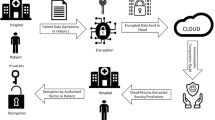
Abstract
Public-key cryptography is today recognized as an important tool in the provision of information security. This article gives an overview of the field on the occasion of its 22nd birthday.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ajtai and C. Dwork, A public-key cryptosystem with worst-case/average-case equivalence, In 29th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (1997) pp. 284–293.
M. Bellare and P. Rogaway, Random oracles are practical: a paradigm for designing efficient protocols, 1st ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (1993) pp. 62–73.
M. Bellare and P. Rogaway, Optimal asymmetric encryption, Advances in Cryptology: EUROCRYPT '94 (A. De Santis, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 950 (1995) pp. 92–111.
M. Bellare and P. Rogaway, The exact security of digital signatures-how to sign with RSA and Rabin, Advances in Cryptology: EUROCRYPT '96 (U. M. Maurer, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 1070 (1996) pp. 399–416.
D. Boneh, R. A. DeMillo, and R. J. Lipton, On the importance of checking cryptographic protocols for faults, Advances in Cryptology-EUROCRYPT '97 (W. Fumy, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 1233 (1997) pp. 37–51.
D. Boneh and R. Venkatesan, Breaking RSA may not be equivalent to factoring, Advances in Cryptology-EUROCRYPT '98 (K. Nyberg, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 1403 (1998) pp. 59–71.
J. Buchmann and H. Williams, A key-exchange system based on imaginary quadratic fields, Journal of Cryptology, Vol. 1 (1988) pp. 107–118.
D. Chaum, A. Fiat, and M. Naor, Untraceable electronic cash, Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO '88 (S. Goldwasser, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 403 (1990) pp. 319–327.
D. W. Price and W. L. Price, Security for Computer Networks, 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1989).
Y. Desmedt, Threshold cryptography, European Transactions on Telecommunications,Vol. 5 (1994) pp. 449–457.
W. Diffie and M. E. Hellman, New directions in cryptography, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol. IT-22, No. 6 (November 1976) pp. 644–654.
U. Feige, A. Fiat, and A. Shamir, Zero-knowledge proofs of identity, Journal of Cryptology, Vol. 1 (1988) pp. 77–94.
FIPS 186, Digital Signature Standard, Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 186, U. S. Department of Commerce/N. I. S. T., National Technical Information Service, Springfield, Virginia (1994).
M. R. Garey and D. S. Johnson, Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-completeness, W. H. Freeman, San Francisco (1979).
O. Goldreich, Foundations of Cryptography (Fragments of a Book) (1995). Available at http://theory.lcs.mit.edu/ oded/
S. Goldwasser and S. Micali, Probabilistic encryption, Journal of Computer and System Sciences, Vol. 28 (1984) pp. 270–299.
S. Goldwasser, S. Micali, and C. Rackoff, The knowledge complexity of interactive proof systems, SIAM Journal of Computing, Vol. 18 (1989) pp. 186–208.
M. E. Hellman and R. C. Merkle, Public key cryptographic apparatus and method, U. S. Patent # 4,218,582, 19 Aug 1980.
N. Koblitz, Elliptic curve cryptosystems, Mathematics of Computation, Vol. 48 (1987) pp. 203–209.
N. Koblitz, Hyperelliptic cryptosystems, Journal of Cryptology, Vol. 1 (1989) pp. 139–150.
N. Koblitz, A. J. Menezes, and S. A. Vanstone, The state of elliptic curve cryptography, In the current volume.
P. Kocher, Timing attacks on implementations of Diffie-Hellman, RSA, DSS, and other systems, Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO '96 ( N. Koblitz, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 1109 (1996) pp. 104–113.
A. K. Lenstra, Integer factoring, In the current volume.
C. H. Lim and P. J. Lee, A key recovery attack on discrete log-based schemes using a prime order subgroup, Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO'97 (B.S. Kaliski Jr., ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 1294 (1997) pp. 249–263.
U. M. Maurer and S. Wolf, The Diffie-Hellman protocol, In the current volume.
A. J. Menezes, M. Qu, and S. A. Vanstone, Key agreement and the need for authentication, Presentation at PKS '95, Toronto, Canada (November 1995).
A. J. Menezes, P. C. van Oorschot, and S. A. Vanstonen Handbook of Applied Cryptography, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida (1997).
S. Micali, Fair public-key cryptosystems, Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO '92 (E. F. Brickell, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 740 (1993) pp. 113–138.
V. Miller, Uses of elliptic curves in cryptography, Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO '85 (H. C.Williams, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 218 (1985) pp. 417–426.
A. M. Odlyzko, Discrete logarithms: the past and the future, In the current volume.
B. Preneel, Cryptographic Hash Functions, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston (to appear).
R. L. Rivest, A. Shamir, L. M. Adleman, A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems, Communications of the ACM, Vol. 21 (1978) pp. 120–126.
J. Rompel, One-way functions are necessary and sufficient for secure signatures. In 22nd ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (1990) pp. 387–394.
B. Schneier, Applied Cryptography: Protocols, Algorithms, and Source Code in C, 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1996).
V. Shoup, Lower bounds for discrete logarithms and related problems, Advances in Cryptology-EUROCRYPT '97 (W. Fumy, ed.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer-Verlag, 1233 (1997) pp. 256–266.
G. J. Simmons (editor), Contemporary Cryptology: The Science of Information Integrity, IEEE Press (1992).
D. R. Stinson, Cryptography: Theory and Practice, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blake-Wilson, S. Information Security, Mathematics, and Public-Key Cryptography. Designs, Codes and Cryptography 19, 77–99 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008345904539
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008345904539