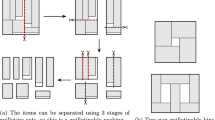
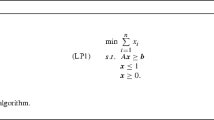
Abstract
We consider geometric problems in which rectangles have to be packed in (identical) squares, that turn out to be very hard in practice and for which ILP formulations in which variables specify the coordinates in the packing perform very poorly. While most methods developed until the end of last century are based on simple geometric considerations, a recent landmark result of Fekete and Schepers suggests to put these geometric aspects aside and use the most advanced tools for the 1-dimensional case. In this paper we make additional progress in this direction, especially on the basic question “Does a given set of rectangles fit in a square?”, that turns out to be the bottleneck of all the approaches known.
Given a set of rectangles and the associated convex hull of the incidence vectors of rectangle subsets that fit in a square, we derive a wide class of valid inequalities for this convex hull from a complete description of the two knapsack polytopes associated with the widths and the heights of the rectangles, respectively. Additionally, we illustrate how to solve the associated separation problem as a bilinear program, for which we develop a solution method that turns out to be fast in practice, and show that integer solutions that satisfy all these inequalities generally correspond to vertices of the original convex hull. The same tools are used to derive lower bounds for the 2-dimensional bin packing problem, corresponding to the determination of an optimal pair of so-called dual feasible functions, that in many cases equal the lower bounds obtained by the customary set covering formulation (for which column generation is very hard) being computable within times that are orders of magnitude smaller.
All our results extend immediately to the general problem of packing d-dimensional parallelepipeds in hypercubes.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarie, S., Audet, C., Jaumard, B., Savard, G.: Concavity cuts for disjoint bilinear programming. Mathematical Programming 90, 373–398 (2001)
Al-Khayyal, F.A.: Generalized bilinear programming: Part I. Models, applications and linear programming relaxation. European Journal of Operational Research 60, 306–314 (1992)
Audet, C., Hansen, P., Jaumard, B., Savard, G.: A symmetrical linear maxmin approach to disjoint bilinear programming. Mathematical Programming 85, 573–592 (1999)
Berkey, J.O., Wang, P.Y.: Two dimensional finite bin packing algorithms. Journal of the Operational Research Society 38, 423–429 (1987)
Boschetti, M.A., Mingozzi, A.: The two-dimensional finite bin packing problem. Part I: New lower bounds for the oriented case. 4OR 1, 27–42 (2003)
Boschetti, M.A., Mingozzi, A.: Two-dimensional finite bin packing problems. Part II: New lower and upper bounds. 4OR 2, 135–148 (2003)
Caprara, A.: Packing 2-dimensional bins in harmony. In: Proceedings of the 43- rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS 2002), pp. 490–499 (2002)
Caprara, A., Monaci, M.: On the 2-dimensional knapsack problem. Operations Research Letters 32, 5–14 (2004)
Fekete, S.P., Schepers, J.: New classes of fast lower bounds for bin packing problems. Mathematical Programming 91, 11–31 (2001)
Fekete, S.P., Schepers, J.: A combinatorial characterization of higher-dimensional orthogonal packing. Mathematics of Operations Research 29, 353–368 (2004)
Fekete, S.P., Schepers, J.: A general framework for bounds for higher-dimensional orthogonal packing problems. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research 60, 311–329 (2004)
Fekete, S.P., Schepers, J.: An exact algorithm for higher-dimensional orthogonal packing. Technical Report, Technische Universität Braunschweig (2004), Available at http://www.math.tu-bs.de/fekete/publications.html
de la Vega, W.F., Lueker, G.S.: Bin packing can be solved within 1+ε in linear time. Combinatorica 1, 349–355 (1981)
Floudas, C.A., Visweswaran, V.: Quadratic optimization. In: Horst, R., Pardalos, P.M. (eds.) Handbook of Global Optimization. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1995)
Gilmore, P.C., Gomory, R.E.: Multistage cutting problems of two and more dimensions. Operations Research 13, 94–119 (1965)
Grötschel, M., Lovász, L., Schrijver, A.: The ellipsoid method and its consequences in combinatorial optimization. Combinatorica 1, 169–197 (1981)
Lee, C.C., Lee, D.T.: A simple on-line bin packing algorithm. Journal of the ACM 32, 562–572 (1985)
Karmarkar, N., Karp, R.M.: An efficient approximation scheme for the onedimensional bin-packing problem. In: Proceedings of the 23-rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS 1982), pp. 312–320 (1982)
Martello, S., Pisinger, D., Vigo, D.: The three-dimensional bin packing problem. Operations Research 48, 256–267 (2000)
Martello, S., Vigo, D.: Exact solution of the two-dimensional finite bin packing problem. Management Science 44, 388–399 (1998)
McCormick, G.P.: Computability of global solutions to factorable nonconvex programs – Part I – Convex underestimating problems. Mathematical Programming 10, 147–175 (1976)
Monaci, M., Toth, P.: A set-covering based heuristic approach for bin-packing problems. To appear in INFORMS Journal on Computing (2005)
Pisinger, D., Sigurd, M.M.: On using decomposition techniques and constraint programming for solving the two-dimensional bin packing problem. DIKU-rapport 03/01, Department of Computer Science, University of Copenhagen (2003), Available at http://www2.adm.ku.dk/publikationer/publ/5100
Seiden, S.S., van Stee, R.: New bounds for multi-dimensional packing. Algorithmica 36, 261–293 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Caprara, A., Locatelli, M., Monaci, M. (2005). Bidimensional Packing by Bilinear Programming. In: Jünger, M., Kaibel, V. (eds) Integer Programming and Combinatorial Optimization. IPCO 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3509. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11496915_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11496915_28
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26199-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32102-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)