Abstract
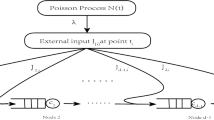
We consider a queueing network of d single server stations. Each station has a finite capacity waiting buffer, and all customers served at a station are homogeneous in terms of service requirements and routing. The routing is assumed to be deterministic and hence feedforward. A server stops working when the downstream buffer is full. We show that a properly normalized d-dimensional queue length process converges in distribution to a fd-dimensional semimartingale reflecting Brownian motion (RBM) in a d-dimensional box under a heavy traffic condition. The conventional continuous mapping approach does not apply here because the solution to our Skorohod problem may not be unique. Our proof relies heavily on a uniform oscillation result for solutions to a family of Skorohod problems. The oscillation result is proved in a general form that may be of independent interest. It has the potential to be used as an important ingredient in establishing heavy traffic limit theorems for general finite buffer networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Bardhan and S. Mithal, Heavy-traffic limits for an open network of finite-buffer overflow queues: The single class case, preprint (1993).
A. Bernard and A. El Kharroubi, Régulations déterministes et stochastiques dans le premier “orthant” de Rn, Stochastics Stochastics Rep. 34(1991) 149–167.
D. Bertsekas and R. Gallagher, Data Networks (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1992).
P. Billingsley, Convergence of Probability Measures (Wiley, New York, 1968).
M. Bramson, Convergence to equilibria for fluid models of FIFO queueing networks, Queueing Systems 22(1996) 5–45.
M. Bramson, Convergence to equilibria for fluid models of head-of-the-line proportional processor sharing queueing networks, Queueing Systems 23(1997) 1–26.
M. Bramson, State space collapse with application to heavy traffic limits for multiclass queueing networks, Queueing Systems 30(1998) 89–148.
A. Brondstred, An Introduction to Convex Polytopes (Springer, New York, 1983).
J.A. Buzacott, Automatic transfer lines with buffer stocks, Internat. J. Prod. Res. 5(1967) 183–200.
H. Chen and H. Zhang, Stability of multiclass queueing networks under FIFO service discipline, Math. Oper. Res. 22(1997) 691–725.
H. Chen and H. Zhang, Diffusion approximations for multiclass FIFO queueing networks, preprint.
D.W. Cheng, Second order properties in a tandem queue with general blocking, Oper. Res. Lett. 12 (1992) 139–144.
D. Cheng and D.D. Yao, Tandem queues with general blocking: A unified model and comparison results, Discrete Event Dyn. Systems 2(1993) 207–234.
K.L. Chung and J.R. Williams, Introduction to Stochastic Integration (Birkhäuser, Boston, 1983).
J.G. Dai and J.M. Harrison, Steady-state analysis of RBM in a rectangle: Numerical methods and a queueing application, Ann. Appl. Probab. 1(1991) 16–35.
J.G. Dai and T.G. Kurtz, A multiclass station with Markovian feedback in heavy traffic, Math. Oper. Res. 20(1995) 721–742.
J.G. Dai, G. Wang and Y. Wang, Nonuniqueness of the Skorohod problem arising from FIFO Kelly type network, private communication (1992).
J.G. Dai and R.J.Williams, Existence and uniqueness of semimartingale reflecting Brownian motions in convex polyhedrons, Theory Probab. Appl. 40(1995) 3–53.
W. Dai, Brownian approximations for queueing networks with finite buffers: modeling, heavy traffic analysis and numerical implementations, Ph.D. thesis, School of Mathematics, Georgia Institute of Technology (1996).
A.I. Elwalid and D. Mitra, Analysis and design of rate-based congestion control of high speed networks, I: Stochastic fluid models, access regulation, Queueing Systems 9(1991) 29–64.
S.N. Ethier and T.G. Kurtz, Markov Processes: Characterization and Convergence (Wiley, New York, 1986).
L.M. Graves, The Theory of Functions of Real Variables (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1956).
A. Gut, Stopped Random Walks: Limit Theorems and Applications (Springer, Berlin, 1988).
J.M. Harrison, Brownian models of queueing networks with heterogeneous customer populations, in: Proc.of the IMA Workshop on Stochastic Differential Systems (Springer, Berlin, 1988).
D.L. Iglehart and W. Whitt, Multiple channel queues in heavy traffic I, Adv. in Appl. Probab. 2 (1970) 150–177.
D.L. Iglehart and W. Whitt, Multiple channel queues in heavy traffic II, Adv. in Appl. Probab. 2 (1970) 355–364.
D.P. Johnson, Diffusion approximations for optimal filtering of jump processes and for queueing networks, Ph.D. thesis, University of Wisconsin (1983).
T. Konstantopoulos and J. Walrand, On the ergodicity of networks of /GI/1/N queues, Adv. in Appl. Probab. 22(1990) 263–267.
H. Kroner, M. Eberspacher, T.H. Theimer, P.J. Kuhn and U. Briem, Approximate analysis of the end to end delay in ATM networks, in: Proc.of the IEEE INFOCOM’ 92, Florence, Italy (1992) pp. 978–986.
G. Last and A. Brandt, Marked Point Processes on the Real Line: The Dynamic Approach (Springer, New York, 1995).
D. Mitra and I. Mitrani, Analysis of a Kanban discipline for cell coordination in production lines: I, Managm. Sci.36(1990) 1458–1566.
H. Perros and T. Altiok, Queueing networks with blocking: A bibliography, Performance Evaluation Rev.: ACM Sigmetrics 12(1984) 8–12.
W.P. Peterson, A heavy traffic limit theorem for networks of queues with multiple customer types, Math. Oper. Res. 16(1991) 90–118.
M.I. Reiman, Open queueing networks in heavy traffic, Math. Oper. Res. 9(1984) 441–458.
M.I. Reiman, A multiclass feedback queue in heavy traffic, Adv. in Appl. Probab. 20(1988) 179–207.
M.I. Reiman and R.J. Williams, A boundary property of semimartingale reflecting Brownian motions, Probab. Theory Related Fields 77(1988) 87–97and 80 (1989) 633.
L.M. Taylor and R.J. Williams, Existence and uniqueness of semimartingale reflecting Brownian motions in an orthant, Probab. Theory Related Fields 96(1993) 283–317.
R.J.Williams, An invariance principle for semimartingale reflecting Brownian motions in an orthant, Queueing Systems 30(1998) 5–25.
R.J. Williams, Diffusion approximations for open multiclass queueing networks: Sufficient conditions involving state space collapse, Queueing Systems 30(1998) 27–88.
D.D. Yao, Probability Models in Manufacturing Systems, Springer Series in Operations Research (Springer, Berlin, 1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, J., Dai, W. A heavy traffic limit theorem for a class of open queueing networks with finite buffers. Queueing Systems 32, 5–40 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019178802391
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019178802391