Abstract
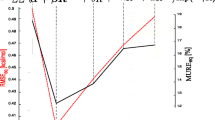
A method (FILO, Field Interaction Ligand Optimization) for obtaining the optimal molecular interaction field was developed on the basis of the Simplex optimization procedure applied to a matrix of interaction energies obtained by performing a GRID computation on a suitable data set. The FILO procedure was tested on a set of nine HIV-1 protease inhibitors with known crystal structures. The results of FILO consist of the optimal molecular interaction field of a putative new ligand with optimal binding affinity. The final FILO model yields R 2 and R 2 CV values of 0.993 and 0.936, respectively, and finds eight negative and four positive interaction nodes for the OH probe taken as an example. The eight H bonding interactions pointed out by FILO identified well the binding site AA-residues Gly A27, Asp A29, water 501, Gly B48 and Asp A25 of HIV-1 protease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cramer III, R.D., Patterson, D.E and Bunce, J.D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110 (1988) 5959.
Goodford, P.J., J. Med. Chem., 28 (1985) 849.
Snyder, J.P. and Rao, S.N., Chem. Design Autom. News, 4 (1989) 13.
Snyder, J.P. and Rao, S.N., Crai Channels, 11 (1990) 12.
Snyder, J.P., Rao, S.N., Kohler, K.F. and Pellicciari, R., In Angeli, P., Gulini, U. and Quaglia, W. (Eds.) Trends in Receptor Research, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1992, pp. 367-403.
Snyder, J.P., Rao, S.N., Kohler, K.F. and Vedani, A., In Kubinyi, H. (Ed.) 3D-QSAR in Drug Design: Theory, Method and Applications, ESCOM, Leiden, 1993, pp. 336-354.
Momany, F., Pitha, R., Klimkowsky, V.J. and Venkatachalam, C.M., In Hohne, B.A. and Pierce, T.H. (Eds.) Expert Systems and Applications in Chemistry, ACS Symp. Ser. 408, 1989, p. 82.
Walters, D.E. and Hints, R.M., J. Med. Chem., 37 (1994) 2527.
Doweyko, A.M., J. Med. Chem., 37 (1994) 1769.
Hahn, M. and Rogers, D., J. Med. Chem., 38 (1995) 2091.
Hahn, M., J. Med. Chem., 38 (1995) 2080.
Vedani, A., Zbinden, P. and Snyder, J.P., J. Receptor Res., 13 (1993) 163.
Vedani, A., Zbinden, P., Snyder, J.P. and Greenidge, P.A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117 (1995) 4987.
Zbinden, P., Dobler, M., Folkers, G. and Vedani, A., Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat., 17 (1998) 122.
Lucasius, C.B. and Kateman, G., Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst., 25 (1994) 99.
Baroni, M., Costantino, G., Cruciani, G., Riganelli, D., Valigi, R. and Clementi, S., Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat., 12 (1993) 9.
Pastor, M., Cruciani, G. and Clementi, S., J. Med. Chem., 40 (1997) 1455.
InsightII 97.0, Molecular Simulations, San Diego, CA, USA.
SYBYL-Molecular Modeling Software, 6.4, Tripos Incorporated, St. Louis, MO, USA.
GRID v. 16, Molecular Discovery Ltd., University of Oxford, England, SGI.
Nelder, J.A. and Mead, R., Comput. J., 7 (1965) 308.
Spendeley, W., Hext, G.R. and Himsworth, F.R., Technometrics, 4 (1962) 441.
Bernstein, F.C., Koetzle, T.F., Williams, G.J.B., Meyer, E.F. Jr., Brice, M.D., Rodgers, J.R., Kennard, O., Shimanouchi, T. and Tasumi, M., J. Mol. Biol., 112 (1977) 535.
Dreyer, G.B., Lambert, D.M., Meek, T.D., Carr, T.J., Tomaszek, T.A., Jr., Fernandez, A.V., Bartus, H., Caccivillani, E., Hassell, A.M., Minnich, M., Petteway, S.R., Jr. and Metcalf, B.W., Biochemistry, 31 (1992) 6646.
Hoog, S.S., Zhao, B., Winborne, E., Fisher, S., Green, D.W., DesJarlais, R.L., Newlander, K.A., Callahan, J.F., Moore, M.L., Huffam, W.F. and Abdel-Meguid, S.S., J. Med. Chem., 38 (1995) 3246.
Abdel-Meguid, S.S., Zhao, B., Murthy, K.H.M., Winborne, E., Choi, J., DesJarlais, R.L., Minnich, M.D., Culp, J.S., Debouck, C., Tomaszek, T.A., Jr., Meek, T.D. and Dreyer, G.B., Biochemistry, 32 (1993) 7972.
Kim, E.E., Baker, C.T., Dwyer, M.D., Murcko, M.A., Rao, B.G., Tung, R.D. and Navia, M.A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117 (1995) 1181.
Jhoti, H., Singh, O.M.P., Weir, M.P., Cooke, R., Murray-Rust, P. and Wonacott, A., Biochemistry, 33 (1994) 8417.
Hosur, M.V., Bhat, N., Kempf, D.J., Baldwin, E.T., Liu, B., Gulnik, S., Wideburg, N.E., Norbeck, D.W., Appelt, K. and Erickson, J.W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 116 (1994) 847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melani, F., Gratteri, P., Adamo, M. et al. FILO (Field Interaction Ligand Optimization): A simplex strategy for searching the optimal ligand interaction field in drug design. J Comput Aided Mol Des 15, 57–66 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011178027463
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011178027463