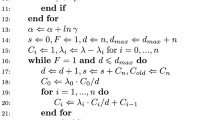Abstract
This paper proposes a parameter fitting procedure using Markov Modulated Poisson Processes (MMPPs) that leads to accurate estimates of queuing behavior for network traffic exhibiting long-range dependence behavior. The procedure matches both the autocovariance and marginal distribution of the counting process. A major feature is that the number of states is not fixed a priori, and can be adapted to the particular trace being modeled. The MMPP is constructed as a superposition of L 2-MMPPs and one M-MMPP. The 2-MMPPs are designed to match the autocovariance and the M-MMPP to match the marginal distribution. Each 2-MMPP models a specific time-scale of the data. The procedure starts by approximating the autocovariance by a weighted sum of exponential functions that model the autocovariance of the 2-MMPPs. The autocovariance tail can be adjusted to capture the long-range dependence characteristics of the traffic, up to the time-scales of interest to the system under study. The procedure then fits the M-MMPP parameters in order to match the marginal distribution, within the constraints imposed by the autocovariance matching. The number of states is also determined as part of this step. The final MMPP with M2L states is obtained by superposing the L 2-MMPPs and the M-MMPP. We apply the inference procedure to traffic traces exhibiting long-range dependence and evaluate its queuing behavior through simulation. Very good results are obtained, both in terms of queuing behavior and number of states, for the traces used, which include the well-known Bellcore traces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Andersen and B. Nielsen, A Markovian approach for modeling packet traffic with long-range dependence, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 16(5) (1998) 719–732.
J. Beran, R. Sherman, M. Taqqu and W. Willinger, Long-range dependence in variable-bit rate video traffic, IEEE Transactions on Communications 43(2-4) (1995) 1566–1579.
C. Blondia, A discrete-time batch Markovian arrival process as B-ISDN traffic model, Belgian Journal of Operations Research, Statistics and Computer Science 32 (1993) 3–23.
C. Blondia and O. Casals, Statistical multiplexing of VBR sources: A matrix-analytic approach, Performance Evaluation 16(1-3) (1992) 5–20.
M. Crovella and A. Bestavros, Self-similarity in World Wide Web traffic: Evidence and possible causes, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 5(6) (1997) 835–846.
L. Deng and J. Mark, Parameter estimation for Markov modulated Poisson processes via the EM algorithm with time discretization, Telecommunication Systems 1 (1993) 321–338.
A. Elwalid and D. Mitra, Effective bandwidth of general Markovian traffic sources and admission control of high speed networks, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 1(3) (1993) 329–343.
A. Erramilli, O. Narayan, A. Neidhardt and I. Saniee, Performance impacts of multi-scaling in wide area TCP/IP traffic, in: Proc. of INFOCOM 2000, 2000.
A. Feldmann, A.C. Gilbert, P. Huang and W. Willinger, Dynamics of IP traffic: A study of the role of variability and the impact of control, in: Proc. of SIGCOMM 99, 1999, pp. 301–313.
A. Feldmann, A.C. Gilbert and W. Willinger, Data networks as cascades: Investigating the multifractal nature of Internet WAN traffic, in: Proc. of SIGCOMM 98, 1998, pp. 42–55.
A. Feldmann and W. Whitt, Fitting mixtures of exponentials to long-tail distributions to analyze network performance models, Performance Evaluation 31(3/4) (1997) 245–279.
W. Fischer and K. Meier-Hellstern, The Markov-modulated Poisson process (MMPP) cookbook, Performance Evaluation 18(2) (1993) 149–171.
F. Geerts and C. Blondia, Superposition of Markov sources and long range dependence, in: Proc. of the IFIP/ICCC Internat. Conf. on Information Network and Data Communication, 1996.
M. Grossglauser and J.C. Bolot, On the relevance of long-range dependence in network traffic, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 7(5) (1999) 629–640.
R. Grünenfelder and S. Robert, Which arrival law parameters are decisive for queueing system performance, in: Proc. of ITC 14, 1994.
B. Hajek and L. He, On variations of queue response for inputs with the same mean and autocorrelation function, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 6(5) (1998) 588–598.
S. Kang and D. Sung, Two-state MMPP modelling of ATM superposed traffic streams based on the characterisation of correlated interarrival times, in: Proc. of IEEE GLOBECOM 95, November 1995, pp. 1422–1426.
