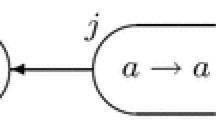Abstract
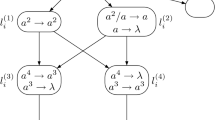
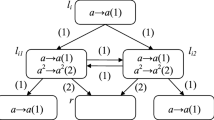
By abstracting the structure and function of nervous systems and neurons, spiking neural P systems (SN P systems) were first proposed in 2006. Many variants of such systems have been discussed and investigated by introducing some biological and mathematical considerations into SN P systems. For the purpose of proposing small universal systems with as few as possible neurons, we present a new class of SN P systems, improved SN P systems with multiple channels and autapses (ISNP-MCA systems). ISNP-MCA systems combine some interesting discoveries in biology, multiple ion channels in synapses and the special synapses that connect the axon of a neuron onto itself (autapses). In the ISNP-MCA systems, multiple channels are used to ensure the spikes transmitted to the correct neurons, and the autapses could drive the neurons to perform self-excitation. Additionally, for saving neurons, the number of spikes is used to represent different instruction labels. We build an ISNP-MCA system which is proved universal in computing functions, with only nine neurons, eight of them representing eight registers and the other one used for inputting spikes. Additionally, a small universal ISNP-MCA system is proposed to generate numbers, also requiring nine neurons.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artiom, A., Rudolf, F., Sergiu, I., Marion, O., & Sergey V. (2015). Extended spiking neural P systems with white hole rules. Research Group on Natural Computing. Brainstorming Week on Membrane Computing, Sevilla, pp. 46–62.
Bîlbîe, F. D., & Păun, A. (2020). Small SNQ P systems with multiple types of spikes. Theoretical Computer Science, 862, 14–23.
Cabarle, F., Adorna, H., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. (2016). Sequential spiking neural P systems with structural plasticity based on max/min spike number. Neural Computing and Applications, 27(5), 1337–1347.
Cabarle, F., Cruz, R., Cailipan, D., Zhang, D., Liu, X., & Zeng, X. (2019). On solutions and representations of spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses. Information Sciences, 501, 30–49.
Cavaliere, M., Egecioglu, O., Ibarra, O.H., Ionescu, M., Păun, G., & Woodworth, S. (2008). Asynchronous spiking neural P systems: Decidability and undecidability. In: M. H. Garzon, et al. (Eds.), 13th international meeting on DNA computing, DNA 13, 2007, Memphis, USA, in: Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 4848, Springer, pp. 246–255.
Díaz-Pernil, D., Christinal, H., & Gutiérrez-Naranjo, M. (2018). Solving the 3-COL problem by using tissue P systems without environment and proteins on cells. Information Sciences, 430–431, 240–246.
Dong, W., Zhou, K., Qi, H., He, C., & Zhang, J. (2018). A tissue P system based evolutionary algorithm for multi-objective VRPTW. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 39, 310–322.
Garcia, L., Sanchez, G., Vazquez, E., Avalos, G., & Perez, H. (2021). Small universal spiking neural P systems with dendritic/axonal delays and dendritic trunk/feedback. Neural Networks, 138, 126–139.
Guo, P., Quan, C., & Ye, L. (2019). UPSimulator: A general P system simulator. Knowledge-Based Systems, 170, 20–25.
Ibarra, O., Păun, A., & Rodríguez-Patón, A. (2009). Sequential SNP systems based on min/max spike number. Theoretical Computer Science, 410(30–32), 2982–2991.
Ionescu, M., Păun, G., & Yokomori, T. (2006). Spiking neural P systems. Fundamenta Informaticae, 71(2), 279–308.
Korec, I. (1996). Small universal register machines. Theoretical Computer Science, 168(2), 267–301.
Macababayao, I. C. H., Cabarle, F. G. C., de la Cruz, R. T. A., & Zeng, X. (2022). Normal forms for spiking neural P systems and some of its variants. Information Sciences, 595, 344–363.
Macías-Ramos, L., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. (2012). Spiking neural P systems with functional astrocytes. In: Proceeding of the 13th International Conference on Membrane Computing, CMC 2012, Budapest (pp. 228–242).
Minsky, M. (1967). Computation: Finite and Infinite Machines. Prentice Hall.
Neary, T. (2008). Three small universal spiking neural P systems. Theoretical Computer Science, 567, 2–20.
Pan, L., Zeng, X., Zhang, X., & Jiang, Y. (2012). Spiking neural P systems with weighted synapses. Neural Processing Letters, 35(1), 13–27.
Pan, L., & Zeng, X. (2009). A note on small universal spiking neural P systems. Springer.
Pan, L., & Păun, G. (2009). Spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. International Journal of Computers, Communications & Control, 4(3), 273–282.
Pan, L., Păun, G., Zhang, G., & Neri, F. (2017). Spiking neural P systems with communication on request. International Journal of Neural Systems, 27(8), 1750042.
Pan, L., Zeng, X., & Zhang, X. (2010). Small universal asynchronous spiking neural P systems. In: 5th International conference on bio-inspired computing: theories and applications, BIC-TA, Changsha (pp. 622–630).
Păun, A., & Păun, G. (2007). Small universal spiking neural P systems. Bio Systems, 90(1), 48–60.
Păun, G. (2007). Spiking neural P systems with astrocyte-like control. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 13(11), 1707–1721.
Păun, G. (2018). A dozen of research topics in membrane computing. Theoretical Computer Science, 736, 76–78.
Peng, H., Wang, J., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., Wang, H., Shao, J., & Wang, T. (2013). Fuzzy reasoning spiking neural P system for fault diagnosis. Information Sciences, 235, 106–116.
Peng, H., Yang, J., Wang, J., Wang, T., Sun, Z., Song, X., Lou, X., & Huang, X. (2017). Spiking neural P systems with multiple channels. Neural Network, 95, 66–71.
Peng, H., Wang, J., Shi, P., Pérez-Jiménez, M., & Riscos-Núñez, A. (2017). Fault diagnosis of power systems using fuzzy tissue-like P systems. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 24(4), 401–411.
Peng, H., Wang, J., Ming, J., Shi, P., Pérez-Jiménez, M., Yu, W., & Tao, C. (2018). Fault diagnosis of power systems using intuitionistic fuzzy spiking neural P systems. IEEE Transaction on Smart Grid, 9(5), 4777–4784.
Peng, H., Wang, J., Pérez-Jiménez, M., & Riscos-Núñez, A. (2019). Dynamic threshold neural P systems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 163, 875–884.
Singh, G., & Deep, K. (2016). A new membrane algorithm using the rules of particle swarm optimization incorporated within the framework of cell-like P-systems to solve Sudoku. Applied Soft Computing, 45, 27–39.
Song, B., Zhang, C., & Pan, L. (2017). Tissue-like P systems with evolutional symport/antiport rules. Information Sciences, 378, 177–193.
Song, T., Pan, L., & Păun, G. (2013). Asynchronous spiking neural P systems with local synchronization. Information Sciences, 219, 197–207.
Song, T., Jiang, Y., Shi, X., & Zeng, X. (2013). Small universal spiking neural P systems with anti-Spikes. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 10(4), 999–1006.
Song, T., Pan, L., & Păun, G. (2014). Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses. Theoretical Computer Science, 529, 82–95.
Song, T., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., & Chen, Z. (2014). Homogenous spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. Neural Computing and Applications, 24(7–8), 1833–1841.
Song, T., Gong, F., Liu, X., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, X. (2016). Spiking neural P systems with white hole neurons. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 15(7), 666–673.
Song, T., & Pan, L. (2016). Spiking neural P systems with request rules. Neurocomputing, 193, 193–200.
