Abstract
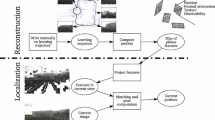
The autonomous operation of an intelligent service robot in practical applications requires that the robot builds up a map of the environment by itself. A prerequisite for building large scale consistent maps is that the robot is able to recognise previously mapped areas and relocalise within these areas.
The recognition is based on constructing partial maps of geometric landmarks which are then compared to yield the optimal correspondence between these landmarks. For each landmark a signature is constructed which contains additional information about its immediate environment and its non-geometric properties. It is ensured that the signatures are robust with respect to missing landmarks, rotation and translation of landmarks and varying landmark lengths.
Both simulation and experiments on real robots have shown that the approach is capable of recognising previously mapped areas robustly in real-time.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellman, R.: Dynamic Programming. Princeton University Press, Oxford University Press, London (1957)
Borenstein, J., Everett, H.R., Feng, L.: Navigating Mobile Robots, Systems and Techniques. AK Peters, Wellesley Massachusetts (1996)
Crowley, J.L., Mely, S.: Mobile Robot Perception Using Vertical Line Stereo. In: Kanade, T., et al. (eds.) Intelligent Autonomous Systems, vol. 2, pp. 597–607 (1989)
Chatila, R., Laumond, J.-P.: Position referencing and consistent world modeling for mobile robots. In: ICRA Proceedings (1985)
Elfes, A.: Robot Navigation: Integrating Perception, Environmental Constraints and Task Execution Within a Probabilistic Framework. In: Dorst, L., Voorbraak, F., van Lambalgen, M., et al. (eds.) RUR 1995. LNCS, vol. 1093, pp. 93–130. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Iyengar, S.S., Elfes, A. (eds.): Automous Mobile Robots, Perception, Mapping, and Navigation. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (1991)
Karch, O., Noltemeier, H.: Robot Localisation - Theory and Practice. In: IROS Proceedings, pp. 850–856 (1997)
Leonard, J.J., Durrant-Whyte, H.F., Cox, I.J.: Dynamic Map building for an autonomous mobile robot. Internal Journal of Robotics Research 11(4), 89–96 (1992)
Lu, F., Milios, E.: Globally consistent range scan alignment for environment mapping. Autonomous Robots 4, 333–349 (1997)
Rencken, W.D.: Concurrent localisation and map building for mobile robots using ultrasonic sensors. In: IROS Proceedings, pp. 2129–2197 (1993)
Thrun, S., Burgard, W., Fox, D.: A Probabilistic Approach for Concurrent Map Aquisition and Localization for Mobile Robots. Technical Report, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, CMU-CS-97-183
Weiss, G., von Puttkamer, E.: A Map based on Laserscans without Geometric Interpretation. In: Rembold, U., et al. (eds.) Intelligent Autonomous Systems, pp. 403–407. IOS Press, Amsterdam (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rencken, W.D., Feiten, W., Zöllner, R. (1999). Relocalisation by Partial Map Matching. In: Christensen, H.I., Bunke, H., Noltemeier, H. (eds) Sensor Based Intelligent Robots. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 1724. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/10705474_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/10705474_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-66933-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46619-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive