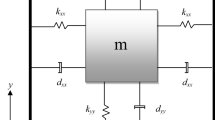
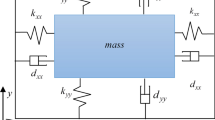
Abstract
One of the inevitable problems with real-time control systems is the presence of the uncertainties and external disturbances. The existence of these uncertainties in the fabrication processes of the MEMS Gyroscope devices can deeply impact the performance of the devices. In this paper, five adaptive finite time robust control methods are employed based on SMC method for a Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) Gyroscope with mismatched uncertainties and external disturbances to achieve trajectory tracking goal. A new Stepping SMC method is proposed in this study to improve some deficiencies of conventional and existing methods including Simple SMC, Classical SMC, Cubic SMC, and Hexagonal SMC. The upper bound of mismatched uncertainties is estimated in finite time and their estimation is utilized in the control inputs for all five control methods. The elimination of chattering phenomenon is considered in this paper. The system finite time stability proof is obtained using Lyapunov stability theory. The numerical simulation is performed in Simulink/MATLAB for the MEMS gyroscope system to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed control method, Stepping SMC, compared with four other methods. To make an extensive comparison among results, the performance criterion, Integral of the square value (ISV), is used.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Brahmi, B., Saad, M., Ochoa-Luna, C., Rahman, M.H., and Brahmi, A., Adaptive tracking control of an exoskeleton robot with uncertain dynamics based on estimated time-delay control, IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics, 2018, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 575–585.
Bibi, Y., Bouhali, O., and Bouktir, T., Petri type 2 fuzzy neural networks approximator for adaptive control of uncertain non-linear systems, IET Control Theory Appl., 2017, vol. 11, no. 17, pp. 3130–3136.
Gao, F., Hu, X., Li, S.E., Li, K., and Sun, Q., Distributed adaptive sliding mode control of vehicular platoon with uncertain interaction topology, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2018, vol. 65, no. 8, pp. 6352–6361.
Kazemy, A. and Cao, J., Consecutive synchronization of a delayed complex dynamical network via distributed adaptive control approach, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 2656–2664.
Mobayen, S., Adaptive global terminal sliding mode control scheme with improved dynamic surface for uncertain nonlinear systems, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1692–1700.
Chen, K.-Y., Robust optimal adaptive sliding mode control with the disturbance observer for a manipulator robot system, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1701–1715.
Chen, H.-G., Wang, Y.-H., and Zhang, L.-l., Adaptive control based on extended neural network for SISO uncertain nonlinear systems, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 27–38.
Wang, C., Li, Z., Zhao, K., and Guo, Q.J.I.C., Efficient self-powered convertor with digitally controlled oscillator-based adaptive maximum power point tracking and RF kick-start for ultralow-voltage thermoelectric energy harvesting, Devices Syst., 2016, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 147–155.
Zhang, Y., Li, H., Liu, J., Zeng, R., and Lei, J., Research on adaptive sliding synchronization of Rikitake chaotic system with single unknown control coefficient, Autom. Control Comput. Sci., 2017, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 311–320.
Zhang, Q., Xu, D.-Z., and Zhan, K.-K., Model reference robust adaptive H∞ controller design, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2017, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 1507–1514.
Taheri-Kalani, J. and Zarei, N., An adaptive technique for trajectory tracking control of a wheeled mobile robots without velocity measurements, Autom. Control Comput. Sci., 2016, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 441–452.
Neila, M.B.R. and Tarak, D., Adaptive terminal sliding mode control for rigid robotic manipulators, Int. J. Autom. Comput., 2011, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 215–220.
Mnasri, C., Chorfi, D., and Gasmi, M., Robust integral sliding mode control of uncertain networked control systems with multiple data packet losses, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 2093–2102.
Zhao, H. and Niu, Y., Guaranteed cost sliding mode control of switched systems with known sojourn probabilities, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 2822–2831.
Liu, Y., Sliding mode control for a class of uncertain discrete switched systems, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1716–1723.
Ghabi, J. and Dhouibi, H., Discrete time sliding mode controller using a disturbance compensator for nonlinear uncertain systems, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 1156–1164.
Hosseinabadi, P.A., Abadi, A.S.S., and Mekhilef, S., Adaptive adaptive terminal sliding mode control of hyper-chaotic uncertain 4-order system with one control input, 2018 IEEE Conference on Systems, Process and Control (ICSPC), 2018, pp. 94–99.