Song, T., Pan, L., Wu, T., Zheng, P., Wong, M. D., & Rodríguez-Patón, A. (2019). Spiking neural P systems with learning functions. IEEE transactions on nanobioscience, 18(2), 176–190.
Song, X., Peng, H., Wang, J., Ning, G., Wang, T., Sun, Z., & Xia, Y. (2018). On small universality of spiking neural P systems with multiple channels. In: International Conference on Membrane Computing, CMC 2018, Dresden (pp. 229–245).
Song, X., Peng, H., Wang, J., Ning, G., Wang, T., Sun, Z., & Yang, F. (2018). Spiking neural P system with multiple channels and anti-spikes. Bio Systems, 169–170, 13–19.
Song, X., Peng, H., Wang, J., Ning, G., & Sun, Z. (2020). Small universal asynchronous spiking neural P systems with multiple channels. Neurocomputing, 378, 1–8.
Song, X., Valencia-Cabrera, L., Peng, H., Wang, J., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2021). Spiking neural P systems with delay on synapses. International Journal of Neural Systems, 31(1), 2050042.
Song, X., Valencia-Cabrera, L., Peng, H., & Wang, J. (2021). Spiking neural P systems with autapses. Information Sciences, 570, 383–402.
Verlan, S., Freund, R., Alhazov, A., Ivanov, S., & Pan, L. (2020). A formal framework for spiking neural P systems. Journal of Membrane Computing, 2(4), 355–368.
Wang, J., Shi, P., Peng, H., Pérez-Jiménez, M., & Wang, T. (2013). Weighted fuzzy spiking neural P systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 21(2), 209–220.
Wang, T., Zhang, G., Zhao, J., He, Z., Wang, J., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. (2015). Fault diagnosis of electric power systems based on fuzzy reasoning spiking neural P systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 30(3), 1182–1194.
Wu, T., Zhang, Z., Păun, G., & Pan, L. (2016). Cell-like spiking neural P systems. Theoretical Computer Science, 623, 180–189.
Wu, T., Pan, L., Yu, Q., & Tan, K. C. (2020). Numerical spiking neural P systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 32(6), 2443–2457.
Yuan, Y., Jiang, K., Chen, Z., & Xu, J. (2014). Small universal spiking neural P systems with astrocytes. Romanian Journal of Information Science and Technology, 17(1), 19–32.
Zeng, X., Xu, L., Liu, X., & Pan, L. (2014). On languages generated by spiking neural P systems with weights. Information Sciences, 278, 423–433.
Zeng, X., Zhang, X., Song, T., & Pan, L. (2014). Spiking neural P systems with thresholds. Neural Computation, 26(7), 1340–1361.
Zeng, X., Pan, L., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2014). Small universal simple spiking neural P systems with weights. Science Chine Information Sciences, 57(9), 1–11.
Zhang, G., Rong, H., Neri, F., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2014). An optimization spiking neural P system for approximately solving combinatorial optimization problems. International Journal of Neural Systems, 24(5), 1440006.
Zhang, X., Zeng, X., & Pan, L. (2008). Smaller universal spiking neural P systems. Fundamenta Informaticae, 87(1), 117–136.
Zhang, X., Zeng, Z., & Pan, L. (2014). Weighted spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses. Fundamenta Informaticae, 134(1–2), 201–218.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 2022YFG0327), Chunhui Project Foundation of the Education Department of China (No. Z2017082). The work of Luis Valencia-Cabrera was supported by FEDER/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación – Agencia Estatal de Investigación/Proyecto (TIN2017-89842-P)—MABICAP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We would like to submit the enclosed manuscript entitled “Small Universal Improved Spiking Neural P Systems with Multiple Channels and Autapses”, which we wish to be considered for publication in “Journal of Membrane Computing”. No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, G., Valencia-Cabrera, L. & Song, X. Small universal improved spiking neural P systems with multiple channels and autapses. J Membr Comput 4, 153–165 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00100-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00100-x