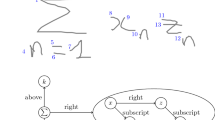
Abstract
The recent advances in sketch-based applications and digital-pen protocols make visual languages useful tools for Human Computer Interaction. Graphical symbols are the core elements of a sketch and, hence a visual language. Thus, symbol recognition approaches are the basis for visual language parsing. In this paper we propose an adjacency grammar to represent graphical symbols in a sketchy framework. Adjacency grammars represent the visual syntax in terms of adjacency relations between primitives. Graphical symbols may be either diagram components or gestures. An on-line parsing method is also proposed. The performance of the recognition is evaluated using a benchmarking database of 5000 on-line symbols. Finally, an application framework for sketching architectural floor plans is described.
This work has been partially supported by the spanish project CICYT TIC2003-09291 and catalan project CeRTAP PVPC.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bunke, H.: String grammars for syntactic pattern recognition. In: Bunke, H., Sanfeliu, A. (eds.) Syntactic and Structural Pattern Recognition. Theory and Applications, pp. 29–54. World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore (1990)
Min, W., Tang, Z., Tang, L.: Using web grammar to recognize dimensions in engineering drawings. Pattern Recognition 26, 1407–1916 (1993)
Bunke, H.: Attributed programmed graph grammars and their application to schematic diagram interpretation. IEEE Trans. on PAMI 4, 574–582 (1982)
Fahmy, H., Blonstein, D.: A graph grammar programming style for recognition of music notation. Machine Vision and Applications 6, 83–99 (1993)
Fahmy, H., Blostein, D.: A survey of graph grammars: Theory and applications. In: Proceedings of 12th. Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition (a), Jerusalem, Israel, pp. 294–298 (1994)
Jorge, J., Glinert, E.: Online parsing of visual languages using adjacency grammars. In: Proceedings of the 11th International IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages, pp. 250–257 (1995)
Tombre, K., Ah-Soon, C., Dosch, P., Masini, G., Tabonne, S.: Stable and robust vectorization: How to make the right choices. In: Chhabra, A.K., Dori, D. (eds.) GREC 1999. LNCS, vol. 1941, pp. 3–18. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Sezgin, T., Stahovich, T., Davis, R.: Sketch based interfaces: Early processing for sketch understanding. In: Proceedings of 2001 Perceptive User Interfaces Workshop (PUI 2001), ACM Digital Library (2001) ISBN 1-58113-448-7
Rekers, J., Schurr, A.: Defining and parsing visual languages with layered graph grammars. Journal of Visual Languages and Computing 8, 27–55 (1997)
Al-Mulhem, M., Ather, M.: Mrg parser for visual languages. Inf. Sci. 131, 19–46 (2001)
Logitech: IO digital pen (2004), www.logitech.com
Sánchez, G., Valveny, E., Lladós, J., Mas, J., Lozano, N.: A platform to extract knowledge from graphic documents. application to an architectural sketch understanding scenario. In: Marinai, S., Dengel, A. (eds.) Document Analysis Systems VI, pp. 349–365. World Scientific, Singapore (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mas, J., Sánchez, G., Lladós, J. (2005). An Adjacency Grammar to Recognize Symbols and Gestures in a Digital Pen Framework. In: Marques, J.S., Pérez de la Blanca, N., Pina, P. (eds) Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. IbPRIA 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3523. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11492542_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11492542_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26154-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32238-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)