Abstract
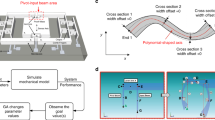
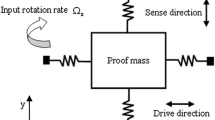
We propose a tuning method for Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) gyroscopes based on evolutionary computation to increase the accuracy of MEMS gyroscopes through electrostatic tuning. The tuning method was tested for the second generation JPL/Boeing Post-resonator MEMS gyroscope using the measurement of the frequency response of the MEMS device in open-loop operation. We also report on the development and preliminary results of a hardware platform for integrated tuning based on “switched drive-angle” of MEMS gyroscopes whereby the same gyro is operated with its drive direction first at 0° and then at 90°. The control of this device is implemented through a digital design on a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). The hardware platform easily transitions to an embedded solution that allows for the miniaturization of the system to a single chip.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., et al. “A control and signal processing integrated circuit for the JPL-Boeing micro-machined gyroscopes”, (submitted to IEEE).
Ferguson, M. I., et al. 2005. Effect of Temperature on MEMS Vibratory Rate Gyroscope. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, March 2005.
Hayworth, K. 2003. Continuous Tuning and Calibration of Vibratory Gyroscopes. In NASA. Tech Brief, Oct 2003 (NPO-30449).
Hayworth, K., et al. 2004. “Electrostatic Spring Softening in Redundant Degree of Freedom resonators”, patent US 6,823,734 Bl, JPL and Boeing, Nov. 30, 2004.
Holland, J. H. 1975. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems. Ann Arbor, Michigan: The University of Michigan Press, 1975.
Kirkpatrick, S., C. D. Gelat, and M. P. Vecchi. 1983. “Optimization by Simulated Annealing”, Science, 220, 671–680, 1983.
Leland, R. P. 2003. “Adaptive mode tuning vibrational gyroscopes”, IEEE Trans. Control. Systems Tech., vol. 11, no. 2, 242–247, March 2003.
M’Closkey, R. and D. Kim. 2005. “Real-time tuning of JPL-Boeing MEMS gyro”, Personal. Communication, JPL, March 2005.
Metropolis, N., et al. 1953. “Equation of State Calculation by Fast Computing Machines”, J of Chem. Phys., 21, 1087–1091, 1953.
Painer, C. C. and A. M. Shkel. 2003. “Active structural error suppression in MEMS vibratory rate integrating gyroscopes”, IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 3, no. 5, 595–606, Oct. 2003.
Stanney, Kay, Ed., 2002. Handbook of Virtual Environment Technology. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2002.
Terrile, R. J., et al. 2005. Evolutionary Computation Technologies for Space Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, March 2005.
Yuret, D. and M. de la Maza. 1993. Dynamic Hill Climbing — Overcoming limitations of optimization techniques. In Proceedings of the 2 nd Turkish Symposium of AL and ANN, 254–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Keymeulen, D. et al. (2006). Hardware Platforms for Electrostatic Tuning of Mems Gyroscope Using Nature-Inspired Computation. In: Higuchi, T., Liu, Y., Yao, X. (eds) Evolvable Hardware. Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. Springer, Boston, MA . https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-31238-2_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-31238-2_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-24386-3
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-31238-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)