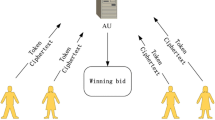
Abstract
Auction systems allow many entities, each possessing a unique secret value, to interact in order to reveal the winning value from the set of secret values, based on the rules of interaction. A platform to achieve this goal is sealed bid auction. We propose a schema and a concrete design to achieve this goal in a simple, efficient and secure fashion. The schema will facilitate the use of existing and future knowledge in providing anonymity.
Research supported by the Australian Research Council grant A49804059
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cramer, R., Damgård, I.: Zero-knowledge proofs for finite field arithmetic, or: Can zero-knowledge be for free? In: Krawczyk, H. (ed.) CRYPTO 1998. LNCS, vol. 1462, pp. 424–441. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Fiat, A., Shamir, A.: How to prove yourself: Practical solutions to identification and signature problems. In: Odlyzko, A.M. (ed.) CRYPTO 1986. LNCS, vol. 263, pp. 186–194. Springer, Heidelberg (1987)
Frankel, Y., Tsiounis, Y., Yung, M.: Indirect discourse proofs: Achieving efficient fair off-line e-cash. In: Kim, K.-c., Matsumoto, T. (eds.) ASIACRYPT 1996. LNCS, vol. 1163. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Goldwasser, S., Micali, S.: Probabilistic encryption. Journal of Computer and System Sciences 28, 270–299 (1984)
Franklin, M.K., Reiter, M.K.: The design and implementation of a secure auction service. IEEE Transaction on Software Engineering 22, 302–312 (1996)
Harkavy, M., Tyger, D., Kikuchi, H.: Electronic auctions with private bids. In: Third USENIX Workshop on Electronic Commerce (1998)
Kikuchi, H., Harkavy, M., Tygar, D.: Multi-round anonymous auction protocols. TIEICE: IEICE Transactions on Communications/Electronics/Information and Systems (1999)
Milgrom, P.: Auctions and bidding: A primer. Journal of Economic Perspectives 3(3), 3–22 (1989)
Pedersen, T.: Non-interactive and information-theoretic secure verifiable secret sharing. In: Feigenbaum, J. (ed.) CRYPTO 1991. LNCS, vol. 576, pp. 129–140. Springer, Heidelberg (1992)
Sako, K.: An auction protocol which hides bids of losers. In: Imai, H., Zheng, Y. (eds.) PKC 2000. LNCS, vol. 1751, pp. 422–432. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Sakurai, K., Miyazaki, S.: A bulletin-board based digital auction scheme with bidding down strategy. In: Proceedings of CrypTEC 1999, July 1999, pp. 180–187. City University of Hong Kong Press (1999)
Schnorr, C.P.: Efficient signature generation for smart cards. Journal of Cryptology 4, 161–174 (1991)
Schoenmakers, B.: A simple publicly verifiable secret sharing scheme and its application to electronic voting. In: Wiener, M. (ed.) CRYPTO 1999. LNCS, vol. 1666, p. 148. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Stadler, M.: Publicly verifiable secret sharing. In: Maurer, U.M. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 1996. LNCS, vol. 1070, pp. 190–199. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Viswanathan, K., Boyd, C., Dawson, E. (2000). A Three Phased Schema for Sealed Bid Auction System Design. In: Dawson, E.P., Clark, A., Boyd, C. (eds) Information Security and Privacy. ACISP 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1841. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/10718964_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/10718964_34
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67742-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45030-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive