Article contents
CoreALMlib: An  $\mathscr{ALM}$ library translated from the Component Library
$\mathscr{ALM}$ library translated from the Component Library
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 October 2016
Abstract
This paper presents CoreALMlib, an 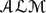 $\mathscr{ALM}$ library of commonsense knowledge about dynamic domains. The library was obtained by translating part of the Component Library (CLib) into the modular action language
$\mathscr{ALM}$ library of commonsense knowledge about dynamic domains. The library was obtained by translating part of the Component Library (CLib) into the modular action language 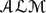 $\mathscr{ALM}$. CLib consists of general reusable and composable commonsense concepts, selected based on a thorough study of ontological and lexical resources. Our translation targets CLibstates (i.e., fluents) and actions. The resulting
$\mathscr{ALM}$. CLib consists of general reusable and composable commonsense concepts, selected based on a thorough study of ontological and lexical resources. Our translation targets CLibstates (i.e., fluents) and actions. The resulting 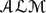 $\mathscr{ALM}$ library contains the descriptions of 123 action classes grouped into 43 reusable modules that are organized into a hierarchy. It is made available online and of interest to researchers in the action language, answer-set programming, and natural language understanding communities. We believe that our translation has two main advantages over its CLib counterpart: (i) it specifies axioms about actions in a more elaboration tolerant and readable way, and (ii) it can be seamlessly integrated with ASP reasoning algorithms (e.g., for planning and postdiction). In contrast, axioms are described in CLib using STRIPS-like operators, and CLib's inference engine cannot handle planning nor postdiction.
$\mathscr{ALM}$ library contains the descriptions of 123 action classes grouped into 43 reusable modules that are organized into a hierarchy. It is made available online and of interest to researchers in the action language, answer-set programming, and natural language understanding communities. We believe that our translation has two main advantages over its CLib counterpart: (i) it specifies axioms about actions in a more elaboration tolerant and readable way, and (ii) it can be seamlessly integrated with ASP reasoning algorithms (e.g., for planning and postdiction). In contrast, axioms are described in CLib using STRIPS-like operators, and CLib's inference engine cannot handle planning nor postdiction.
- Type
- Regular Papers
- Information
- Theory and Practice of Logic Programming , Volume 16 , Special Issue 5-6: 32nd International Conference on Logic Programming , September 2016 , pp. 800 - 816
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2016
References
- 5
- Cited by




