Abstract
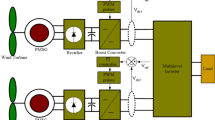
We propose a new power conversion system for a permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) based grid-connected wind energy conversion system (WECS) operating with fully-controlled back-to-back current-source converters. On the generator side, two independent current-source rectifiers (CSRs) with space-vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) are employed to regulate and stabilize DC-link currents. Between DC-link and the electrical grid, a direct-type three-phase five-level current-source inverter (CSI) is inserted as a buffer to regulate real and reactive power fed to the grid and thus adjusts the grid side power-factor. We also present a current-based maximum power point tracking (MPPT) scheme, which helps the generator extract the maximum power through closed-loop regulation of the generator speed. By applying the multilevel modulation and control strategies to the grid-side five-level CSI, a multilevel output current waveform with less distortion is produced, and the bulk requirement of the output capacitor filter to eliminate the harmonic current is reduced. All the proposed concepts are verified by simulation models built in a PSIM environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh, O., Yazdani, A., 2013. A strategy for real power control in a direct-drive PMSG-based wind energy conversion system. IEEE Trans. Power Del., 28(3):1297–1305. [doi:10.1109/TPWRD.2013.2258177]
Bai, Z., Ma, H., Xu, D., et al., 2013. Control strategy with a generalized DC current balancing method for multimodule current-source converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 29(1):366–373. [doi:10.1109/TPEL.2013. 2252628]
Bao, J.Y., Bao, W.B., Zhang, Z.C., 2010a. Generalized multilevel current source inverter topology with self-balancing current. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. C (Comput. & Electron.), 11(7):555–561. [doi:10.1631/jzus.C0910605]
Bao, J.Y., Bao, W.B., Wang, S., et al., 2010b. Multilevel current source inverter topologies based on the duality principle. Proc. 25th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conf. and Expo, p.1097–1100. [doi:10.1109/APEC.2010. 5433367]
Chung, S.K., 2000. A phase tracking system for three phase utility interface inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 15(3):431–438. [doi:10.1109/63.844502]
Dai, J., Xu, D., Wu, B., 2009. A novel control scheme for current-source-converter-based PMSG wind energy conversion systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 24(4): 963–972. [doi:10.1109/TPEL.2008.2010259]
Dash, P.P., Kazerani, M., 2011. Dynamic modeling and performance analysis of a grid-connected current-source inverter-based photovoltaic system. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy, 2(4):443–450. [doi:10.1109/TSTE.2011.2149551]
Dupczak, B.S., Perin, A.J., Heldwein, M.L., 2012. Space vector modulation strategy applied to interphase transformers-based five-level current source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 27(6):2740–2751. [doi:10.1109/TPEL. 2011.2177479]
Melício, R., Mendes, V.M.F., Catalão, J.P.S., 2010. Power converter topologies for wind energy conversion systems: integrated modeling, control strategy and performance simulation. Renew. Energy, 35(10):2165–2174. [doi:10. 1016/j.renene.2010.03.009]
Melício, R., Mendes, V.M.F., Catalão, J.P.S., 2011. Comparative study of power converter topologies and control strategies for the harmonic performance of variable-speed wind turbine generator systems. Energy, 36(1):520–529. [doi:10.1016/j.energy.2010.10.012]
Nikolic, A., Jeftenic, B., 2010. Current source converter topologies for PMSG wind turbine applications. Proc. 14th Int. Power Electronics and Motion Control Conf., p.S14-27–S14-32. [doi:10.1109/EPEPEMC.2010.5606535]
Popat, M., Wu, B., Liu, F., et al., 2012a. Coordinated control of cascaded current-source converter based offshore wind farm. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy, 3(3):557–565. [doi:10. 1109/TSTE.2012.2191986]
Popat, M., Wu, B., Zargari, N.R., 2012b. A novel decoupled interconnecting method for current-source converter-based offshore wind farms. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 27(10):4224–4233. [doi:10.1109/TPEL.2012.2191982]
Popat, M., Wu, B., Zargari, N.R., 2013. Fault ride-through capability of cascaded current-source converter-based offshore wind farm. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy, 4(2): 314–323. [doi:10.1109/TSTE.2012.2223246]
Sahan, B., Araújo, S.V., Nöding, C., et al., 2011. Comparative evaluation of three-phase current source inverters for grid interfacing of distributed and renewable energy systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 26(8):2304–2318. [doi:10. 1109/TPEL.2010.2096827]
Senturk, O.S., Helle, L., Munk-Nielsen, S., et al., 2012. Power capability investigation based on electrothermal models of press-pack IGBT three-level NPC and ANPC VSCs for multimegawatt wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Power Electr., 27(7):3195–3206. [doi:10.1109/TPEL.2011.2182661]
Sharma, S., Singh, B., 2012. Control of permanent magnet synchronous generator-based stand-alone wind energy conversion system. IET Power Electr., 5(8):1519–1526. [doi:10.1049/iet-pel.2011.0367]
Singh, M., Khadkikar, V., Chandra, A., 2011. Grid synchronisation with harmonics and reactive power compensation capability of a permanent magnet synchronous generator-based variable speed wind energy conversion system. IET Power Electr., 4(1):122–130. [doi:10.1049/iet-pel. 2009.0132]
Teshirogi, T., Nishikata, S., 2011. Effects of system parameters on the performance characteristics of a wind turbine generating system using a current-source thyristor inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 47(1):252–257. [doi:10. 1109/TIA.2010.2091376]
Wang, J.C., Dai, J.Y., Wu, B., et al., 2011. Megawatt wind energy conversion system with diode rectifier and multilevel current source inverter. Proc. IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, p.871-876. [doi:10. 1109/ECCE.2011.6063862]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51277164) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (No. Y1111002)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Jy., Bao, Wb. & Li, Yl. A power conversion system for PMSG-based WECS operating with fully-controlled current-source converters. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 15, 232–240 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300231
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300231