Abstract
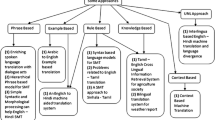
Interlingua and transfer-based approaches tomachine translation have long been in use in competing and complementary ways. The former proves economical in situations where translation among multiple languages is involved, and can be used as a knowledge-representation scheme. But given a particular interlingua, its adoption depends on its ability (a) to capture the knowledge in texts precisely and accurately and (b) to handle cross-language divergences. This paper studies the language divergence between English and Hindi and its implication to machine translation between these languages using the Universal Networking Language (UNL). UNL has been introduced by the United Nations University, Tokyo, to facilitate the transfer and exchange of information over the internet. The representation works at the level of single sentences and defines a semantic net-like structure in which nodes are word concepts and arcs are semantic relations between these concepts. The language divergences between Hindi, an Indo-European language, and English can be considered as representing the divergences between the SOV and SVO classes of languages. The work presented here is the only one to our knowledge that describes language divergence phenomena in the framework of computational linguistics through a South Asian language.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, D. and L. des Tombes: 1987. 'Basic Theory and Methodology in EUROTRA', in Nirenburg (1987), pp. 114-135.
Arnold, Doug and Louisa Sadler: 1990. 'Theoretical Basis of MiMo', Machine Translation 5, 195-222.
Bhandari, V.: 2002. 'Machine Translation of Phrasal Verbs from English to Hindi', Bachelor of Technology Project Report, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India.
Bharati, Akshar, Vineet Chaitanya and Rajeev Sangal: 1995. Natural Language Processing: A Pāainian Perspective. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India.
Boitet, Christian: 1988. 'Pros and Cons of the Pivot and Transfer Approaches in Multilingual Machine Translation', in Toon Witkam (eds): 1988. New Directions in Machine Translation. Dordrecht: Foris Maxwell et al. (1988), pp. 93-106.
Carbonell, Jaime G. and Masaru Tomita: 1987. 'Knowledge Based Machine Translation, the CMU Approach', in Nirenburg (1987), pp. 68-89.
Dorr, Bonnie J.: 1992. 'The Use of Lexical Semantics in Interlingual Machine Translation', Machine Translation 7, 135-193.
Dorr, Bonnie J.: 1993. Machine Translation: A View from the Lexicon. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
D'Souza, Rayner, G. V. Shivakumar, D. Swathi and Pushpak Bhattacharyya: 2001. 'Natural Language Generation from Semantic Net like Structures with application to Hindi', in STRANS-2001: Symposium on Translation Support Systems, Kanpur, India.
Gopinathan, S. and S. Kandaswamy (eds): 1993. [Problems of Translation], New Delhi, Lokbharti Prakashan.
Guha, R. V. and D. B. Lenat: 1990. 'Cyc: A Midterm Report', AI Magazine 11, 32-59.
Hardt, S. L.: 1987. 'Primitives', in Shapiro (1987), pp. 759-761.
Katz, J.: 1966. The Philosophy of Language, New York: Harper and Row.
King, M. (ed.): 1987. Machine Translation Today: The State of the Art, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
King, M. and S. Perschke: 1987. 'EUROTRA', in King (1987), pp. 373-391.
Landsbergen, Jan.: 1987. 'Isomorphic Grammars and Their Use in the ROSETTA Translation System', in King (1987), pp. 351-372.
Lytinen, Steven and Roger C. Schank: 1982. 'Representation and Translation', Technical Report, Department of Computer Science, Yale University, New Haven, CT.
Martin, John C.: 1991. Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation, New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Maxwell, Dan, Klaus Schubert and Toon Witkam (eds): 1988. New Directions in Machine Translation. Dordrecht: Foris.
Monju, M., T. Shilpa, D. Smita, Leena Giri, Shachi Dave and Pushpak Bhattacharyya: 2000. 'Knowledge Extraction from Hindi Text', in Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Based Computer Systems (KBCS 2000), Mumbai, India, pp. 193-204.
Muraki, Kazunori: 1987. 'PIVOT: Two-Phase Machine Translation System', in MT Summit Manuscripts and Program, Hakone, Japan, pp. 81-83.
Nirenburg, Sergei (ed.): 1987. Machine Translation: Theoretical and Methodological Issues. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nirenburg, Sergei, Jaime Carbonell, Masaru Tomita and Kenneth Goodman: 1992. Machine Translation: A Knowledge Based Approach. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann.