Djelal, N., Saadia, N., and Ramdane-Cherif, A., Adaptive force-vision control of robot manipulator using sliding mode and fuzzy logic, Autom. Control Comput. Sci., 2019, vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 203–213.
Pourhashemi, A., Ramezani, A., and Siahi, M., Design of new fractional sliding mode control due to complete synchronization of commensurate and incommensurate fractional order chaotic systems, Autom. Control Comput. Sci., 2018, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 505–516.
Teimoori, H., Pota, H.R., Garratt, M., and Samal, M.K., Attitude control of a miniature helicopter using optimal sliding mode control, 2012 2nd Australian Control Conference, 2012, pp. 295–300.
Eaton, R., Katupitiya, J., Pota, H., and Siew, K.W., Robust sliding mode control of an agricultural tractor under the influence of slip, 2009 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, 2009, pp. 1873–1878.
Abadi, A.S.S. and Hosseinabadi, P.A., Fuzzy adaptive finite time control ship fin stabilizing systems model of fuzzy Takagi-Sugeno with unknowns and disturbances, 2018 6th Iranian Joint Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Systems (CFIS), 2018, pp. 33–36.
Elsayed, B.A., Hassan, M., and Mekhilef, S., Decoupled third-order fuzzy sliding model control for cart-inverted pendulum system, Appl. Math., 2013, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 193–201.
Khooban, M.H., Niknam, T., Blaabjerg, F., and Dehghani, M., Free chattering hybrid sliding mode control for a class of non-linear systems: electric vehicles as a case study, IET Sci. Measur. Technol., 2016, vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 776–785.
Asad, M., Ashraf, M., Iqbal, S., and Bhatti, A.I., Chattering and stability analysis of the sliding mode control using inverse hyperbolic function, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2017, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 2608–2618.
Abadi, A.S.S., Hosseinabadi, P.A., and Mekhilef, S., Two novel AOTSMC of photovoltaic system using VSC model in smart grid, Smart Grid Conference (SGC), 2017, pp. 1–6.
Abadi, A.S.S., Hosseinabadi, P.A., and Mekhilef, S.J.T., Two novel approaches of NTSMC and ANTSMC synchronization for smart grid chaotic systems, Technol. Econ. Smart Grids Sustainable Energy, 2018, vol. 3.
Abadi, A.S.S., Mehrizi, M.H., and Hosseinabadi, P.A., Fuzzy adaptive terminal sliding mode control of SIMO nonlinear systems with TS fuzzy model, 2018 6th Iranian Joint Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Systems (CFIS), 2018, pp. 185–189.
Sui, S., Tong, S., and Chen, C.P., Finite-time filter decentralized control for nonstrict-feedback nonlinear large-scale systems, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2018, vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 3289–3300.
Hwang, C.-L. and Hung, J.Y., Stratified adaptive finite-time tracking control for nonlinear uncertain generalized vehicle systems and its application, IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol., 2019, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 1308–1316.
Zhao, L., Yu, J., and Yu, H., Adaptive finite-time attitude tracking control for spacecraft with disturbances, IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst., 2017, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 1297–1305.
Cao, Z., Niu, Y., and Zhao, H., Finite-time sliding mode control of Markovian jump systems subject to actuator faults, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 2282–2289.
Zhang, W., Li, C., Huang, T., and Huang, J., Finite-time synchronization of neural networks with multiple proportional delays via non-chattering control, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 2473–2479.
Lv, W., Wang, F., and Zhang, L., Adaptive fuzzy finite-time control for uncertain nonlinear systems with dead-zone input, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 2549–2558.
Mishra, J.P., Yu, X., and Jalili, M., Arbitrary-order continuous finite-time sliding mode controller for fixed-time convergence, IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs, 2018, vol. 65, no. 12, pp. 1988–1992.
Rouhani, E. and Erfanian, A., A finite-time adaptive fuzzy terminal sliding mode control for uncertain nonlinear systems, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1938–1950.
Ma, R., Jiang, B., and Liu, Y., Finite-time stabilization with output-constraints of a class of high-order nonlinear systems, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst., 2018, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 945–952.
Hosseinabadi, P.A. and Abadi, A.S.S., Adaptive terminal sliding mode control of high-order nonlinear systems, Int. J. Autom. Control, 2019, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 668–678.
