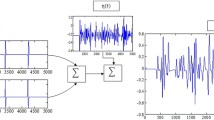
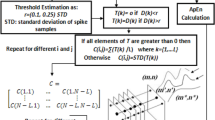
Abstract
Spike separation is a basic prerequisite for analyzing of the cooperative neural behavior and neural code when registering extracellularly. Final performance of any spike sorting method is basically defined by the quality of the discriminative features extracted from the spike waveforms. Here we discuss two features extraction approaches: the Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and methods based on the Wavelet Transform (WT). We show that the WT based methods outperform the PCA only when properly tuned to the data, otherwise their results may be comparable or even worse. Then we present a novel method of spike features extraction based on a combination of the PCA and continuous WT. Our approach allows automatic tuning of the wavelet part of the method by the use of knowledge obtained from the PCA. To illustrate the methods strength and weakness we provide comparative examples of their performances using simulated and experimental data.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewicki, M.: A review of methods for spike sorting: the detection and classification of neural action potentials. Net. Com. Neu. Sys. 9, R53–R78 (1998)
Harris, K.D., Henze, D.A., Csicsvari, J., Hirase, H., Buzsaki, G.: Accuracy of tetrode spike separation as determined by simultaneous intracellular and extracellular measurements. J. Neurophysiol. 84, 401–414 (2000)
Wheeler, B.: Automatic Discrimination of Single Units. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1999)
Kaufman, L., Rousseeuw, P.J.: Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1990)
Downs, G.M., Barnard, J.M.: Clustering methods and their uses in computational chemistry. Rev. Comput. Chem. 18, 1–40 (2002)
Letelier, J., Weber, P.: Spike sorting based on discrete wavelet transform coefficients. J. Neurosc. Methods 101, 93–106 (2000)
Hulata, E., Segev, R., Ben-Jacob, E.: A method for spike sorting and detection based on wavelet packets and Shannon’s mutual information. J. Neurosc. Methods 117, 1–12 (2002)
Quian Quiroga, R., Nadasdy, Z., Ben-Shaul, Y.: Unsupervised spike detection and sorting with wavelets and superparamagnetic clustering. Neur. Comput. 16, 1661–1687 (2004)
Blatt, M., Wiseman, S., Domany, E.: Superparamagnetic clustering of data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 3251–3254 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pavlov, A., Makarov, V.A., Makarova, I., Panetsos, F. (2005). Separation of Extracellular Spikes: When Wavelet Based Methods Outperform the Principle Component Analysis. In: Mira, J., Álvarez, J.R. (eds) Mechanisms, Symbols, and Models Underlying Cognition. IWINAC 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3561. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11499220_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11499220_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26298-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31672-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)