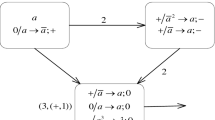
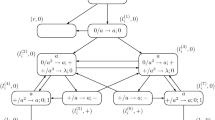
Abstract
To take full advantage of the information transfer mechanism of biological nervous systems, we consider a new computational model of spiking neural P systems with polarizations (PSN P systems). Compared to spiking neural P systems (SN P systems), PSN P systems use more simple formal language rules, and the behavioral changes of each neuron are jointly controlled by the number of spikes and the polarity state (\(+\), 0, − charge), making systems also have a powerful distributed parallel computing capability. Following the fact that SN P systems can operate as different modes, we consider the computation power of sequential PSN P systems in the accepting mode. In this work, we prove Turing universality of PSN P systems using the min-sequentiality and max-sequentiality strategies as number accepting devices by simulating the deterministic register machine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, T., Zhou, N., Lv, Z., Peng, H., & Wang, J. (2020). Sequential dynamic threshold neural P systems. Journal of Membrane Computing, 2(4), 255–268.
Bao, T., Zhou, N., Peng, H., Yang, Q., & Wang, J. (2021). Computational completeness of sequential spiking neural P systems with inhibitory rules. Information and Computation, 281, 104786.
Bibi, A., Xu, F., Adorna, H. N., & Cabarle, F. G. C. (2019). Sequential spiking neural P systems with local scheduled synapses without delay. Complexity, 2019, 2.
Cabarle, F. G. C., de la Cruz, R. T. A., Zhang, X., Jiang, M., Liu, X., & Zeng, X. (2018). On string languages generated by spiking neural P systems with structural plasticity. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 17(4), 560–566.
Chen, H., Freund, R., Ionescu, M., Păun, G., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2007). On string languages generated by spiking neural P systems. Fundamenta Informaticae, 75(1–4), 141–162.
de la Cruz, R. T. A., Cabarle, F. G., & Adorna, H. N. (2019). Generating context-free languages using spiking neural P systems with structural plasticity. Journal of Membrane Computing, 1(3), 161–177.
Díaz-Pernil, D., Gutiérrez-Naranjo, M. A., & Peng, H. (2019). Membrane computing and image processing: a short survey. Journal of Membrane Computing, 1(1), 58–73.
Díaz-Pernil, D., Peña-Cantillana, F., & Gutiérrez-Naranjo, M. A. (2013). A parallel algorithm for skeletonizing images by using spiking neural P systems. Neurocomputing, 115, 81–91.
Garcia, L., Sanchez, G., Vazquez, E., Avalos, G., Anides, E., Nakano, M., Sanchez, G., & Perez, H. (2021). Small universal spiking neural P systems with dendritic/axonal delays and dendritic trunk/feedback. Neural Networks, 138, 126–139.
Gerstner, W., & Kistler, W. M. (2002). Spiking Neuron Models. Single Neurons, Populations, Plasticity. Cambridge University Press.
Ibarra, O. H., Păun, A., & Rodríguez-Patón, A. (2009). Sequential SNP systems based on min/max spike number. Theoretical Computer Science, 410, 2982–2991.
Ionescu, M., Păun, G., Yokomori, T. (2006). Spiking neural P systems. Fundamenta Informaticae 71(2-3), 279–308
Ishdorj, T. O., Leporati, A., Pan, L., Zeng, X., & Zhang, X. (2010). Deterministic solutions to QSAT and Q3SAT by spiking neural P systems with pre-computed resources. Theoretical Computer Science, 411(25), 2345–2358.
Jiang, S., Fan, J., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., & Xu, F. (2020). Spiking neural P systems with polarizations and rules on synapses. Complexity, 2020(1), 1–12.
Leporati, A., Mauri, G., Zandron, C., Păun, G., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2009). Uniform solutions to SAT and Subset Sum by spiking neural P systems. Natural Computing, 8(4), 681–702.
Liu, L., & Jiang, K. (2022). Universality of spiking neural P systems with polarizations working in sequential mode induced by maximum spike number. Journal of Membrane Computing, 4(1), 56–67.
Maass, W. (1997). Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Networks, 10(9), 1659–1671.
Maass, W., & Bishop, C. M. (2001). Pulsed Neural Networks. MIT Press.
Neary, T. (2015). Three small universal spiking neural P systems. Theoretical Computer Science, 567, 2–20.
Pan, L., & Păun, G. (2009). Spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. International Journal of Computers, Communications & Control, 4(3), 273–282.
Pan, L., Păun, G., Zhang, G., & Neri, F. (2017). Spiking neural P systems with communication on request. International Journal of Neural Systems, 27(8), 1750042.
Pan, L., & Zeng, X. (2011). Small universal spiking neural P systems working in exhaustive mode. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 10(2), 99–105.
Pan, T., Shi, X., Zhang, Z., & Xu, F. (2018). A small universal spiking neural P system with communication on request. Neurocomputing, 275, 1622–1628.
Păun, A., & Păun, G. (2007). Small universal spiking neural P systems. BioSystems, 90(1), 48–60.
Păun, G. (2000). Computing with membranes. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 61(1), 108–143.
Păun, G. (2002). Membrane Computing: An Introduction. Springer-Verlag.
Păun, G. (2010). A quick introduction to membrane computing. The Journal of Logic and Algebraic Programming, 79(6), 291–294.
Păun, G., Rozenberg, G., & Salomaa, A. (2010). The Oxford Handbook of Membrane Computing. Oxford University Press.
Peng, H., Wang, J., Ming, J., Shi, P., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., Yu, W., & Tao, C. (2017). Fault diagnosis of power systems using intuitionistic fuzzy spiking neural P systems. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 9(5), 4777–4784.
