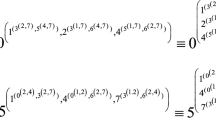Abstract
Zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (ZBDDs) have been introduced by Minato [14–17] who presents applications for cube set representations, fault simulation, timing analysis and the n-queens problem. Here the structural properties of ZBDDs are worked out and a generic synthesis algorithm is presented and analyzed. It is proved that ZBDDs can be at most by a factor n + 1 smaller or larger than ordered BDDs (OBDDs) for the same function on n variables. Using ZBDDs the best known upper bound on the number of knight's tours on an 8 × 8 chessboard is improved significantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.I. Bahar, E.A. Frohm, C.M. Gaona, G.D. Hachtel, E. Macii, A. Pardo, and F. Somenzi, “Algebraic decision diagrams and their applications,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer-Aided Design ICCAD, pp. 188–191, 1993.
B. Becker, R. Drechsler, and R. Werchner, “On the relation between BDDs and FDDs,” Information and Computation, Vol. 123, pp. 185–197, 1995.
K.S. Brace, R.L. Rudell, and R.E. Bryant, “Efficient implementation of a BDD package,” in Proc. 27. ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, pp. 40–45, 1990.
R.E. Bryant, “Graph-based algorithms for Boolean function manipulation,” IEEE Trans. on Computers, Vol. 35, pp. 677–691, 1986.
R.E. Bryant and Y.-A. Chen, “Verification of arithmetic functions with binary moment diagrams,” in Proc. Design Automation Conf. DAC, pp. 535–541, 1995.
A. Conrad, T. Hindrichs, H. Morsy, and I. Wegener, “Solution of the knight's Hamiltonian path problem on chessboards,” Discrete Applied Mathematics, Vol. 50, pp. 125–134, 1994.
J. Gergov and Ch Meinel, “Efficient analysis and manipulation of OBDDs can be extended to FBDDs,” IEEE Trans. on Computers, Vol. 43, pp. 1197–1209, 1994.
J. Jain, M. Abadir, J. Bitner, D.S. Fussell, and J.A. Abraham, “IBDDs: An efficient functional representation for digital circuits,” in Proc. European Design Automation Conference EDAC, pp. 440–446, 1992.
S.-W. Jeong, B. Plessier, G. Hachtel, and F. Somenzi, “Extended BDDs: Trading off canonicity for structure in verification algorithms,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer-Aided Design ICCAD, pp. 464–467, 1991.
U. Kebschull, E. Schubert, and W. Rosenstiel, “Multilevel logic synthesis based on functional decision diagrams,” in Proc. European Design Automation Conference EDAC, pp. 43–47, 1992.
O. Kyek, I. Parberry, and I. Wegener, “Bounds on the number of knight's tours,” Discrete Applied Mathematics, Vol. 74, pp. 171–181, 1997.
Y.-T. Lai and S. Sastry, “Edge-valued binary decision diagrams for multi-level hierachical verification,” in Proc. 29. Design Automation Conf., pp. 608–613, 1992.
H.-T. Liaw and C.-S. Lin, “On the OBDD representation of general Boolean functions,” IEEE Trans. on Computers, Vol. 41, pp. 661–664, 1992.
S. Minato, “Fast generation of irredundant sum-of-products forms from binary decision diagrams,” in Proc. Synthesis and System Integration of Mixed Technologies SASIMI, pp. 64–73, 1992.
S. Minato, “Fast weak-division method for implicit cube representation,” in Proc. Synthesis and System Integration of Mixed Technologies SASIMI, pp. 423–432, 1993.
S. Minato, “Zero-suppressed BDDs for set manipulation in combinatorial problems,” in Proc. 30. Design Automation Conference, pp. 272–277, 1993.
S. Minato, “Calculation of unate cube set algebra using zero-suppressed BDDs,” in Proc. 31. Design Automation Conference, pp. 420–424, 1994.
S. Minato, N. Ishiura, and S. Yajima, “Shared binary decision diagrams with attributed edges for efficient Boolean function manipulation,” in Proc. 27. Design Automation Conference, pp. 52–57, 1990.
D. Sieling and I. Wegener, “Reduction of OBDDs in linear time,” Information Processing Letters, Vol. 48, pp. 139–144, 1993.
D. Sieling and I. Wegener, “Graph driven BDDs—A new data structure for Boolean functions,” Theoretical Computer Science, Vol. 141, pp. 283–310, 1995.
I. Wegener, “The size of reduced OBDDs and optimal read-once branching programs for almost all Boolean functions,” IEEE Trans. on Computers, Vol. 43, No. 11, pp. 1262–1269, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröer, O., Wegener, I. The Theory of Zero-Suppressed BDDs and the Number of Knight's Tours. Formal Methods in System Design 13, 235–253 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008681625346
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008681625346