Lin, Y., Zheng, X., Liu, S., Ma, W., and Jin, Z., Temperature-dependence improvement for a MEMS gyroscope using triangular-electrode based capacitive detection method, Micro Nano Lett., vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 828–833.
Antonello, R. and Oboe, R., Exploring the potential of MEMS gyroscopes: Successfully using sensors in typical industrial motion control applications, IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 14–24.
Antonello, R., Oboe, R., Prandi, L., and Biganzoli, F., Automatic mode matching in MEMS vibrating gyroscopes using extremum-seeking control, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2009, vol. 56, no. 10, pp. 3880–3891.
Efimovskaya, A., Lin, Y.-W., and Shkel, A.M., Double-sided process for MEMS SOI sensors with deep vertical thru-wafer interconnects, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 2018, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 239–249.
Yusof, N., Soin, N., and Noorakma, A.C.W., Effect of beams structures on dynamic behavior of piezoresistive accelerometer sensors, J. Telecomm. Electron. Comput. Eng., 2017, vol. 9, nos. 1–4, pp. 77–81.
Khamil, K.N., Leong, K.S., Mohamad, N.B., Soin, N., and Saba, N., Analysis of MEMS accelerometer for optimized sensitivity, Int. J. Eng. Technol., 2015, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 2705–2711.
Batur, C., Sreeramreddy, T., and Khasawneh, Q., Sliding mode control of a simulated MEMS gyroscope, ISA Trans., 2006, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 99–108.
Leland, R.P., Adaptive control of a MEMS gyroscope using Lyapunov methods, IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol., 2006, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 278–283.
Yan, W. and Fei, J., Adaptive control of MEMS gyroscope based on global terminal sliding mode controller, Math. Probl. Eng., 2013, vol. 2013.
Fei, J., Robust adaptive vibration tracking control for a micro-electro-mechanical systems vibratory gyroscope with bound estimation, IET Control Theory Appl., 2010, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1019–1026.
Kocamaz, U.E., Cevher, B., and Uyaroğlu, Y., Control and synchronization of chaos with sliding mode control based on cubic reaching rule, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2017, vol. 105, pp. 92–98.
Park, S., Adaptive control strategies for MEMS gyroscopes, Doctoral Thesis, U.C. Berkeley, 2000.
Bhat, S.P. and Bernstein, D.S., Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems, SIAM J. Control Optim., 2000, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 751–766.
Orlov, Y., Finite time stability and robust control synthesis of uncertain switched systems, SIAM J. Control Optim., 2004, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 1253–1271.
Aghababa, M.P., Khanmohammadi, S., and Alizadeh, G., Finite-time synchronization of two different chaotic systems with unknown parameters via sliding mode technique, Appl. Math. Modell., 2011, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 3080–3091.
Yu, S. and Long, X., Finite-time consensus for second-order multi-agent systems with disturbances by integral sliding mode, Automatica, 2015, vol. 54, pp. 158–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization, A.S.S. Abadi, P.A. Hosseinabadi, and N.B. Soin;
Methodology, A.S.S. Abadi, and P.A. Hosseinabadi;
Software, A.S.S. Abadi, and P.A. Hosseinabadi;
Validation, N.B. Soin, and S. Mekhilef;
Formal Analysis, A.S.S. Abadi, and P.A. Hosseinabadi;
Investigation, A.S.S. Abadi, P.A. Hosseinabadi, N.B. Soin, and S. Mekhilef;
Resources, N.B. Soin, and S. Mekhilef;
Data Curation, A.S.S. Abadi, P.A. Hosseinabadi;
Writing – Original Draft Preparation, P.A. Hosseinabadi, and A.S.S. Abadi, N.B. Soin,;
Writing – Review & Editing, P.A. Hosseinabadi, A.S.S. Abadi, N.B. Soin, and S. Mekhilef;
Visualization, A.S.S. Abadi, and P.A. Hosseinabadi;
Supervision, S. Mekhilef; Project Administration, N.B. Soin, and S. Mekhilef;
Funding Acquisition, S. Mekhilef.
About this article
Cite this article
Abadi, A.S., Hosseinabadi, P.A., Soin, N.B. et al. Chattering-Free Adaptive Finite-Time Sliding Mode Control for Trajectory Tracking of MEMS Gyroscope. Aut. Control Comp. Sci. 54, 335–345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411620040021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411620040021