Peng, H., Wang, J., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., Wang, H., Shao, J., & Wang, T. (2013). Fuzzy reasoning spiking neural P systems for fault diagnosis. Information Sciences, 235, 106–116.
Rodríguez-Chavarría, D., Gutiérrez-Naranjo, M. A., & Borrego-Díaz, J. (2020). Logic negation with spiking neural P systems. Neural Processing Letters, 52(2), 1583–1599.
Rong, H., Duan, Y., & Zhang, G. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of membrane computing (1998–2019). Journal of Membrane Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00098-2
Rong, H., Wu, T., Pan, L., & Zhang, G. (2018). Spiking neural P systems: Theoretical results and applications. In C. Graciani, A. Riscos-Núñez, G. Păun, G. Rozenberg, & A. Salomaa (Eds.), Enjoying Natural Computing (Vol. 11270, pp. 256–268). Springer.
Rong, H., Yi, K., Zhang, G., Dong, J., Paul, P., & Huang, Z. (2019). Automatic implementation of fuzzy reasoning spiking neural P systems for diagnosing faults in complex power systems. Complexity, 2019(1), 1–16.
Song, T., Pan, L., & Păun, G. (2013). Asynchronous spiking neural P systems with local synchronization. Information Sciences, 219, 197–207.
Song, T., Pan, L., Wu, T., Zheng, P., Wong, M. D., & Rodríguez-Patón, A. (2019). Spiking neural P systems with learning functions. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 18(2), 176–190.
Song, T., Pang, S., Hao, S., Rodríguez-Patón, A., & Zheng, P. (2019). A parallel image skeletonizing method using spiking neural P systems with weights. Neural Processing Letters, 50(2), 1485–1502.
Song, T., Zheng, P., Wong, M. D., & Wang, X. (2016). Design of logic gates using spiking neural P systems with homogeneous neurons and astrocytes-like control. Information Sciences, 372, 380–391.
Song, X., Valencia-Cabrera, L., Peng, H., Wang, J., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2020). Spiking neural P systems with delay on synapses. International Journal of Neural Systems, 31(1), 2050042.
Vreeken, J. (2003). Spiking neural networks, an introduction. Utrecht University.
Wang, H., Zhou, K., & Zhang, G. (2018). Arithmetic operations with spiking neural P systems with rules and weights on synapses. International Journal of Computers Communications and Control, 13(4), 574–589.
Wang, J., Peng, H., Yu, W., Ming, J., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., Tao, C., & Huang, X. (2019). Interval-valued fuzzy spiking neural P systems for fault diagnosis of power transmission networks. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 82, 102–109.
Wang, T., Zhang, G., Zhao, J., He, Z., Wang, J., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2014). Fault diagnosis of electric power systems based on fuzzy reasoning spiking neural P systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 30(3), 1182–1194.
Wu, T., & Pan, L. (2020). The computation power of spiking neural P systems with polarizations adopting sequential mode induced by minimum spike number. Neurocomputing, 401, 392–404.
Wu, T., Pan, L., & Alhazov, A. (2019). Computation power of asynchronous spiking neural P systems with polarizations. Theoretical Computer Science, 777, 474–489.
Wu, T., Păun, A., Zhang, Z., & Pan, L. (2018). Spiking neural P systems with polarizations. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29(8), 3349–3360.
Wu, T., Zhang, L., Lyu, Q., & Jin, Y. (2022). Asynchronous spiking neural P systems with local synchronization of rules. Information Sciences, 588, 1–12.
Wu, T., Zhang, T., & Xu, F. (2020). Simplified and yet turing universal spiking neural P systems with polarizations optimized by anti-spikes. Neurocomputing, 414, 255–266.
Zeng, X., Xu, L., Liu, X., & Pan, L. (2014). On languages generated by spiking neural P systems with weights. Information Sciences, 278, 423–433.
Zhang, G., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., & Gheorghe, M. (2017). Real-life Applications with Membrane Computing. Springer.
Zhang, G., Rong, H., Neri, F., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2014). An optimization spiking neural P system for approximately solving combinatorial optimization problems. International Journal of Neural Systems, 24(5), 1440006.
Zhang, G., Rong, H., Paul, P., He, Y., Neri, F., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2021). A complete arithmetic calculator constructed from spiking neural P systems and its application to information fusion. International Journal of Neural Systems, 31(1), 2050055.
Zhang, X., Zeng, X., & Pan, L. (2008). Smaller universal spiking neural P systems. Fundamenta Informaticae, 87(1), 117–136.
Zhang, X., Zeng, X., & Pan, L. (2009). On languages generated by asynchronous spiking neural P systems. Theoretical Computer Science, 410(26), 2478–2488.
Zhao, J., & Wang, N. (2011). A bio-inspired algorithm based on membrane computing and its application to gasoline blending scheduling. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 35(2), 272–283.
Zhao, Y., Liu, X., & Wang, W. (2016). Spiking neural P systems with neuron division and dissolution. Plos One, 11(9), 0162882.
Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, X., & Sun, M. (2022). Qi: Self adapting spiking neural P systems with refractory period and propagation delay. Information Sciences, 589(12), 80–93.
Zhu, M., Yang, Q., Dong, J., Zhang, G., Gou, X., Rong, H., et al. (2021). An adaptive optimization spiking neural P system for binary problems. International Journal of Neural Systems, 31(1), 2050054.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 1808085MF173), Natural Science Foundation of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province of China (No. KJ2021A0640).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this paper was presented at the 16th International Conference on Bio-inspired Computing: Theories and Applications (BIC-TA 2021), December 2021. This paper was recommended for publication in revised form by the BIC-TA 2021 conference committees.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Jiang, K. Turing universality of sequential spiking neural P systems with polarizations as number accepting devices. J Membr Comput 4, 232–242 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00107-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00107-4