Abstract
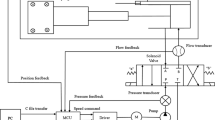
In view of the high energy consumption and low response speed of the traditional hydraulic system for an injection molding machine, a servo motor driven constant pump hydraulic system is designed for a precision injection molding process, which uses a servo motor, a constant pump, and a pressure sensor, instead of a common motor, a constant pump, a pressure proportion valve, and a flow proportion valve. A model predictive control strategy based on neurodynamic optimization is proposed to control this new hydraulic system in the injection molding process. Simulation results showed that this control method has good control precision and quick response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akesson, B.M., Toivonen, H.T., 2006. A neural network model predictive controller. J. Process Contr., 16(9):937–946. [doi:10.1016/j.jprocont.2006.06.001]
Draeger, A., Engell, S., Ranke, H., 1995. Model predictive control using neural networks. IEEE Contr. Syst., 15(5):61–66. [doi:10.1109/37.466261]
Dubay, R., 2002. Self-optimizing MPC of melt temperature in injection moulding. ISA Trans., 41(1):81–94. [doi:10. 1016/S0019-0578(07)60204-3]
Gao, F., Patterson, W.I., Kamal, M.R., 1996. Cavity pressure dynamics and self-tuning control for filling and packing phases of thermoplastics injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci., 36(9):1272–1285. [doi:10.1002/pen.10521]
Gao, F.R., Yang, Y., Shao, C., 2001. Robust iterative learning control with applications to injection molding process. Chem. Eng. Sci., 56(24):7025–7034. [doi:10.1016/S0009- 2509(01)00339-6]
Hopfield, J.J., Tank, D.W., 1985. “Neural” computation of decisions in optimization problems. Biol. Cybern., 52(3):141–152. [doi:10.1007/BF00339943]
Hu, X.L., Wang, J., 2008. An improved dual neural network for solving a class of quadratic programming problems and its k-winners-take-all application. IEEE Tran. Neur. Networks, 19(12):2022–2031. [doi:10.1109/TNN.2008. 2003287]
Huang, S.N., Tan, K.K., Lee, T.H., 1999a. Predictive control of ram velocity in injection molding. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng., 38(2):285–303. [doi:10.1080/0360255990 9351578]
Huang, S.N., Tan, K.K., Lee, T.H., 1999b. Adaptive GPC control of melt temperature in injection moulding. ISA Trans., 38(4):361–373. [doi:10.1016/S0019-0578(99)000 29-4]
Huang, S.N., Tan, K.K, Lee, T.H., 2004. Neural-networkbased predictive learning control of ram velocity in injection molding. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. C, 34(3):363–368. [doi:10.1109/TSMCC.2004.829304]
Kennedy, M.P., Chua, L.O., 1988. Neural networks for nonlinear programming. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst., 35(5):554–562. [doi:10.1109/31.1783]
Liao, J.H., Tsai, C.C., Chang, H.C., 1996. Adaptive generalized predictive PI control of injection molding processes. Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Automation Technology, p.711–718.
Liu, Q.S., Wang, J., 2008. A one-layer recurrent neural network with a discontinuous hard-limiting activation function for quadratic programming. IEEE Trans. Neur. Networks, 19(4):558–570. [doi:10.1109/TNN.2007.910 736]
Liu, S.B., Wang, J., 2006. A simplified dual neural network for quadratic programming with its KWTA application. IEEE Trans. Neur. Networks, 17(6):1500–1510. [doi:10.1109/ TNN.2006.881046]
Mahadevan, R., Doyle, F.J., 2003. Efficient optimization approaches to nonlinear model predictive control. Int. J. Robust Nonl. Contr., 13(3–4):309–329. [doi:10.1002/rnc. 820]
Morari, M., Lee, J.H., 1999. Model predictive control: past, present and future. Comput. Chem. Eng., 23(4–5):667–682. [doi:10.1016/S0098-1354(98)00301-9]
Pan, Y.P., Wang, J., 2009. Model predictive control for nonlinear affine systems based on the simplified dual neural network. IEEE Int. Symp. on Intelligent Control and Control Applications, p.683–688. [doi:10.1109/CCA. 2009.5281106]
Pandelidis, I.O., Agrawal, A.R., 1988. Optimal anticipatory control of ram velocity in injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci., 28(3):147–156. [doi:10.1002/pen.760280305]
Qian, S.J., Badgwell, T.A., 2003. A survey of industrial model predictive control technology. Contr. Eng. Pract., 11(7):733–764. [doi:10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00186-7]
Rafizadeh, M., Patterson, W.I., Kamal, M.R., 1996. Physicallybased model of thermoplastics injection molding for control applications. Int. Polym. Proc., 11(4):352–362.
Tan, K.K., Tang, J.C., 2002. Learning-enhanced PI control of ram velocity in injection molding machines. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., 15(1):65–72. [doi:10.1016/S0952-1976(02) 00032-5]
Tan, K.K., Huang, S.N., Jiang, X., 2001. Adaptive control of ram velocity for the injection moulding machine. IEEE Tran. Contr. Syst. Tech., 9(4):663–671. [doi:10.1109/87. 930978]
Tank, D., Hopfield, J.J., 1986. Simple ‘neural’ optimization networks: an A/D converter, signal decision circuit, and a linear programming circuit. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst., 33(5):533–541. [doi:10.1109/TCS.1986.1085953]
Varela, A.E., 2000. Self-tuning pressure control in an injection moulding cavity during filling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 78(1):79–86. [doi:10.1205/026387600526906]
Xia, Y., Wang, J., 2001. A dual neural network for kinematic control of redundant robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B, 31(1):147–154. [doi:10.1109/3477. 907574]
Yang, Y., Gao, F., 2000. Adaptive control of the filling velocity of thermoplastics injection molding. Contr. Eng. Pract., 8(11):1285–1296. [doi:10.1016/S0967-0661(00) 00060-5]
Zhang, S., Constantinides, A.G., 1992. Lagrange programming neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II, 39(7):441–452. [doi:10.1109/82.160169]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61203299), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2013QNA4021), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Nos. Y1110135 and LY12F03018), and the Qianjiang Talents Program of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2013R10047)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Yg., Wang, J. & Wei, W. Model predictive control of servo motor driven constant pump hydraulic system in injection molding process based on neurodynamic optimization. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 15, 139–146 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300182
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300182