Abstract
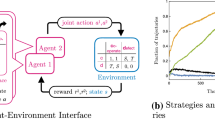
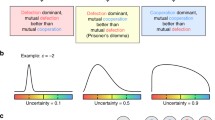
We study the evolution of social behaviors within a behavioral framework. To this end, we define a “minimal social situation” that is experimented with both humans and simulations based on reinforcement learning algorithms. We analyse the dynamics of behaviors in this situation by way of operant conditioning. We show that the best reinforcement algorithm, based on Staddon-Zhang’s equations, has a performance and a variety of behaviors that comes close to that of humans, and clearly outperforms the well-known Q-learning. Though we use here a rather simple, yet rich, situation, we argue that operant conditioning deserves much study in the realm of artificial life, being too often misunderstood, and confused with classical conditioning.
This research is supported by “Conseil Regional Nord-Pas de Calais” (contract n 97 53 0283)
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attonaty, J.M., Chatelin, M.H., Garcia, F., Ndiaye, S.M.: Using extended machine learning and simulation technics to design crop management stategies. In: EFITA First European Conference for Information Technology in Agriculture (1997); Copenhagen
Axelrod, R.: The evolution of cooperation. Basic Book Inc., New York (1984)
Bergen, D.E., Hahn, J.K., Bock, P.: An adaptive approch for reactive actor design. In: Proc. European Conference on Artificial Life (1997)
Boren, J.J.: An experimental social relation between two monkeys. Journal of the experimental analysis of behavior 9, 691–700 (1966)
Touretzky, D.S., Saksida, L.M.: Skinnerbots. In: Maes, P., Mataric, M., Meyer, J.-A., Pollack, J., Wilson, S.W. (eds.) Proc. 4th Int’l Conf. on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior, From Animals to Animats 4. MIT Press, Cambridge (1996)
Dawkins, R.: The Selfish Gene. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1976)
Delepoulle, S., Preux, P., Darcheville, J.C.: Partage des tâches et apprentissage par renforcement. In: Proc. Journées Francophones d’Apprentissage, pp. 201–204 (1998) (in french)
Deneubourg, J.L., Goss, S.: Collective paterns and decision-making. Ethology Ecology and Evolution 1, 295–311 (1989)
Donahoe, J.W., Burgos, J.E., Palmer, D.C.: A selectionist approach to rein- forcement. Journal of the experimental analysis of behavior 60, 17–40 (1993)
Hake, D.F., Vukelich, R.: Analysis of the control exerted by a complex cooperation procedure. Journal of the experimental analysis of behavior 19, 3–16 (1973)
Hamilton, W.D.: The Genetical Evolution of Social Behaviour. Journal of Theoritical Biology 7, 1–52 (1964)
Hemelrijk, C.K.: Cooperation without genes, games or cognition. In: Proc. European Conference on Artificial Life (1997)
Hilgard, E.R., Bower, G.H.: Theories of learning, 4th edn. Prentice- Hall, Enblewood Cliffs
Hutchinson, W.R.: Teaching an agent to speak and listen with understanding: Why and how? In: Proceedings of the Intelligent Information Agents Workshop, CIKM, Baltimore, http://www.cs.umbc.edu/cikm/iia/submitted/viewing/whutchi.html
Hutchinson, W.R.: The 7G operant behavior toolkit: Software and documentation. Behavior System, Boulder, CO
Ito, A.: How do selfish agents learn to cooperate? In: Langton, C.G., Shimohara, K. (eds.) Proc. Artificial life 5, pp. 185–192. MIT Press, Cambridge (1996)
Kaelbling, L.P., Littman, M.L., Moore, A.W.: Reinforcement learning: a survey. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 4, 237–285 (1996)
Langton, C.: Artificial life. In: Langton, R.E. (ed.) Proc. Artificial Life, pp. 1–47. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1987)
McFarland, D.: Towards Robot Cooperation. In: Proc of the International Conference on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior: From Animals to Animats 3, pp. 440–444 (1994)
Murciano, A., Millán, J.R.: Learning signaling behaviors and specialization in cooperative agents. Adaptive Behavior 5(1), 5–28 (1997)
Sidowski, J.B.: Reward and Punishment in a Minimal Social Situation. Journal of Experimental Psychology 55, 318–326 (1957)
Sidowski, J.B., Wyckoff, B., Tabory, L.: The influence of reinforcement and punishment in a minimal socila situation. Journal of Abnormal Social Psychology 52, 115–119 (1956)
Skinner, B.F.: The behavior of organisms. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1938)
Skinner, B.F.: Science and human behavior. Macmillan, New York (1953)
Skinner, B.F.: Selection by consequence. Science 213, 501–514 (1981)
Staddon, J.E.R.: Adaptive Behavior and Learning. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1981)
Staddon, J.E.R., Zhang, Y.: On the Assignment-of-Credit Problem in Operant Learning. In: Caumais, M.L., Grossberg, S. (eds.) Neural Network model of Conditioning and Action, Laurence Erlbaum, Hillsdale (1991)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Time-Derivative Models of Pavlovian Reinforcement. In: Gabriel, M., Moore, J. (eds.) Learning and Computational Neuroscience: Foundations of Adaptive Networks, pp. 497–537. MIT Press, Cambridge (1990), ftp://ftp.cs.umass.edu/pub/anw/pub/sutton/sutton-barto90.ps
Sutton, R.S.: Reinforcement Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Theraulaz, G., Pratte, M., Gervet, J.: Behavioural profiles in Polistes dominulus (Christ) wasp societies: a quantitative study. Behaviour 113, 223–250 (1990)
Thorndike, E.L.: Animal Intelligence: An experimental study of the associative process in animals. Psychology Monographs 2 (1898)
Thorndike, E.L.: Animal Intelligence: Experimental studies. MacMillan, New York (1911)
Watkins, C.J.C.H., Dayan, P.: Q-Learning. Technical Note. Machine Learning 8(3), 279–292 (1992)
Wilson, E.O.: The Insect Societies. The Belknap Press, Harvard University Press (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Delepoulle, S., Preux, P., Darcheville, JC. (2000). Evolution of Cooperation within a Behavior-Based Perspective: Confronting Nature and Animats. In: Fonlupt, C., Hao, JK., Lutton, E., Schoenauer, M., Ronald, E. (eds) Artificial Evolution. AE 1999. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1829. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/10721187_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/10721187_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67846-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44908-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive