Abstract
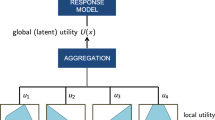
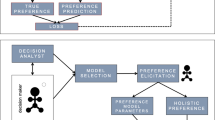
Preference elicitation is a well known bottleneck that prevents the acquisition of the utility function and consequently the set up of effective decision-support systems. In this paper we present a new approach to preference elicitation based on pairwise comparison. The exploitation of learning techniques allows to overcome the usual restrictions that prevent to scale up. Furthermore, we show how our approach can easily support a distributed process of preference elicitation combining both autonomy and coordination among different stakeholders. We argue that a collaborative approach to preference elicitation can be effective in dealing with non homogeneous data representations.
The presentation of the model is followed by an empirical evaluation on a real world settings. We consider a case study on environmental risk assessment to test with real users the properties of our model.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamodt, A., Plaza, E.: Case-based reasoning: Foundational issues, methodological variations, and system approaches. AI Communications 7(1), 39–59 (1994)
Avesani, P., Ferrari, S., Susi, A.: Case-Based Ranking for Decision Support Systems. In: Ashley, K.D., Bridge, D.G. (eds.) ICCBR 2003. LNCS, vol. 2689, pp. 35–49. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Devetag, G., Warglien, M.: Representing others’ preferences in mixed motive games: Was schelling right? Technical Report, Computable and Experimental Economics Lab, University of Trento (2002)
Kumamoto, H., Henley, E.J.: Probabilistic Risk Assessment. IEEE Press, New York (1992)
Freund, Y., Iyer, R., Schapire, R., Singer, Y.: An Efficient Boosting Algorithm for Combining Preferences. In: Proceedings 15th International Conference on Machine Learning (1998)
Freund, Y., Schapire, R.: A Short Introduction to Boosting (1999)
Ha, V., Haddawy, P.: Toward case-based preference elicitation: Similarity measures on preference structures. In: Cooper, G.F., Moral, S. (eds.) Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI-1998), San Francisco, July 24–26, 1998, pp. 193–201. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1998)
Marcus, S.: Algebraic Linguistics: Analytical Models. Academic Press, New York (1967)
Ngo-The, A., Ruhe, G.: Requirements Negotiation under Incompleteness and Uncertainty. In: Software Engineering Knowledge Engineering 2003 (SEKE 2003), San Francisco, CA, USA (July 2003)
Ruhe, G., Eberlein, A., Pfahl, D.: Quantitative winwin - a quantitative method for decisione support in requirements negotiation. In: Proceedings 14th International Conference on Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering (SEKE 2002), pp. 159–166 (2002)
Saaty, T.L.: Fundamentals of the analytic network process. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on Analytical Hierarchy Process (1999)
Saaty, T.L., Vargas, L.G.: Decision Making in Economic, Political, Social and Technological Environments With the Analytic Hierarchy Process. RWS Publications (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Avesani, P., Susi, A., Zanoni, D. (2005). Collaborative Case-Based Preference Elicitation. In: Ali, M., Esposito, F. (eds) Innovations in Applied Artificial Intelligence. IEA/AIE 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3533. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11504894_105
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11504894_105
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26551-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31893-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)