Article contents
Limit laws for large 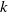 $k$th-nearest neighbor balls
$k$th-nearest neighbor balls
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 July 2022
Abstract
Let 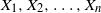 $X_1,X_2, \ldots, X_n$
be a sequence of independent random points in
$X_1,X_2, \ldots, X_n$
be a sequence of independent random points in 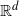 $\mathbb{R}^d$
with common Lebesgue density f. Under some conditions on f, we obtain a Poisson limit theorem, as
$\mathbb{R}^d$
with common Lebesgue density f. Under some conditions on f, we obtain a Poisson limit theorem, as 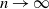 $n \to \infty$
, for the number of large probability kth-nearest neighbor balls of
$n \to \infty$
, for the number of large probability kth-nearest neighbor balls of 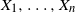 $X_1,\ldots, X_n$
. Our result generalizes Theorem 2.2 of [11], which refers to the special case
$X_1,\ldots, X_n$
. Our result generalizes Theorem 2.2 of [11], which refers to the special case 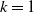 $k=1$
. Our proof is completely different since it employs the Chen–Stein method instead of the method of moments. Moreover, we obtain a rate of convergence for the Poisson approximation.
$k=1$
. Our proof is completely different since it employs the Chen–Stein method instead of the method of moments. Moreover, we obtain a rate of convergence for the Poisson approximation.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Applied Probability Trust
References
- 4
- Cited by





