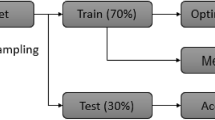
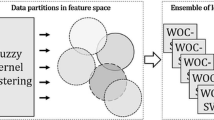
Abstract
Training data modification has shown to be a successful technique for the design of classifier ensemble. Current study is concerned with the analysis of different types of training set distribution and their impact on the generalization capability of multiple classifier systems. To provide a comparative study, several probabilistic measures have been proposed to assess data partitions with different characteristics and distributions. Based on these measures, a large number of disjoint training partitions were generated and used to construct classifier ensembles. Empirical assessment of the resulted ensembles and their performances have provided insights into the selection of appropriate evaluation measures as well as construction of efficient population of partitions.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Multiple Classifiers Systems. In: Roli, F., Kittler, J., Windeatt, T. (eds.) MCS 2004. LNCS, vol. 3077, pp. 233–242. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Multiple Classifiers Systems. In: Windeatt, T., Roli, F. (eds.) MCS 2003. LNCS, vol. 2709. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Kuncheva, L.: Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms. Wiley, Chichester (2004)
Sharkey, A.: Types of Multinet Systems. In: Roli, F., Kittler, J. (eds.) MCS 2002. LNCS, vol. 2364, pp. 108–117. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Tumer, K., Oza, N.: Input Decimated Ensembles. Pattern Analysis and Applications 6(1), 65–77 (2003)
Freund, Y., Schapire, R.: Experiments with a New Boosting Algorithm. In: Proc. of the 13th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, Bari Italy, pp. 148–156 (1996)
Breiman, L.: Bagging Predictors. Machine Learning 24(2), 123–140 (1996)
Dara, R., Kamel, M.: Effect of Sharing Training Patterns on the Performance of Classifier Ensemble. In: Proc. of Int. IEEE Conf. on System Man Cybernetics, The Hague, The Netherlands, pp. 1220–1225 (2004)
Chawla, N., Moore, T., Hall, L., Bowyer, L., Kegelmeyer, P., Springer, C.: Distributed Learning with Bagging-like Performance. Pattern Recognition Letters 24, 455–471 (2003)
Blum, A., Langley, P.: Selection of Relevant Features and Examples in Machine Learning. Artificial Intellignce 97(1-2), 245–271 (1997)
Kamel, M., Wanas, N.: Data Dependence in Combining Classifiers. In: Fourth Int. Workshop on MCS, Guilford UK, pp. 1–14 (2003)
Jiang, W., Tanner, M.: Hierarchical Mixtures of Experts for Generalized Linear Models. Neural Computation 11, 1183–1198 (1999)
Parikh, D., Kim, M., Oagaro, J., Mandayam, S., Polikar, R.: Combining classifiers for multisensor data fusion. In: Proc. of Int. IEEE Conf. on System Man Cybernetics, The Hague, The Netherlands, pp. 1232–1237 (2004)
Frosyniotis, D., Stafylopatis, A., Likas, A.: A Divide-and-Conquer Method for Mutli-Net Classifiers. Pattern Analysis and Applications 6, 32–40 (2003)
Dara, R., Makrehchi, M., Kamel, M.: An Information-Theoretic Measure to Evaluate Data Partitions in Multiple Classifiers. In: Proc. of Int. IEEE Conf. on System Man Cybernetics, The Hague, The Netherlands, pp. 4826–4831 (2004)
Fukunaga, K.: Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1990)
Duda, R., Hart, P., Strok, D.: Pattern Recognition. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester (2000)
Blake, D., Merz, C.: UCI Repository of machine learning databases, http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn/MLRepository.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dara, R.A., Makrehchi, M., Kamel, M.S. (2005). Data Partitioning Evaluation Measures for Classifier Ensembles. In: Oza, N.C., Polikar, R., Kittler, J., Roli, F. (eds) Multiple Classifier Systems. MCS 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3541. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11494683_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11494683_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26306-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31578-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)