Abstract
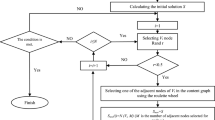
Key nodes identification is an important way to analyze and understand the characteristics, structure, and functions of the complex network. In this paper, links in complex networks are taken as the basic unit, and the overlapping community in complex networks is obtained through the clustering analysis of links. Then, the importance of the node is judged according to the number of associations containing the node and the weight value of the association in the network, because the nodes Shared between communities have more influence on the functional structure of the network. Finally, the method is applied to rank the importance of nodes in IEEE standard 300 node system, and the results are verified by network conductivity. The comparison with the results of the Betweenness algorithm, HITS algorithm and Pagepank algorithm shows that the method presented in this paper can effectively identify the key nodes from the complex network.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Strogatz, S.H., Exploring complex networks, Nature, 2001, vol. 410, no. 6825, pp. 268–276.
Gao, J.X., Barzel, B., and Barabasi, A.L., Universal resilience patterns in complex networks, Nature, 2016, vol. 530, no. 7590, pp. 307–312.
Wen, T. and Jiang, W., Identifying influential nodes based on fuzzy local dimension in complex networks, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2019, vol. 119, no. pp. 332–342.
Wang, X., Trajanovski, S., Kooij, R.E., et al., Degree distribution and assortativity in line graphs of complex networks, Phys. A (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2016, vol. 445, pp. 343–356.
Wandelt, S., Shi, X., and Sun, X.Q., Scalability of betweenness approximation algorithms: An experimental review, IEEE Access, 2019, vol. 7, pp. 104057–104071.
Liu, H.-L., Ma, C., Xiang, B.-B., et al., Identifying multiple influential spreaders based on generalized closeness centrality, Phys. A (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2018, vol. 492, pp. 2237–2248.
Morone, F., Del Ferraro, G., and Makse, H.A., The k-core as a predictor of structural collapse in mutualistic ecosystems, Nat. Phys., 2019, vol. 15, p. 95.
He, B., Han, Z.K., Peng, N., et al., The impact of a new algorithm of complex network based on omega PageRank, J. Internet Technol., 2016, vol. 17, pp. 371–376.
Zitnik, M., Sosič, R., and Leskovec, J., Prioritizing network communities, Nat. Commun., 2018, vol. 9, artic. no. 2544.
Wu, D., Ma, F., Javadi, M., et al., A study of the impacts of flow direction and electrical constraints on vulnerability assessment of power grid using electrical betweenness measures, Phys. A (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2017, vol. 466, pp. 295–309.
Kleinberg, J.M., Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment, J. ACM, 1999, vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 604–632.
Danon, L., Díaz-Guilera, A., and Arenas, A., The effect of size heterogeneity on community identification in complex networks, J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp., 2006, vol. 2006, no. 11.
Wu, D.D., The Structure and Function of Biological Networks, Drexel Univ., 2010.
Newman, M.E.J., The structure of scientific collaboration networks, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2001, vol. 98, no. 2, pp. 404–409.
Newman, M.E.J., The structure and function of complex networks, SIAM Rev., 2003, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 167–256.
Funding
This work is supported partially by Science and Technology Project of Jilin Provincial Department of Education in the 13th Five-year Plan Period (JJKH20190643KJ) and (JJKH20200042KJ), partially by the Project of Development and Reform Commission of Jilin Province (2019C058-1), partially by the Youth development fund project of Beihua university: (2017QNJJL04), partially by School-enterprise cooperative education program of Jilin Province (201801060050), partially by education and teaching reform project of Beihua University(XJYB2019047, XJZD2019024), partially by “Golden Class” Construction Project of Beihua University “VC++ program design and data structure” and “Signals and Systems cross-school joint gold course construction,” partially by educational science planning project of Jilin Province(GH20272), partially by higher education teaching reform of Jilin Province “Research and practice of information identification course module teaching content reform.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Qingyu Zou, Li, Y., Yang, X. et al. Identification of Key Nodes in Directed Network Based on Overlapping Community Structure. Aut. Control Comp. Sci. 55, 167–176 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411621020103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411621020103