Abstract
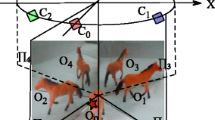
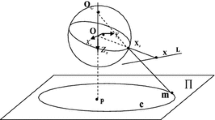
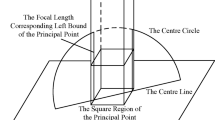
Central catadioptric cameras have been extensively adopted in robotics and surveillance due to their extensive field of view. To attain precise 3D information in these applications, it is important to calibrate the catadioptric cameras accurately. The existing calibration techniques either require prior knowledge of the mirror types, or highly depend on a conic estimation procedure, which might be ruined if there are only small portions of the conic visible on calibration images. In this paper, we design a novel planar pattern with concurrent lines as a calibration rig, which is more robust in conic estimation since the relationship among lines is taken into account. Based on the line properties, we propose a rough-to-fine approach suitable for the new planar pattern to calibrate central catadioptric cameras. This method divides the nonlinear optimization calibration problem into several linear sub-problems that are much more robust against noise. Our calibration method can estimate intrinsic parameters and the mirror parameter simultaneously and accurately, without a priori knowledge of the mirror type. The performance is demonstrated by both simulation and a real hyperbolic catadioptric imaging system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barreto, J., 2003. General Central Projection System Modelling, Calibration and Visual Servoing. PhD Thesis, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal.
Barreto, J., Araujo, H., 2002. Geometric Properties of Central Catadioptric Line Images and Their Application in Calibration. European Conf. on Computer Vision, p.237–251. [doi:10.1007/s11263-007-0082-8]
Barreto, J., Araujo, H., 2005. Geometric properties of central catadioptric line images and their application in calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 27(8): 1327–1333. [doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2005.163]
Barreto, J., Araujo, H., 2006. Fitting conics to paracatadioptric projections of lines. Comput Vis. Image Understand., 101(3):151–165. [doi:10.1016/j.cviu.2005.07.002]
Caron, G., Marchand, E., Mouaddib, E.M., 2009. 3D Model Based Pose Estimation for Omnidirectional Stereovision. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, p.5228–5233. [doi:10.1109/IROS.2009.5353955]
Ding, Y., Xiao, J., Tan, K., Yu, J., 2009. Catadioptric Projectors. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.2528–2535. [doi:10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206622]
Fitzgibbon, R., Pilu, M., 1999. Direct least square fitting of ellipses. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 21(5): 476–480. [doi:10.1109/34.765658]
Geyer, C., Daniilidis, K., 2000. A Unifying Theory for Central Panoramic Systems and Practical Implications. European Conf. on Computer Vision, p.455–461.
Geyer, C., Daniilidis, K., 2002. Paracatadioptric camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 24(5): 687–695. [doi:10.1109/34.1000241]
Hadj-Abdelkader, H., Mezouar, Y., Martinet, P., Chaumette, F., 2008. Catadioptric visual servoing from 3-D straight lines. IEEE Trans. Robot., 24(3):652–665. [doi:10.1109/TRO.2008.919288]
Hartley, R., Zisserman, A., 2000. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA. [doi:10.2277/0521540518]
Hu, B., 2009. It’s All Done with Mirrors: Calibration-and-Correspondence-Free 3D Reconstruction. Canadian Conf. on Computer and Robot Vision, p.148–154. [doi:10.1109/CRV.2009.29]
Mei, C., Rives, P., 2007. Single View Point Omnidirectional Camera Calibration from Planar Grids. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, p.3945–3950. [doi:10.1109/ROBOT.2007.364084]
Rossi, R., Savatier, X., Ertaud, J.Y., Mazari, B., 2009. Real-Time 3D Reconstruction for Mobile Robot Using Catadioptric Cameras. IEEE Int. Workshop on Robotic and Sensors Environments, p.104–109. [doi:10.1109/ROSE.2009.5355981]
Scaramuzza, R., Martinelli, A., Siegwart, R., 2006. A Flexible Technique for Accurate Omnidirectional Camera Calibration and Structure from Motion. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision Systems, p.45–52. [doi:10.1109/ICVS.2006.3]
Semple, J., Kneebone, G., 1952. Algebraic Projective Geometry. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Weng, P., Herniou, M., 1992. Camera calibration with distortion models and accuracy evaluation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 14(10):965–980. [doi:10.1109/34.159901]
Ying, X., Hu, Z., 2004. Catadioptric camera calibration using geometric invariants. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 26(10):1260–1271. [doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2004.79]
Zhang, B., Li, Y.F., 2008. A Method for Calibrating the Central Catadioptric Camera via Homographic Matrix. Int. Conf. on Information and Automation, p.972–977. [doi:10.1109/ICINFA.2008.4608140]
Zhang, L., Du, X., Zhu, Y., Liu, J., 2009. Central Catadioptric Camera Calibration with Single Image. IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, p.1253–1256. [doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4959818]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (Nos. 60502006, 60534070, and 90820306) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Du, X. & Liu, Jl. Using concurrent lines in central catadioptric camera calibration. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 12, 239–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1000043
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1000043