Abstract
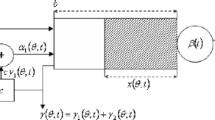
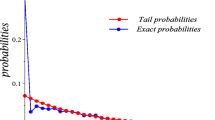
We analyse the deviant behavior of a queue fed by a large number of traffic streams. In particular, we explicitly give the most likely trajectory (or ‘optimal path’) to buffer overflow, by applying large deviations techniques. This is done for a broad class of sources, consisting of Markov fluid sources and periodic sources. Apart from a number of ramifications of this result, we present guidelines for the numerical evaluation of the optimal path.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Anick, D. Mitra and M. Sondhi, Stochastic theory of a data-handling system with multiple sources, Bell System Technic. J. 61 (1982) 1871–1894.
D. Botvich and N. Duffield, Large deviations, the shape of the loss curve, and economies of scale in large multiplexers, Queueing Systems 20 (1995) 293–320.
A. Brandt and M. Brandt, On the distribution of the number of packets in the fluid flow approximation of packet arrival streams, Queueing Systems 17 (1994) 275–315.
C. Courcoubetis and R. Weber, Buffer overflow asymptotics for a buffer handling many traffic sources, J. Appl. Probab. 33 (1996) 886–903.
C. Courcoubetis and R. Weber, Private communication (1997).
A. Dembo and O. Zeitouni, Large Deviations Techniques and Applications (Jones and Bartlett, Boston, 1993).
R. Ellis, Entropy, Large Deviations, and Statistical Mechanics (Springer, New York, 1985).
A. Elwalid, D. Mitra and R. Wentworth, A new approach for allocating buffers and bandwidth to heterogeneous regulated traffic in ATM node, IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 15 (1995) 1115–1127.
J. Garcia, J. Barceló and O. Casals, An exact model for the multiplexing of worst case traffic sources, in: Proc.of the 6th Internat.Conf.on Data Communication Systems and their Performance (1995).
I. Gelfand and S. Fomin, Calculus of Variations (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1963).
R. Gibbens and F. Kelly, Measurement-based connection admission control, in: Proc.of the 15th Internat.Teletraffic Congress, eds. V. Ramaswami and P. Wirth (1997) pp. 879–888.
F. Kelly, Charging and accounting for bursty connections, in: Internet Economics, eds. L. McKnight and J. Bailey (1996).
F. Kelly, Notes on effective bandwidths, in: Stochastic Networks: Theory and Applications, eds. F. Kelly, S. Zachary and I. Ziedins (1996).
G. Kesidis, J. Walrand and C.S. Chang, Effective bandwidths for multiclass Markov fluids and other ATM sources, IEEE/ACM Trans. Network. 1 (1993) 424–428.
L. Kosten, Stochastic theory of data-handling systems with groups of multiple sources, in: Performance of Computer-Communication Systems, eds. H. Rudin and W. Bux (Elsevier Amsterdam, 1984) pp. 321–331.
K. Kvols and S. Blaabjerg, Bounds and approximations for the periodic on-off queues with application to ATM traffic control, in: Proc.of the IEEE Infocom (1992) pp. 487–494.
M. Mandjes, Overflow asymptotics for large communication systems with general Markov fluid sources, Probab. Engrg. Inform. Sci. 10 (1996) 501–518.
M. Mandjes and A. Ridder, Finding the conjugate of Markov fluid processes, Probab. Engrg. Inform. Sci. 9 (1995) 297–315.
J. Roberts, U. Mocci, J. Virtamo, eds., Broadband Network Teletraffic, Performance Evaluation and Design of Broadband Multiservice Networks, Final Report of Action COST 242, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 1155 (Springer, Heidelberg, 1996).
A. Shwartz and A. Weiss, Large Deviations for Performance Analysis, Queues, Communication, and Computing (Chapman and Hall, New York, 1995).
A. Simonian and J. Guibert, Large deviations approximation for fluid queues fed by a large number of on/off sources, IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 13 (1995) 1017–1027.
H. Tijms, Stochastic Models: An Algorithmic Approach (Wiley, New York, 1994).
A. Weiss, A new technique of analyzing large traffic systems, Adv. Appl. Probab. 18 (1986) 506–532.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandjes, M., Ridder, A. Optimal trajectory to overflow in a queue fed by a large number of sources. Queueing Systems 31, 137–170 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019154129708
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019154129708