D. Karlis and E. Xekalaki, Robust inference for finite Poisson mixtures, Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 93 (2001) 93–115.
G. Kesidis, J. Walrand and C. Chang, Effective bandwidths for multiclass Markov fluids and other ATM sources, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 1(4) (1993) 424–428.
W. Leland, M. Taqqu, W. Willinger and D. Wilson, On the self-similar nature of ethernet traffic (extended version), IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 2(1) (1994) 1–15.
S. Li and C. Hwang, On the convergence of traffic measurement and queuing analysis: A statistical-match and queuing (SMAQ) tool, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (February 1997) 95–110.
D.M. Lucantoni, The BMAP/G/1 queue: A tutorial, in: Models and Techniques for Performance Evaluation of Computer and Communication Systems, eds. L. Donatiello and R. Nelson (Springer, Berlin, 1993) pp. 330–358.
K. Meier-Hellstern, A fitting algorithm for Markov-modulated Poisson process having two arrival rates, European Journal of Operational Research 29 (1987).
A. Nogueira and R. Valadas, Analyzing the relevant time scales in a network of queues, in: Proc. of Internet Performance and Control of Network Systems II, ITCom 2001, SPIE, Vol. 4523, August 2001, pp. 243–252.
C. Nunes and A. Pacheco, Parametric estimation in MMPP(2) using time discretization, in: Proc. of the 2nd Internat. Symposium on Semi-Markov Models: Theory and Applications, December 1998.
M. Osborne and G. Smyth, A modified Prony algorithm for fitting sums of exponential functions, SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing 16 (1995) 119–138.
V. Paxson and S. Floyd, Wide-area traffic: The failure of Poisson modeling, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 3(3)(1995) 226–244.
N. Rananand, Markov approximations to D-BMAPs: information-theoretic bounds on queueing performance, Stochastic Models 11(4) (1995) 713–734.
A. Ridder, Fast simulation of discrete time queues with Markov modulated batch arrivals and batch departures, AEU International Journal of Electronics and Communications 52 (1998) 127–132.
R. Riedi and J.L. Véhel, Multifractal properties of TCP traffic: a numerical study, Technical Report No 3129, INRIA Rocquencourt, France (1997); available at www.dsp.rice.edu/?riedi.
S. Robert and J. Le Boudec, New models for self-similar traffic, Performance Evaluation 30(1/2) (1997).
B. Ryu and A. Elwalid, The importance of long-range dependence of VBR video traffic in ATM traffic engineering: Myths and realities, ACM Computer Communication Review 26 (1996) 3–14.
P. Salvador and R. Valadas, A fitting procedure for Markov modulated Poisson processes with an adaptive number of states, in: Proc. of the 9th IFIP Working Conf. on Performance Modelling and Evaluation of ATM & IP Networks, June 2001.
P. Salvador and R. Valadas, Framework based on Markov modulated Poisson processes for modeling traffic with long-range dependence, in: Proc. of Internet Performance and Control of Network Systems II, ITCom 2001, SPIE, Vol. 4523, August 2001, pp. 221–232.
S. Shah-Heydari and T. Le-Ngoc, MMPP models for multimedia traffic, Telecommunication Systems 15(3/4) (2000) 273–293.
P. Skelly, M. Schwartz and S. Dixit, A histogram-based model for video traffic behaviour in an ATM multiplexer, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (August 1993) 446–458.
D. Veitch and P. Abry, A wavelet based joint estimator for the parameters of LRD, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 45(3) (1999).
W. Willinger, V. Paxson and M. Taqqu, Self-similarity and Heavy Tails: Structural Modeling of Network Traffic, A Practical Guide to Heavy Tails: Statistical Techniques and Applications (Birkhäuser, Basel, 1998).
W. Willinger, M. Taqqu, R. Sherman and D.Wilson, Self-similarity through high-variability: Statistical analysis of Ethernet LAN traffic at the source level, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 5(1) (1997) 71–86.
T. Yoshihara, S. Kasahara and Y. Takahashi, Practical time-scale fitting of self-similar traffic with Markov-modulated Poisson process, Telecommunication Systems 17(1/2) (2001) 185–211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salvador, P., Valadas, R. & Pacheco, A. Multiscale Fitting Procedure Using Markov Modulated Poisson Processes. Telecommunication Systems 23, 123–148 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023672904130
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023672904130