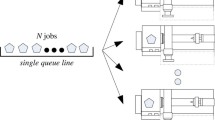
Abstract
A model for scheduling grouped jobs on identical parallel machines is addressed in this paper. The model assumes that a set-up time is incurred when a machine changes from processing one type of component to a different type of component, and the objective is to minimize the total earliness-tardiness penalties. In this paper, the algorithm of soft computing, which is a fuzzy logic embedded Genetic Algorithm is developed to solve the problem. The efficiency of this approach is tested on several groups of random problems and shows that the soft computing algorithm has potential for practical applications in larger scale production systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, K. R. and Scudder, G. (1987) Sequencing with earliness and tardiness penalties: A review. Operations Research, 38, 26-36.
Chan, K. C. and Tansri, H. (1994) A study of genetic crossover operations on the facilities layout problem. Computers and Industry Engineering, 26, 537-550.
Chen, Z. (1997) Scheduling with batch setup times and earliness-tardiness penalties. European Journal of Operational Research, 3, 518-537.
Chen, A. (1996) Scheduling and common due date assignment with earliness-tardiness penalties and batch delivery costs. European Journal of Operation Research, 93, 49-60.
Cheng, T. C. E. and Gupta, M. C. (1989) Survey of scheduling research involving due date determination decisions. European Journal of Operational Research, 38, 156-166.
Cheng, E. and Chen, Z. L. (1994) Parallel machine scheduling with earliness and tardiness penalties. Journal of Operational Research Society, 45, 685-695.
Croce, F. D., Tadei, R. and Volta, G. (1995) A genetic algorithm for job shop problem. Computers and Operations Research, 22, 15-24.
Davis, J. S. and Kanet, J. J. (1993) Single-machine scheduling with early tardy completion costs. Naval Research Logistics, 40, 85-101.
Federgruen, A. and Mosheiov, G. (1993) Simultaneous optimization of efficiency and performance balance measures in single-machine scheduling problems. Naval Research Logistics, 40, 951-970.
Hall, N. and Poster, M. (1991) Earliness-tardiness scheduling problems, I: Weighted deviation of completion times about a common duedate. Operations Research, 39, 836-846.
Hall, N. G., Kubiak, W. and Sethi, S. P. (1991) Earliness-tardiness scheduling problems, II: Deviation of completion times about a restrictive common due date. Operations Research, 39, 847-856.
Herman, J. and Lee, C. (1993) On scheduling to minimize earliness-tardiness and batch delivery costs with a common due date. Operational Research, 70, 272-288.
Hyer, N. I. and Wemmerlov, U. (1989) Group technology in the US manufacturing industry: A survey of current practices. International Journal of Production Research, 27, 1287-1304.
Isermann, R. (1998) On fuzzy logic applications for automatic control, supervision, and fault diagnosis. IEEE Transaction, on SMC Part A: Systems and Human, 28, 221-235.
Kanet, J. (1981) Minimizing the average diviation of job completion times about a common due date. Naval Research Logistics, 3, 76-91.
Lee, C., Danusaputro, S. and Lin, C. (1991) Minimizing weighted number of tardy jobs and weighted earliness-tardiness penalties about a common due date. Computers and Operations Research, 18, 379-389.
Li, C. and Cheng, T. (1994) The parallel machine min-max weighted absolute lateness scheduling problem. Noval Res. Log. Qua, 41, 33-36.
Liman, S. and Lee, C. (1993) Error bound of a heuristic for the common due date scheduling problem. ORSA Journal on Computing, 5, 420-425.
Monma, C. L. and Potts, C. N. (1989) On the complexity of scheduling with batch setup times. Operations Research, 37, 798-804.
Olsen, T. L. (1999) A practical scheduling method for multiclass production systems with setups. Management Science, 45, 116-130.
Panwalkar, S. S. and Iskander, W. (1992) A survey of scheduling rules. Operations Research, 25, 45-61.
Potts, C. N. and Wassenhove, L. V. (1992) Integrating scheduling with batch and lot-sizing: A review of algorithms and complexity. Journal of Operations Research Society, 43, 395-406.
Psaraftis, H. N. (1980) A dynamic programming approach for sequencing groups of identical jobs. Operations Research, 28, 1347-1359.
Sung, C. and Joo, U. (1992) A single machine scheduling problem with earliness-tardiness and starting time penalties under a common due date. Computer and Operations Research, 19, 757-766.
Wang, D. W., Fang, S. C. and Nuttle, H. L. (1999) Soft computing for multi-customer due-date bargaining. IEEE Transactions on SMC Part C: Application and Reviews, 29(4), 566-575.
Wang, D. W. (1999) Fuzzy rule quantification and its application in fuzzy due-date bargaining, Proceeding of IFSA Congress 1999, Taiwan, August.
Wang, D. W. (1999) Scheduling grouped jobs on single machine with genetic algorithm. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 36, 309-324.
Wang, D. W., Yung, K. L. and Ip, W. H. (2001) A heuristic genetic algorithm for subcontractor selection in a global manufacturing environment, IEEE Transactions on SMC Part C: Applications and Reviews, 31, 189-198.
Webster, S. and Baker, K. R. (1995) Scheduling groups of jobs on a single machine. Operations Research, 43, 692-703.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Y., Wang, D.W. Soft computing for scheduling with batch setup times and earliness-tardiness penalties on parallel machines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 14, 311–322 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024697625512
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024697625512