Nirenburg, Sergei, Victor Raskin and Allen B. Tucker: 1987. 'The Sturcture of Interlingua in TRANSLATOR', in Nirenburg (1987), pp. 90-113.
Okumura, Akitoshi, Kazunori Muraki and Susume Akamine: 1991. 'Multi-Lingual Sentence Generation from the PIVOT Interlingua', in MT Summit III, Washington, DC, pp. 67-71.
Parikh, Jignashu and Pushpak Bhattacharyya: 2001. 'Towards Realising The Semantic Web', submitted to Natural Language Engineering.
Parikh, Jignashu, Trilok Soni and Chirag Shah: 2000. 'Conversion of English Language Texts to Universal Networking Language', Bachelor of Engineering Dissertation, Dharamsinh Desai Institute of Technology, Nadiad, India.
Perschke, Sergei: 1989. 'EUROTRA', in MT Summit II, Munich, pp. 113-119.
Rao, Durgesh, Kavita Mohanraj, Jayprakash Hegde, Vivek Mehta and Parag Mahadane: 2000. 'A Practical Framework for Syntactic Transfer of Compound-Complex Sentences for English-Hindi Machine Translation', in International Conference on Knowledge Based Computer Systems (KBCS 2000), Mumbai, India, pp. 343-354.
Schank, Roger C.: 1972. 'Conceptual Dependency: A Theory of Natural Language Understanding', Cognitive Psychology 3, 552-631.
Schank, Roger C.: 1973. 'Identification of Conceptualizations Underlying Natural Language', in Roger C. Schank and K. M. Colby (eds) Computer Models of Thought and Language, San Francisco, CA: Freeman, pp. 187-247.
Schank, Roger C. (ed.): 1975. Conceptual Information Processing. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers.
Schank, Roger C. and Robert Abelson: 1977. Scripts, Plans, Goals and Understanding. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Schubert, K.: 1988. 'The Architectre of DLT — Interlingual or Double Direct?', in Toon Witkam (eds): 1988. New Directions in Machine Translation. Dordrecht: Foris Maxwell et al. (1988), pp. 131-143.
Schütz, Jörg, Gregor Thurmair and Roberto Cencioni: 1991. 'An Architecture Sketch of Eurotra-II', in MT Summit III, Washington, DC, pp. 3-10.
Senniappan, Kumarvel and Pushpak Bhattacharyya: 2000. 'Automatic Generation of Hyperlinks using Semantic Information', International Conference on Information Technology (CIT 2000), Bhubaneshwar, pp. 43-48.
Shapiro, S. C. (ed.): 1987. Encyclopedia of Artificial Intelligence. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.
Tiwari Bholanath and Naresh Kumar: 1987. [Problems of translation from various foreign languages], New Delhi, Prabhat Prakashan.
Uchida, Hiroshi: 1989. 'ATLAS', in MT Summit II, Munich, pp. 152-157.
UNL: 1998. 'The Universal Networking Language (UNL) Specifications Version 3.0', Technical Report, United Nations University, Tokyo.
UNU: 2000a. DeConverter Specification Version 2.0. UNU/IAS/UNL Center, Tokyo.
UNU: 2000b. EnConverter Specification Version 2.1. UNU/IAS/UNL Center, Tokyo.
Vauquois, Bernard: 1975. La traduction automatique à Grenoble, Paris: Dunod.
Vauquois, Bernard and Christian Boitet: 1985. 'Automated Translation at Grenoble University', Computational Linguistics 11, 28-36.
Wahlster, W.: 1993. 'Verbmobil: Translation of Face-to-Face Dialogs', in The Fourth Machine Translation Summit: MT Summit IV, Kobe, Japan, pp. 127-135.
Wilks, Yorick: 1972. Grammar, Meaning and the Machine Analysis of Language. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Wilks, Yorick: 1987. 'Primitives', in Shapiro (1987), pp. 759-761.
Witkam, T.: 1988. 'DLT — An Industrial R&D Project for Multilingual MT', in COLING Budapest: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Budapest, pp. 756-759.
Woods, W. A.: 1985. 'What's in a Link: Foundations for Semantic Networks', in R. J. Brachman and H. J. Levesque (eds) Readings in Knowledge Representation, San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, pp. 218-241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dave, S., Parikh, J. & Bhattacharyya, P. Interlingua-based English–Hindi Machine Translation and Language Divergence. Machine Translation 16, 251–304 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021902704523
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021902704523