Zhang, K., Zhan, J.M., Wu, W.Z.: On multi-criteria decision-making method based on a fuzzy rough set model with fuzzy \(\alpha\)-neighborhoods. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3001670
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 17(2), 191–209 (1990)
Yue, X.D., Chen, Y.F., Miao, D.Q., Qian, J.: Tri-partition neighborhood covering reduction for robust classification. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 83, 371–384 (2017)
Wang, C.Z., Huang, Y., Shao, M.W., Fan, X.D.: Fuzzy rough set-based attribute reduction using distance measures. Knowl. Based Syst. 164, 205–212 (2019)
Ziarko, W.: Variable precision rough set model. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 46(1), 39–59 (1993)
Slezak, D., Ziarko, W.: The investigation of the Bayesian rough set model. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 40(1–2), 81–91 (2005)
Yao, Y.Y.: Decision-theoretic rough set models. Lecture Notes Artif. Intell. 4481, 1–12 (2007)
Yao, Y.Y.: Probabilistic rough set approximations. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 49(2), 255–271 (2008)
Greco, S., Matarazzo, B., Slowinski, R.: Parameterized rough set model using rough membership and Bayesian confirmation measures. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 49(2), 285–300 (2008)
Qian, Y.H., Liang, J.Y., Yao, Y.Y., Dang, C.Y.: MGRS: a multi-granulation rough set. Inf. Sci. 180(6), 949–970 (2010)
Qian, Y.H., Zhang, H., Sang, Y.L., Liang, J.Y.: Multigranulation decision-theoretic rough sets. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 55(1), 225–237 (2014)
Yao, Y.Y.: Three-way decision: an interpretation of rules in rough set theory. Lecture Notes Artif. Intell. 5589, 642–649 (2009)
Feng, T., Mi, J.S.: Variable precision multigranulation decision-theoretic fuzzy rough sets. Knowl. Based Syst. 91, 93–101 (2016)
Zhang, Q.H., Xie, Q., Wang, G.Y.: A novel three-way decision model with decision-theoretic rough sets using utility theory. Knowl. Based Syst. 159, 321–335 (2018)
Jiao, L., Yang, H.L., Li, S.G.: Three-way decision based on decision-theoretic rough sets with single-valued neutrosophic information. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 11, 657–665 (2020)
Zhao, X.R., Hu, B.Q.: Three-way decisions with decision-theoretic rough sets in multiset-valued information tables. Inf. Sci. 507, 684–699 (2020)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975)
Raj, D., Gupta, A., Garg, B., Tanna, K., Rhee, F.C.: Analysis of data generated from multidimensional type-1 and type-2 fuzzy membership functions. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 681–693 (2018)
Pal, S.S., Kar, S.: A hybridized forecasting method based on weight adjustment of neural network using generalized type-2 fuzzy set. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(1), 308–320 (2019)
Wang, H.D., Yao, J.L., Yan, J., Dong, M.G.: An extended TOPSIS method based on gaussian interval type-2 fuzzy set. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(6), 1831–1843 (2019)
Karnik, N.N., Mendel, J.M., Liang, Q.L.: Type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 7(6), 643–658 (2000)
Mendel, J.M., John, R.I.B.: Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 10(2), 117–127 (2002)
Hu, B.Q., Wang, C.Y.: On type-2 fuzzy relations and interval-valued type-2 fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 236(2), 1–32 (2014)
Wang, C.Y.: Type-2 fuzzy rough sets based on extended t-norms. Inf. Sci. 305, 165–183 (2015)
Lu, J., Li, D.Y., Zhai, Y.H., Li, H., Bai, H.X.: A model for type-2 fuzzy rough sets. Inf. Sci. 328(20), 359–377 (2016)
Singh, S., Garg, H.: Distance measures between type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their application to multicriteria decision-making process. Appl. Intell. 46(4), 88–799 (2017)
Li, J.W., John, R., Coupland, S., Kendall, G.: On Nie-Tan operator and type-reduction of interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 1036–1039 (2018)
Wu, D.R., Mendel, J.M.: Similarity measures for closed general type-2 fuzzy sets: overview, comparisons, and a geometric approach. Inf. Sci. 27(3), 515–526 (2019)
Feng, T., Mi, J.S., Zhang, S.P.: Belief functions on general intuitionistic fuzzy information systems. Inf. Sci. 271(1), 143–158 (2014)
Lin, G.P., Liang, J.Y., Qian, Y.H., Li, J.J.: A fuzzy multigranulation decision-theoretic approach to multi-source fuzzy information systems. Knowl. Based Syst. 91, 102–113 (2016)
Li, Z.W., Liu, X.F., Zhang, G.Q., Xie, N.X., Wang, S.C.: A multi-granulation decision-theoretic rough set method for distributed \(fc\)-decision information systems: an application in medical diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 56, 233–244 (2017)
Zhang, X.X., Chen, D.G., Tsang, E.C.C.: Generalized dominance-based rough set model for the dominance intuitionistic fuzzy information systems. Inf. Sci. 378, 1–25 (2017)
Zhang, G.Q., Li, Z.W., Wu, W.Z., Liu, X.F., Xie, N.X.: Information structures and uncertainty measures in a fully fuzzy information system. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 101, 119–149 (2018)
Liu, X.F., Li, Z.W., Zhang, G.Q., Xie, N.X.: Measures of uncertainty for a distributed fully fuzzy information system. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 48(6), 625–655 (2019)
Mendel, J.M.: Advances in type-2 fuzzy sets and systems. Inf. Sci. 177(1), 84–110 (2007)
De Luca, A., Termini, S.: A definition of non-probabilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy sets theory. Inf. Control 20, 301–312 (1972)
Sanchez, E.: Inverses of fuzzy relations: applications to possibility distributions and medical diagnosis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2, 75–86 (1979)
John, R., Mendel, J., Carter, J.: The extended sup-star composition for type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 7212–7216 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61976089, 61473259, 61070074, 60703038), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ30451), and the Hunan Provincial Science & Technology Project Foundation (2018RS3065, 2018TP1018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Dai, J. A Fuzzy Decision-Theoretic Rough Set Approach for Type-2 Fuzzy Conditional Information Systems and Its Application in Decision-Making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 622–634 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01167-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01167-x